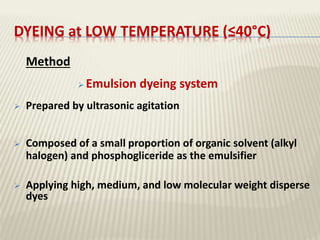
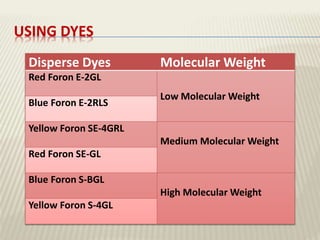
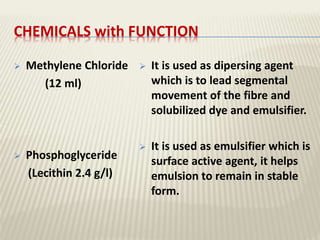
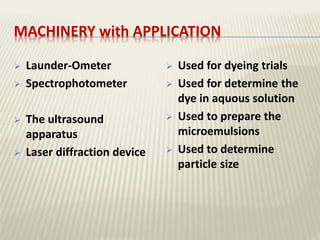
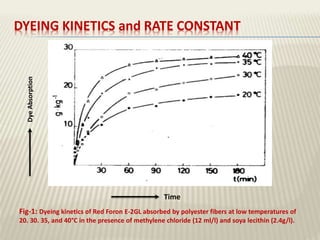
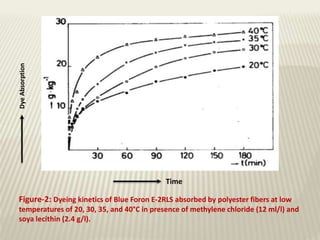
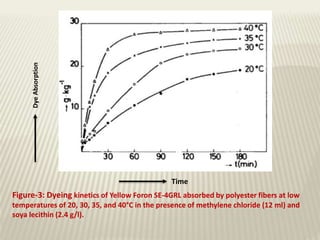
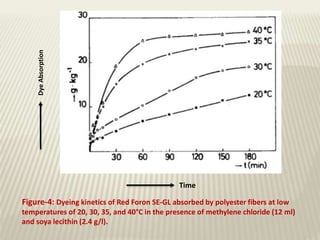
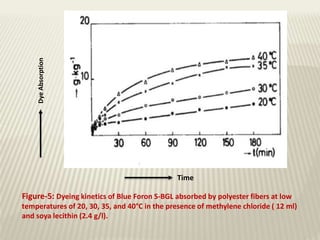
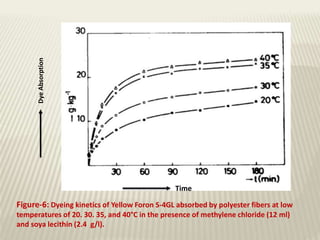
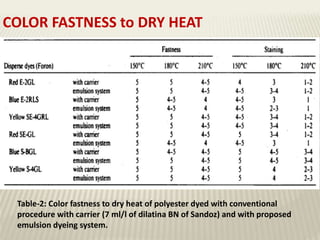
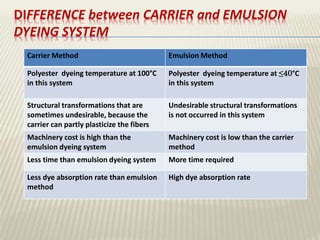
The document discusses the emulsion dyeing system for polyester fibers, highlighting its advantages over traditional carrier methods, such as lower temperatures, reduced costs, and higher dye absorption rates. It details the use of methylene chloride and lecithin in stabilizing the dyeing process and presents findings on dyeing kinetics, with exhaustion rates exceeding 90% at 40°C for low and intermediate molecular weight dyes. Additionally, the document provides activation energy values, indicating that they range from 20-40 kcal/mol, similar to traditional methods.