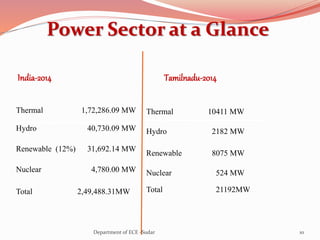
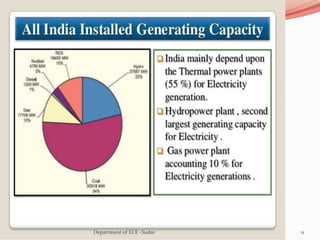
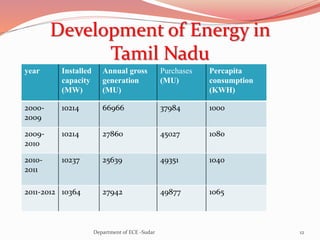
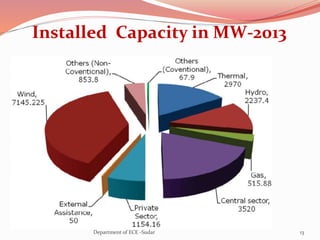
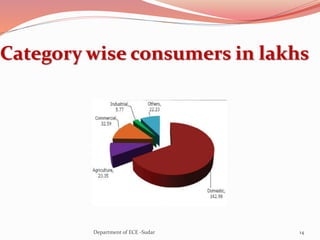
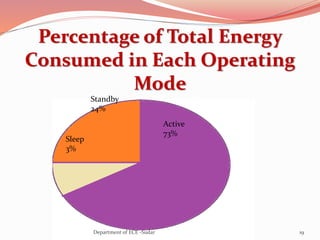
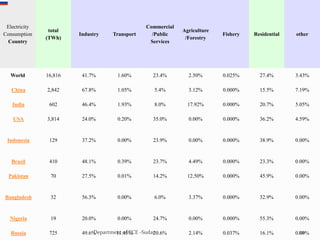
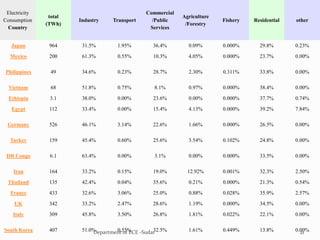
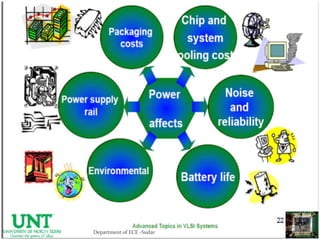
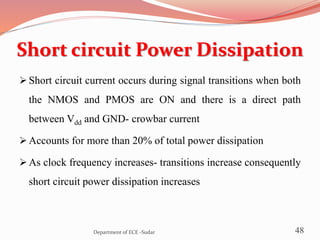
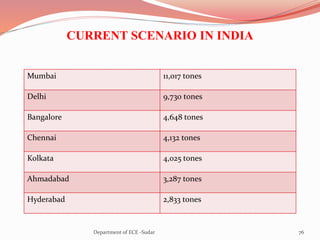
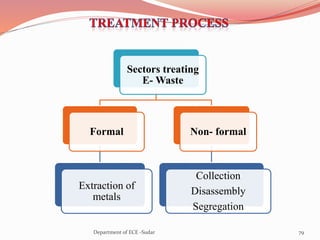
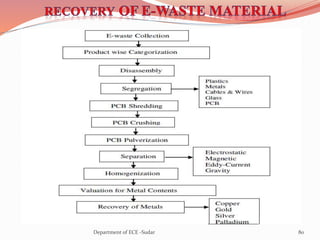
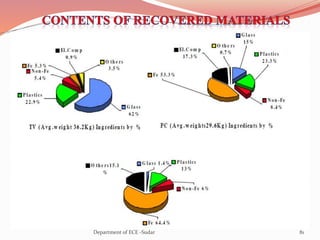
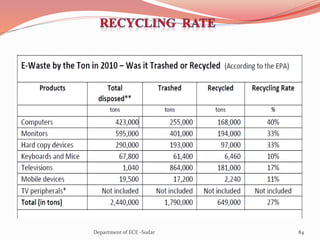
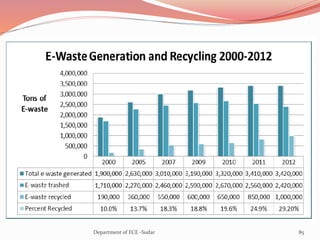
The document discusses various topics related to power generation and electricity consumption. It provides information on different methods of power generation including fossil fuels, nuclear power, hydropower, wind energy, solar power, and geothermal energy. It also discusses fossil fuels in more detail, noting they were formed over millions of years from prehistoric plants and animals. Additionally, it covers electricity consumption patterns around the world and strategies for reducing energy usage.