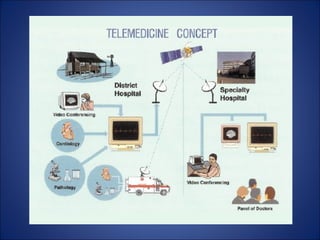
Telemedicine allows patients to visit with physicians through video conferencing for immediate care or send medical images and data to physicians for diagnosis and treatment. It provides access to healthcare for remote populations and enables a single radiologist to provide services to multiple hospitals around the world through electronic transmission of medical images. Key requirements for teleradiology include medical imaging systems, radiology information systems, and secure high-speed connectivity between sites.