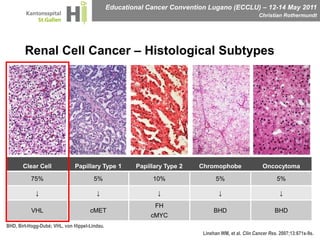
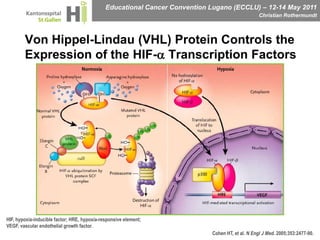
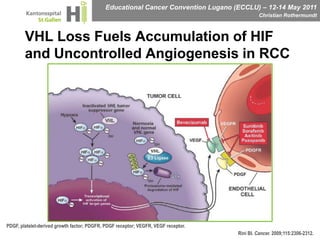
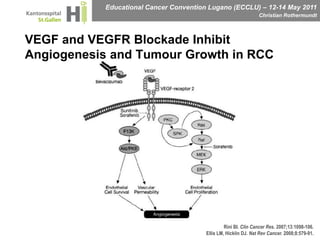
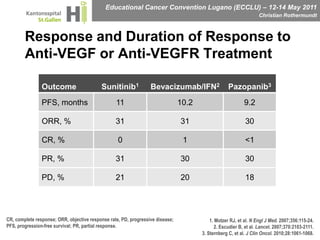
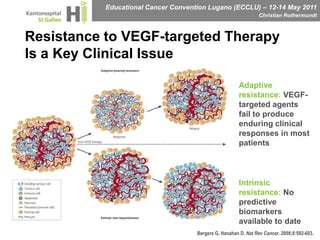
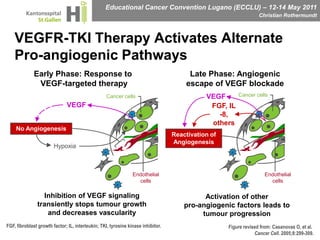
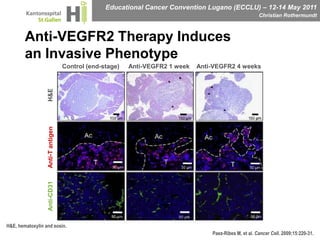
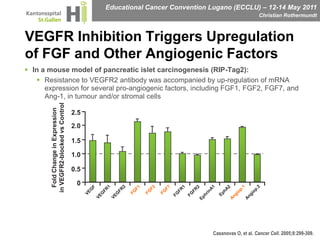
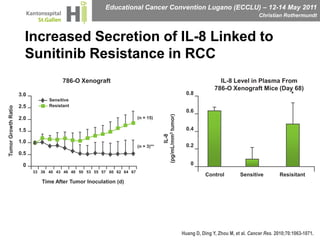
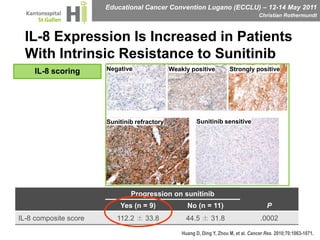
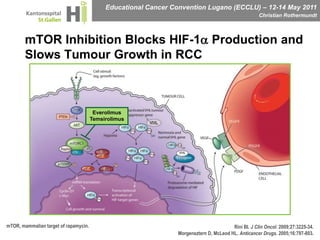
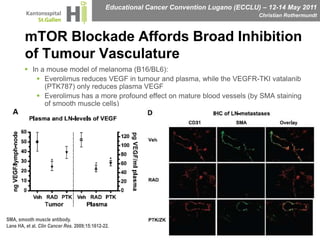
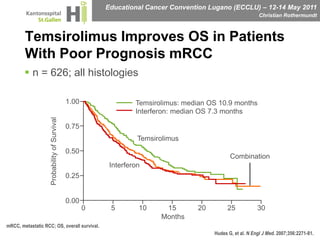
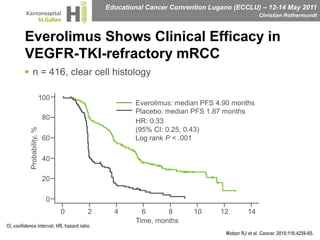
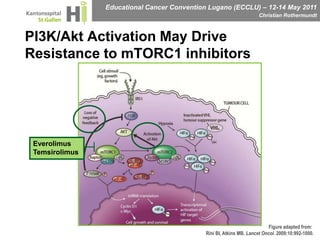
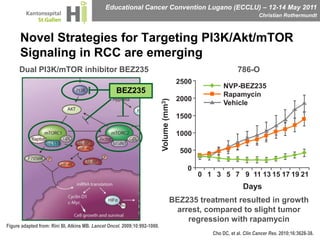
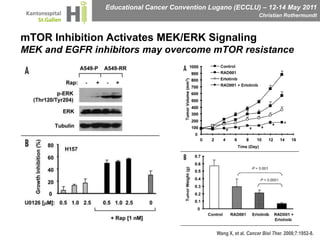
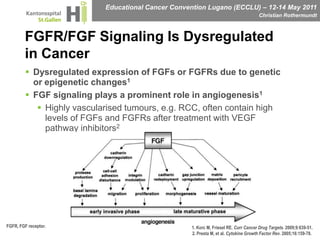
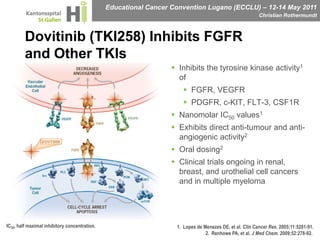
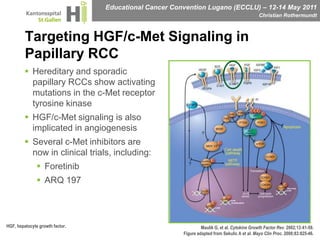
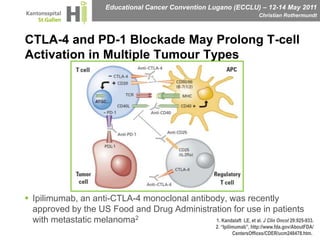
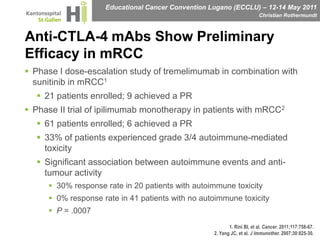
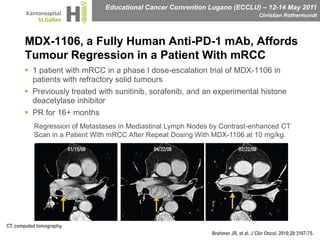
This document discusses mechanisms of action in modern renal cell carcinoma (RCC) treatment. It summarizes that loss of the VHL gene leads to uncontrolled angiogenesis driven by HIF and VEGF overexpression. VEGF inhibitors are standard first-line treatment but resistance develops via alternative angiogenic pathways. mTOR inhibitors overcome VEGF resistance and temsirolimus is standard for poor-prognosis RCC. Resistance to mTOR inhibitors may involve PI3K/Akt activation. FGFR, c-Met, and immune checkpoint inhibitors are investigational targets for RCC treatment. Defining resistance mechanisms and biomarkers for treatment selection remains an ongoing challenge.