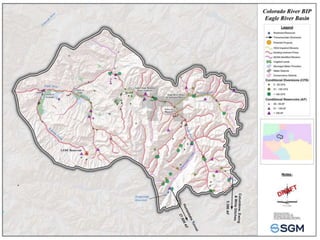
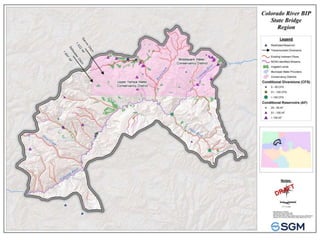
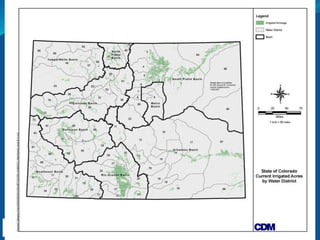
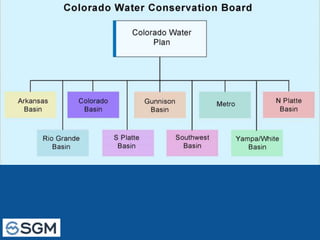
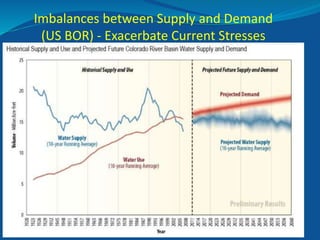
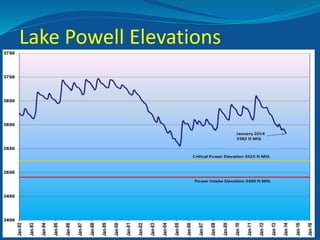
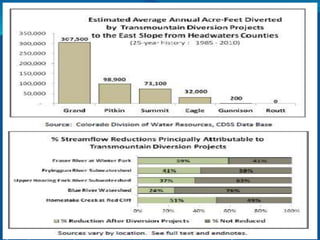
The document summarizes an Eagle County Town Hall meeting about water issues in the Colorado River Basin. It provides background on water history in Eagle County, the Colorado Water Plan, and the Basin Implementation Plan (BIP) process. It discusses key themes from public outreach, the status of BIP projects, and upcoming opportunities for public input into the plan. The goal is to develop a grassroots document through the BIP process that identifies projects, policies, and processes to help address the projected gap between future water supply and demand in Colorado through 2050.









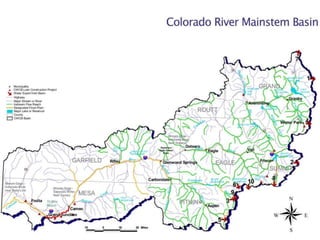
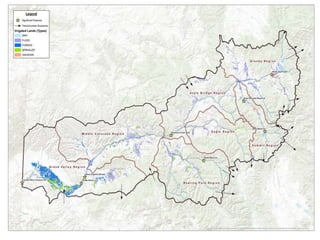








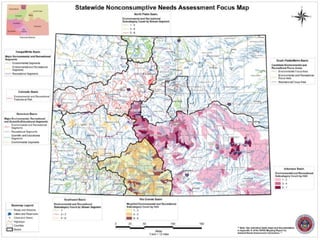
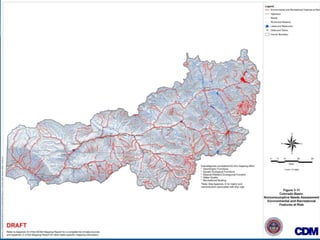

![Nonconsumptive Needs
Assessment (NCNA)
Part of the Statewide Water Supply Initiative (SWSI)
2010
Environmental and recreational mapping – focus areas
and projects and methods
Habitat restoration (bank stabilization or instream
habitat restoration)
Flow protection [voluntary flow agreements, instream
flow (ISF) donations, voluntary re-operation of
reservoirs for environmental and recreational benefit]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eaglecounty032714final-140408105934-phpapp02/85/Eagle-County-Town-Hall-Meeting-30-320.jpg)