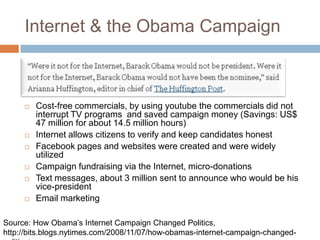
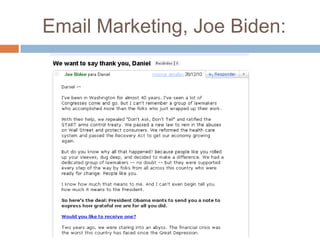
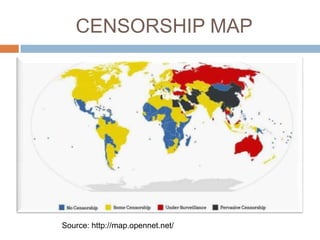
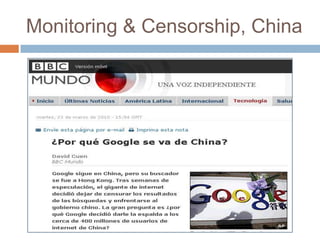
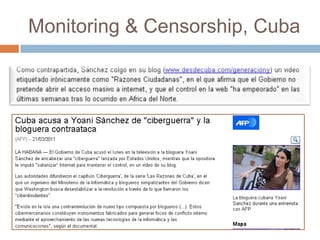
The document discusses how the proliferation of digital technologies and the internet has contributed to the emergence of a nonpolar international system characterized by numerous centers of power beyond just states. It notes how globalization and new communication forms have empowered non-state actors and weakened states. The US still maintains military dominance but has lost economic dominance. The document also provides examples of how social movements and political campaigns have leveraged digital tools and social media to organize and spread information.