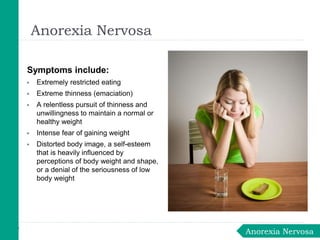
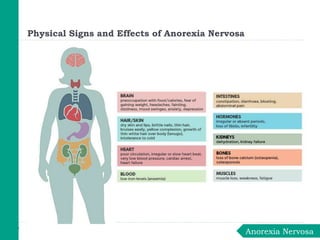
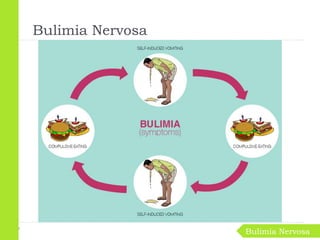
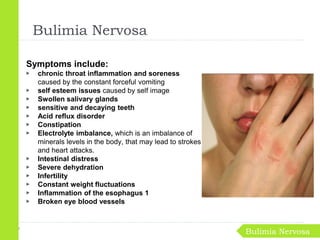
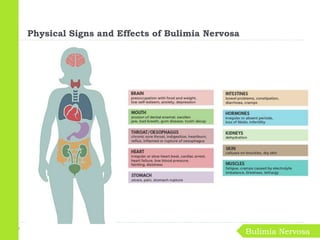
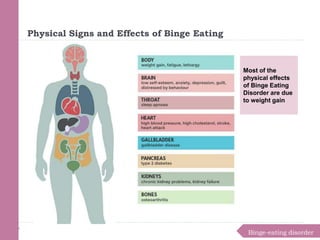
Eating disorders are medical conditions characterized by irregular eating habits and excessive concern with body weight and shape. The three main types are anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder. Eating disorders have biological, psychological, and social causes and can develop in both females and males. Anorexia involves restricted eating and pursuit of thinness despite being underweight. Bulimia involves binge eating followed by purging. Binge-eating disorder involves eating large amounts of food without purging. Treatment involves psychotherapy, medical monitoring, nutritional counseling, and sometimes medications.