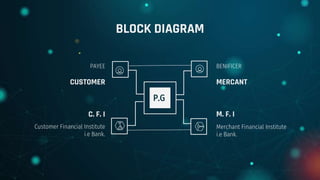
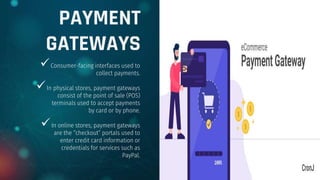
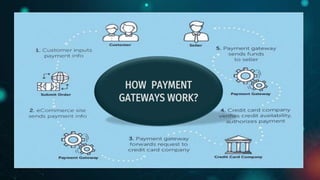
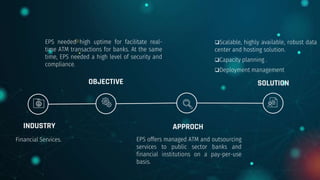
The document discusses traditional and electronic payment systems, highlighting their differences in medium, risk levels, and requirements. It also explains how payment gateways function, detailing protocols like the Secure Electronic Transaction, and the risks associated with e-payments such as stolen credentials and lack of anonymity. A case study focuses on Electronic Payment & Services (EPS) and its partnership with HPE to ensure secure, real-time ATM transactions for banks.