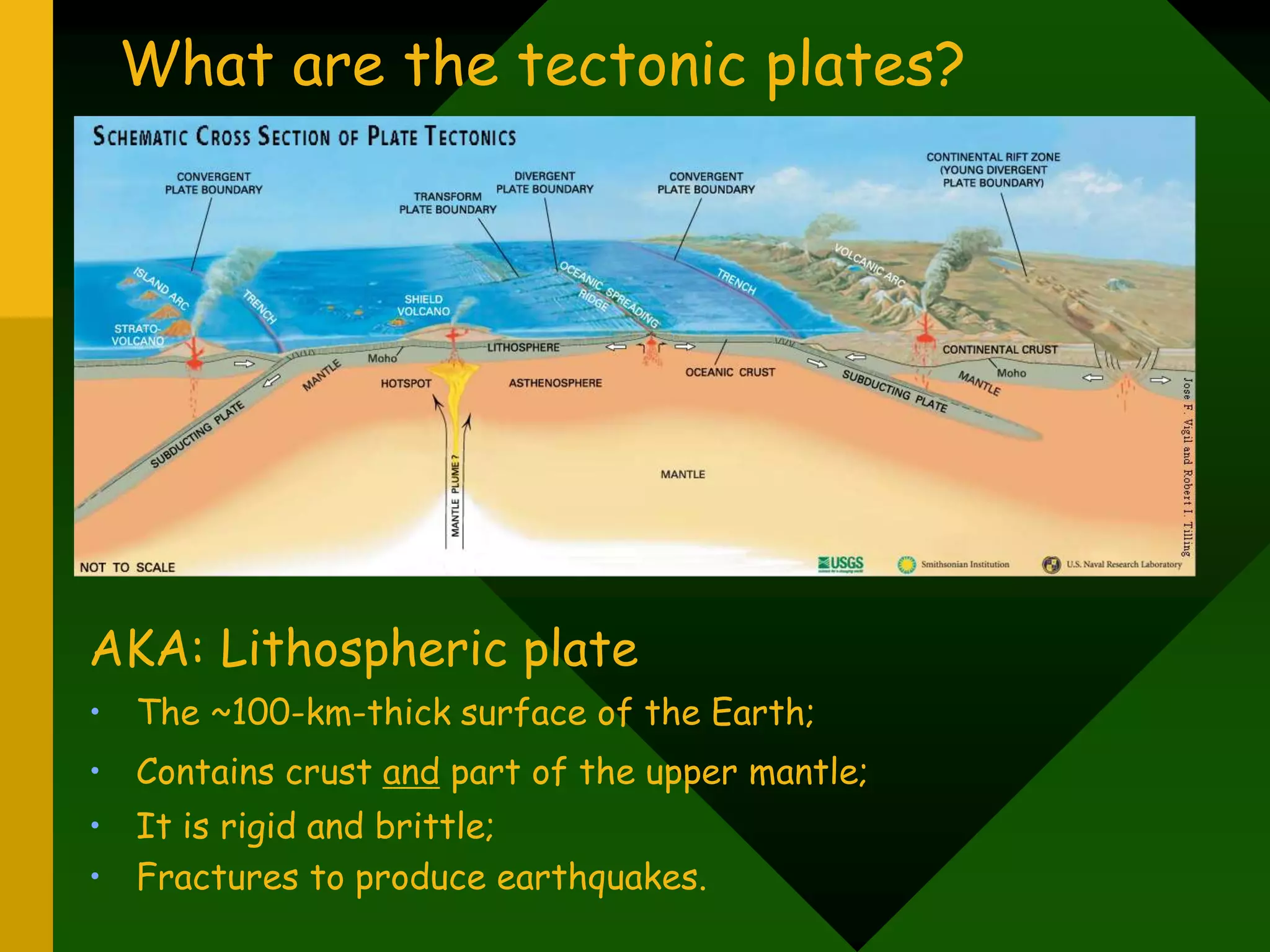
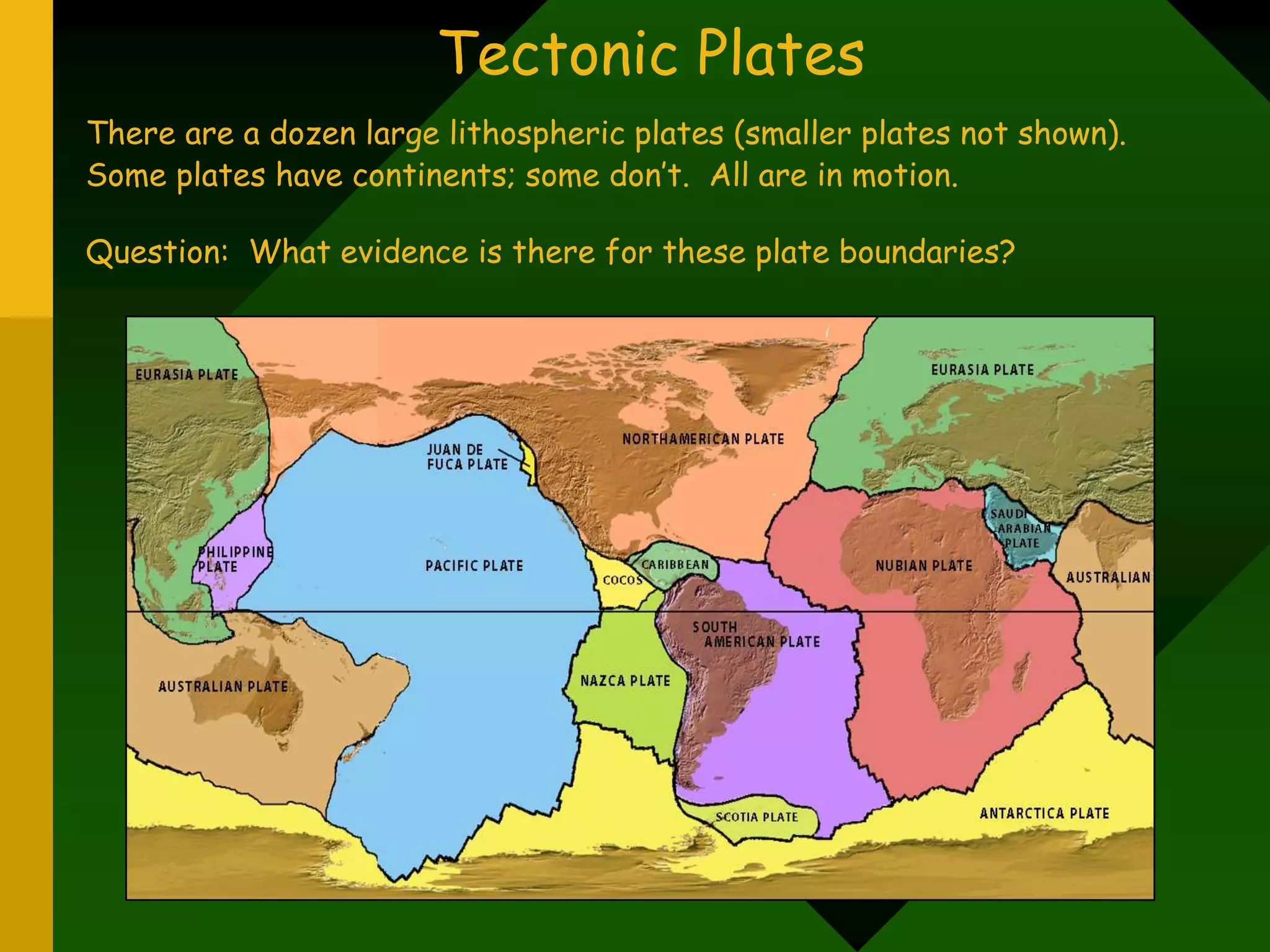
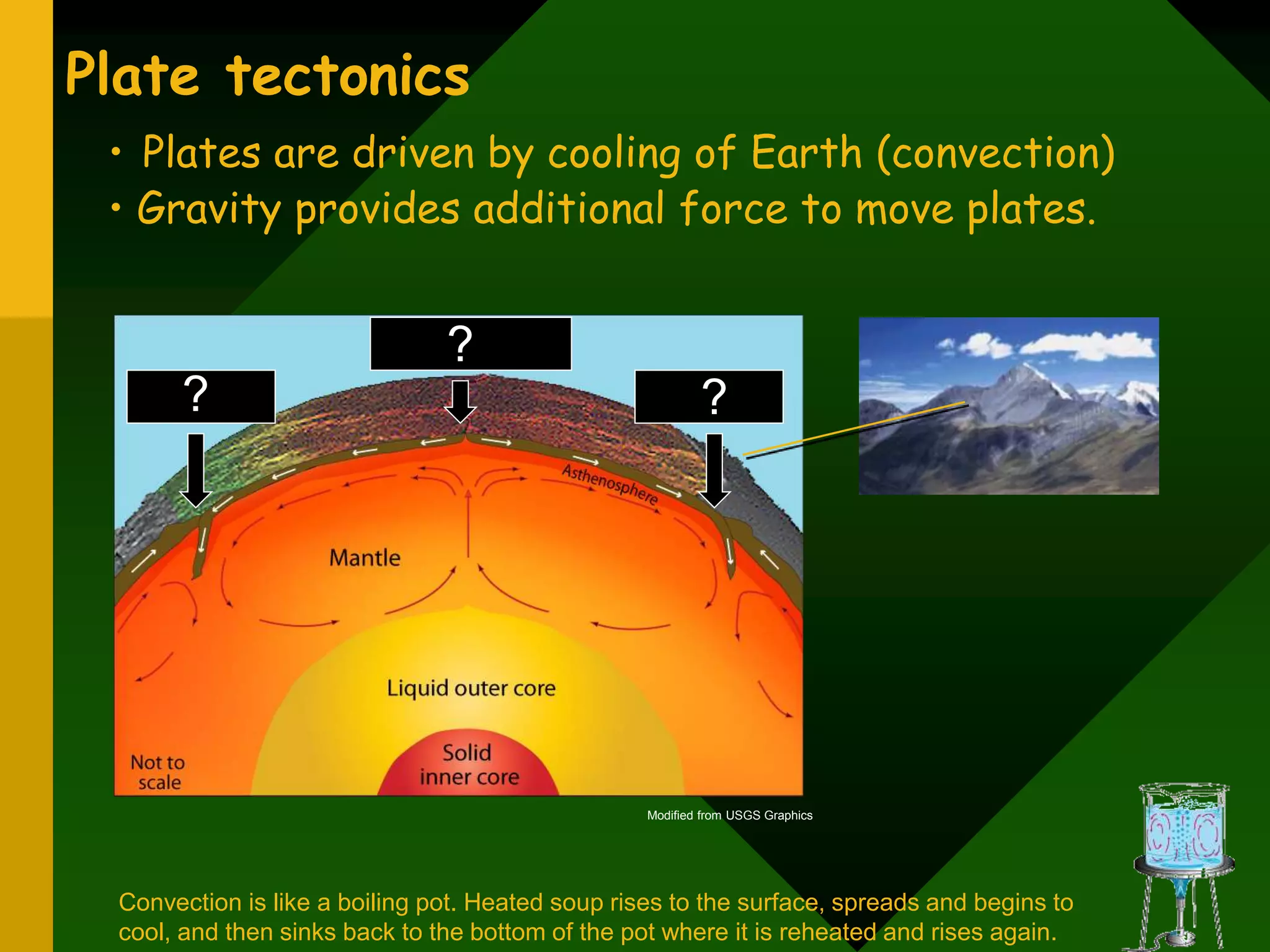
