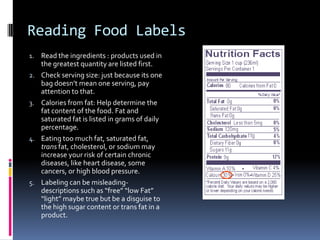
The document provides information on eating a healthy diet and discusses important dietary recommendations. It recommends eating whole foods that are minimally processed, like whole grains and oatmeal. It also emphasizes loading up on fruits and vegetables due to their nutrient density and health benefits. The document notes that individuals have different dietary needs and advises eating a variety of foods that make one feel their best. It also discusses the importance of portion control and limiting simple carbohydrates.