Embed presentation
Downloaded 362 times








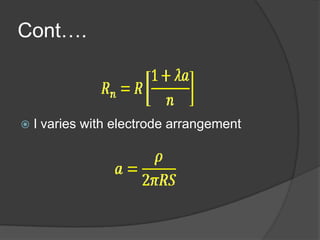





The document discusses different methods of earthing electrical systems. It defines earthing as providing a direct path for fault current and achieving a common reference potential. It describes designing earthing using rods, strips, infill material or foundations. It also discusses soil resistivity testing to determine the resistivity based on moisture, temperature and depth. It provides formulas to calculate the resistance to earth of rods, strips and infill material based on factors like soil resistivity, length, diameter and material used.