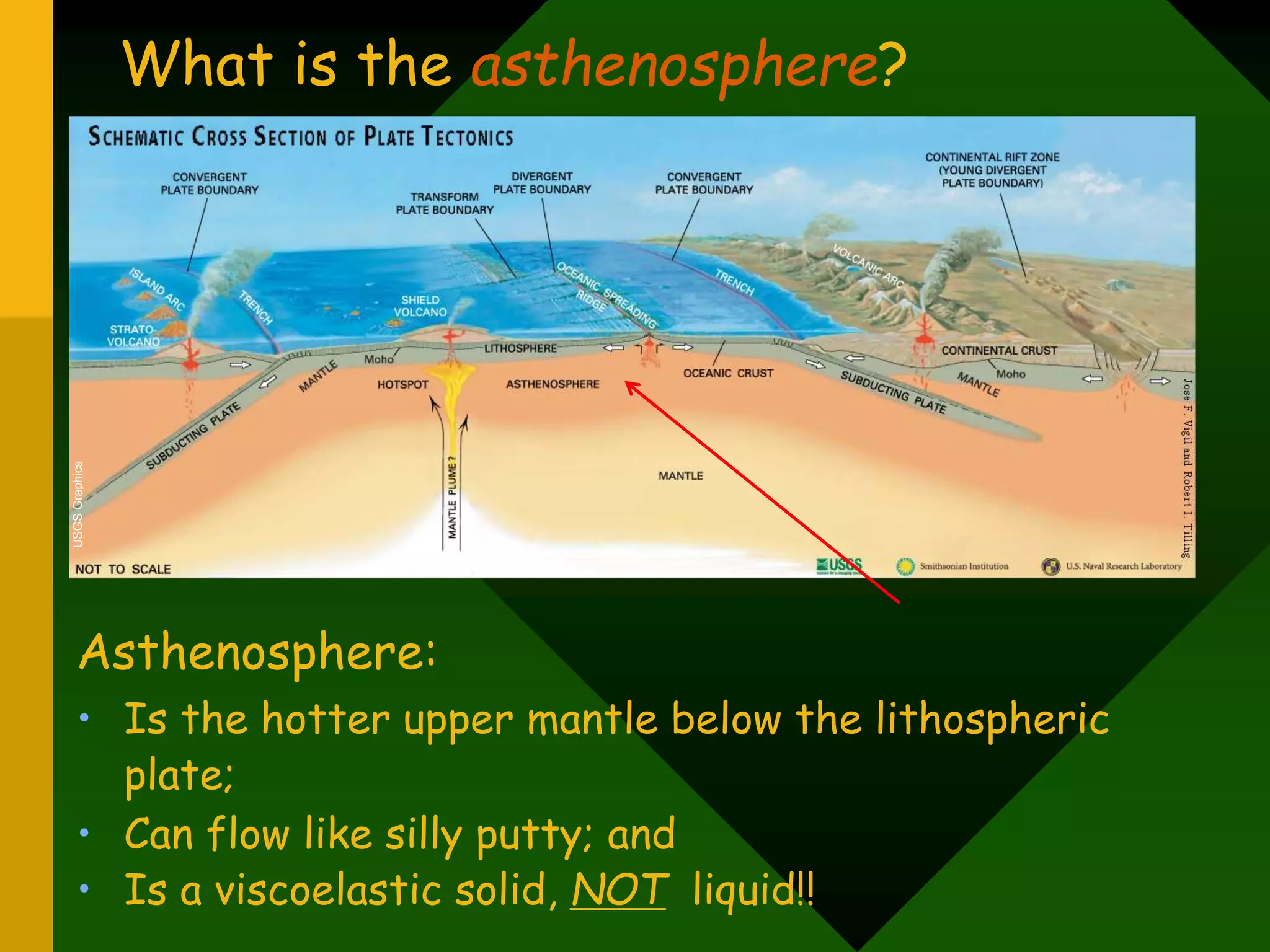
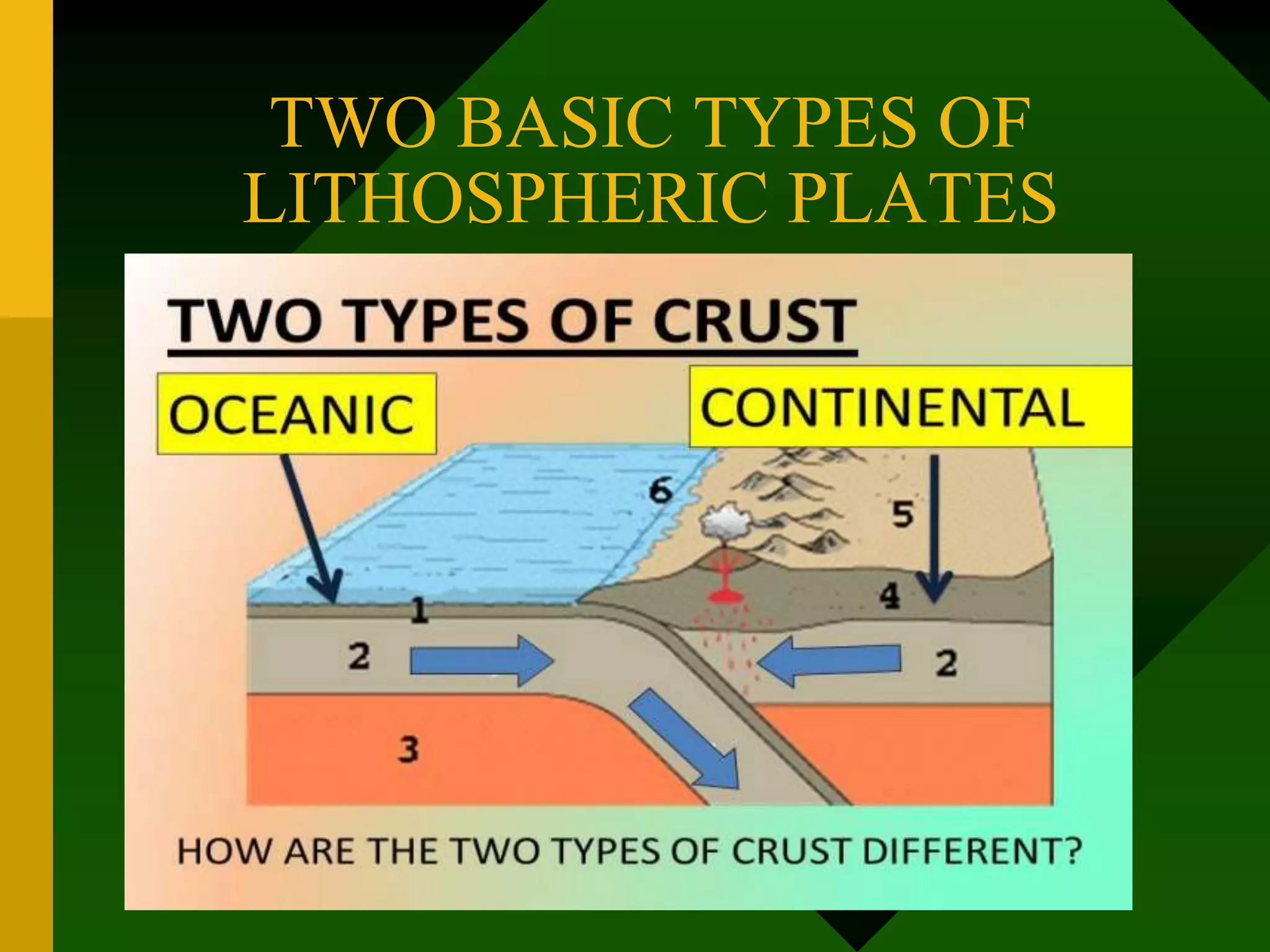
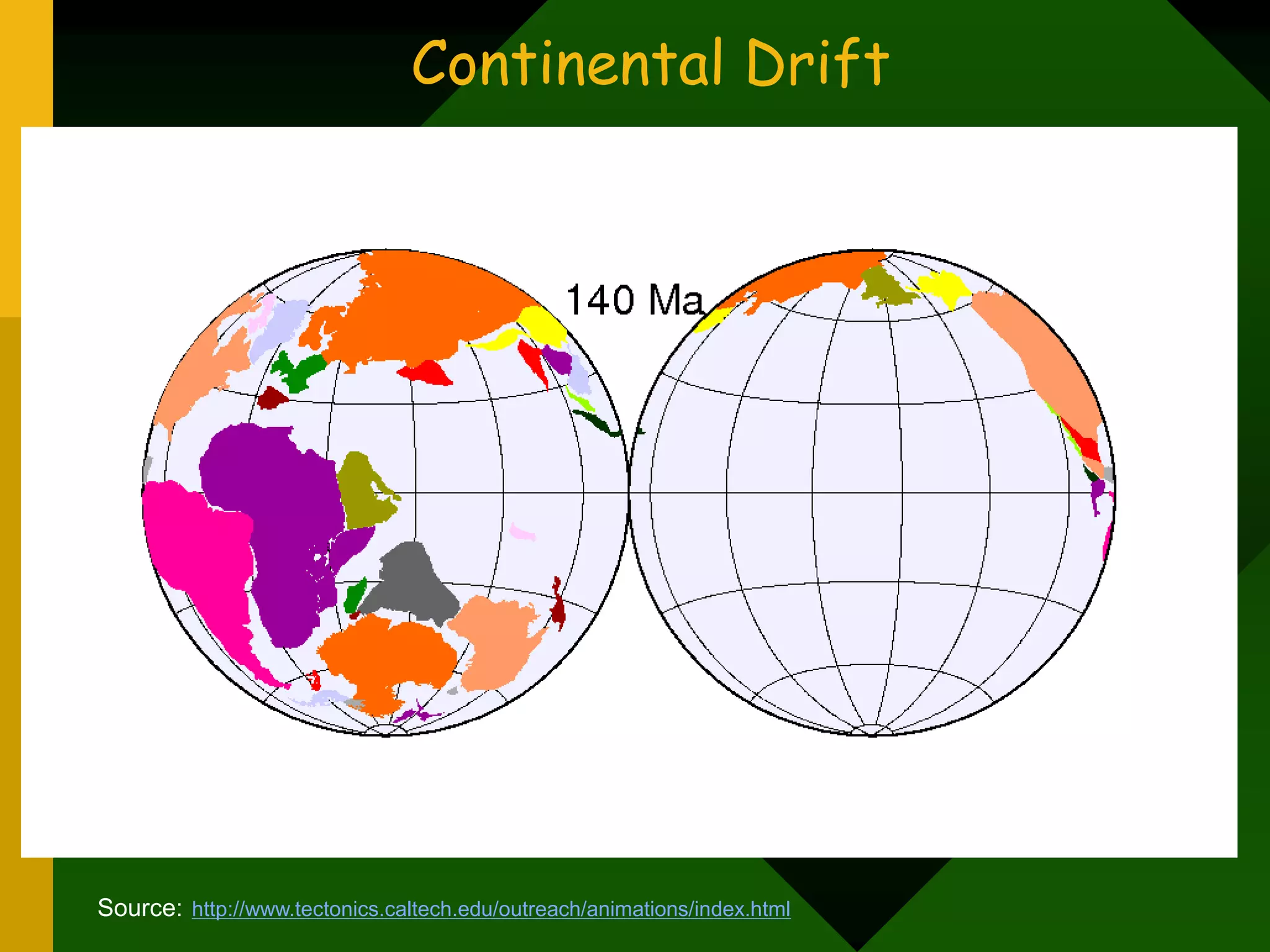
