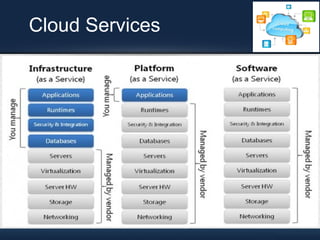
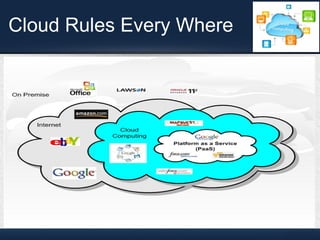
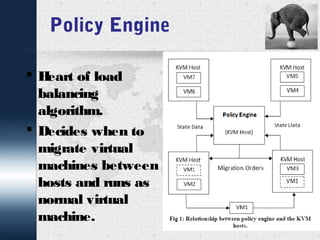
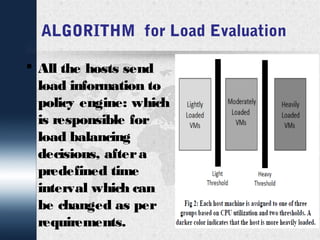
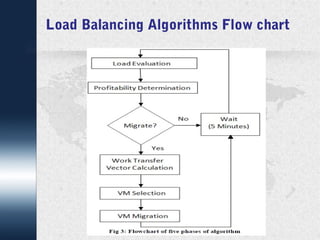
This document discusses dynamic load balancing on Linux-based private clouds. It begins by providing background on cloud computing and virtualization. It then describes live migration, load balancing algorithms and phases, and a proposed load balancing algorithm using a policy engine. The document concludes that load balancing plays an important role in cloud computing and that future work could focus on additional load parameters like memory, disk I/O, and network load.