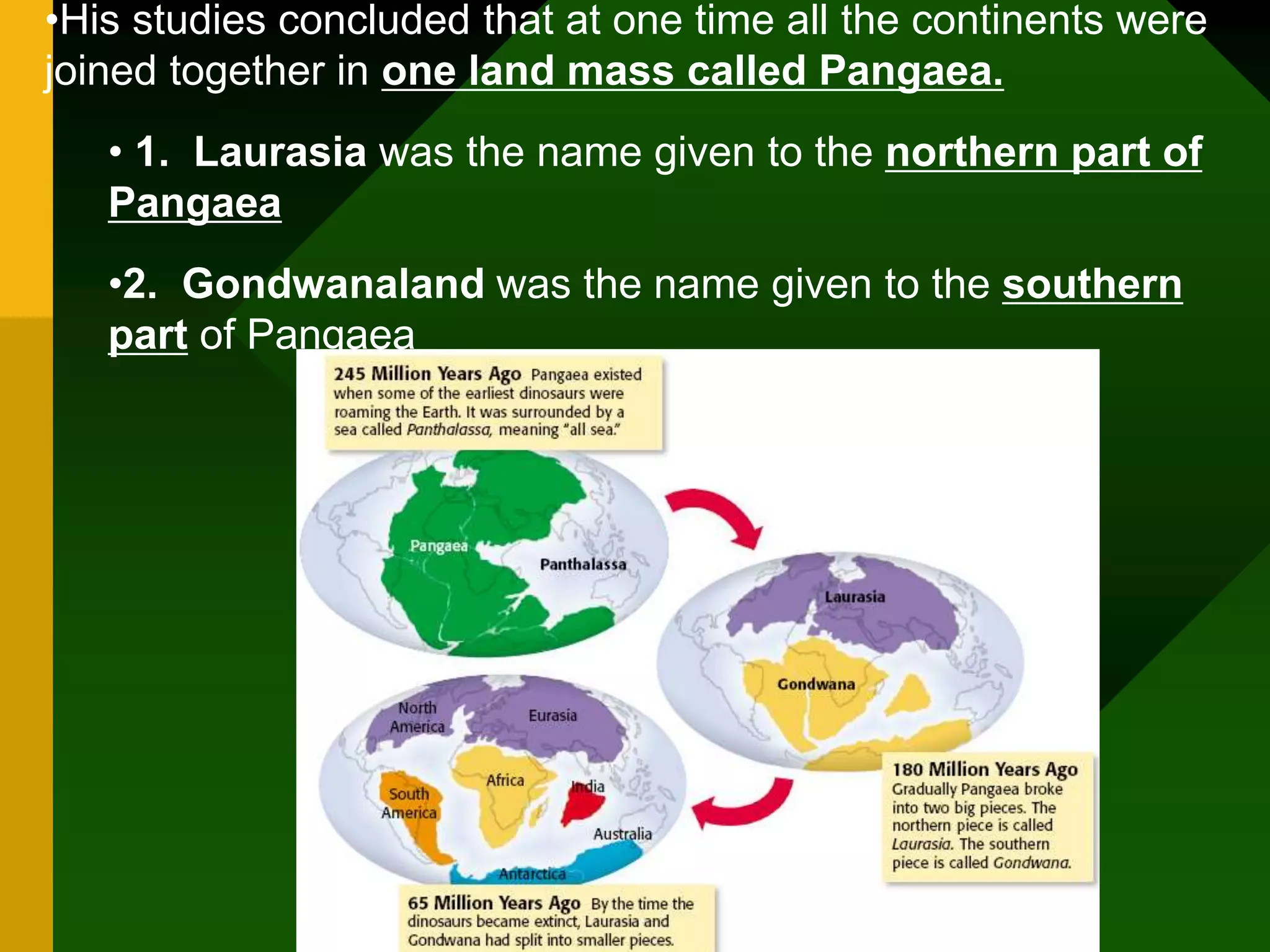
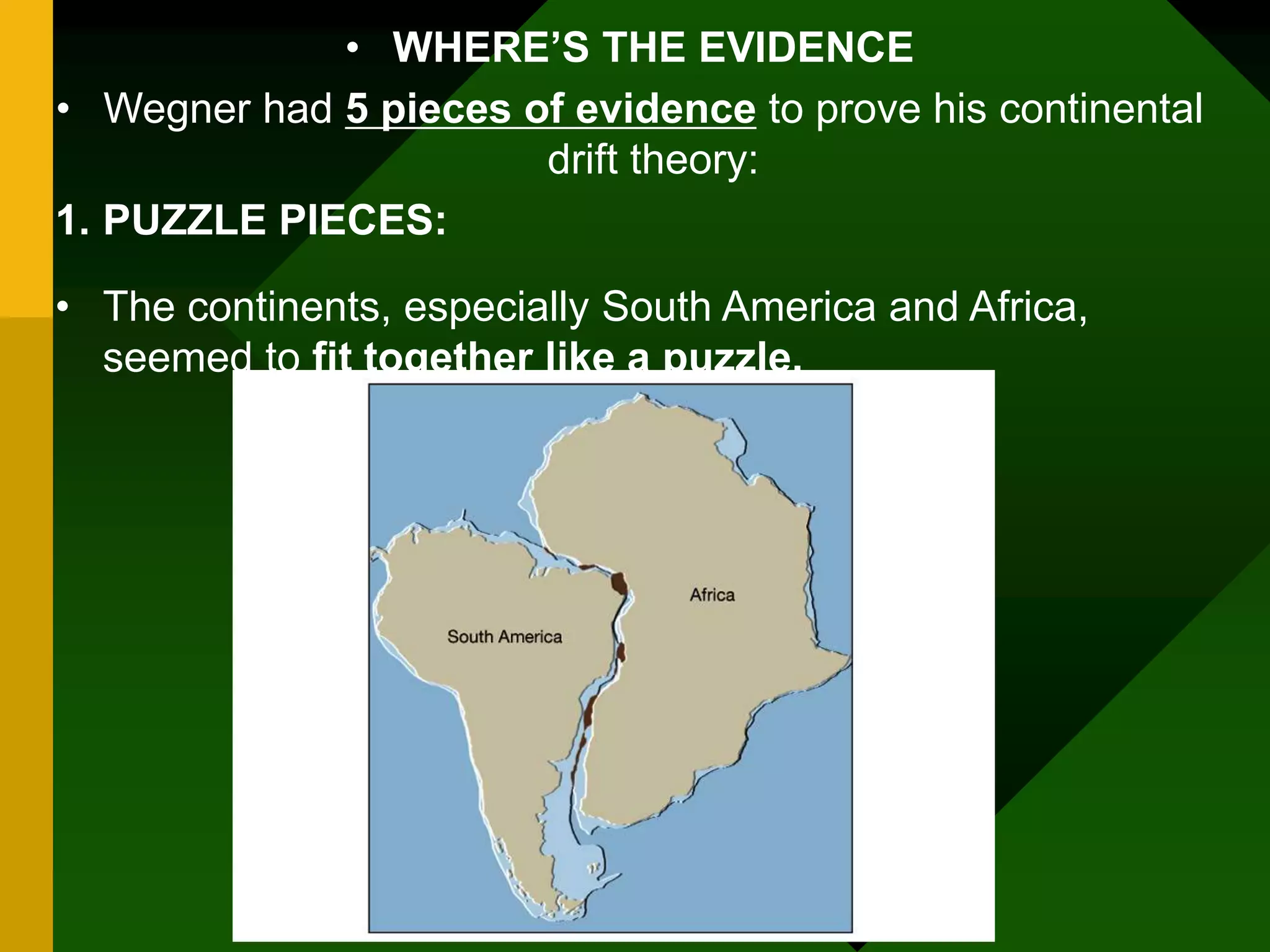
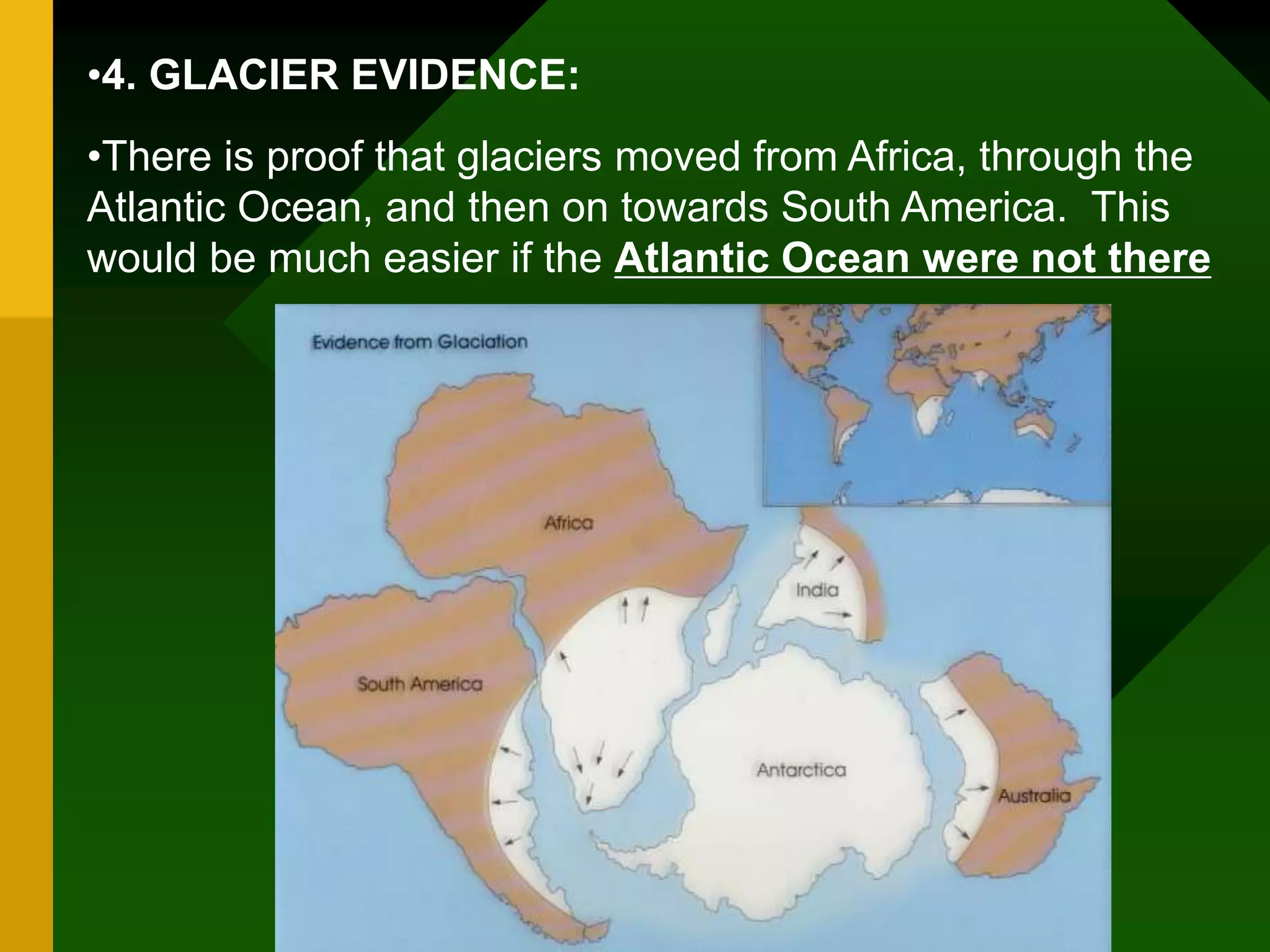
The document discusses plate tectonics and provides evidence that supports the theory of continental drift. It describes how the Earth's crust is broken into plates that move relative to each other. The plates interact in different ways as they move, including colliding, pulling apart, and scraping past one another, which causes geological features like mountains and volcanoes to form. It also explains Alfred Wegener's early theory of continental drift and the fossil, geological, and geographical evidence he used to support the idea that the continents were once joined together in a supercontinent called Pangaea.