This document summarizes a presentation on dummy variables and innovation in the manufacturing sector in Pakistan. It includes:
1) References several books on econometrics and a research paper on determinants of innovation in manufacturing in Pakistan.
2) Defines dummy variables, product innovation, and process innovation. Large firms, exporting firms, and firms with more educated managers are more likely to innovate.
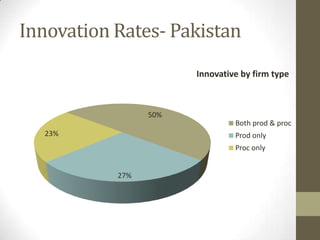
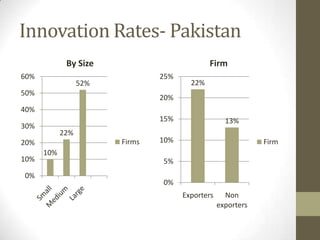
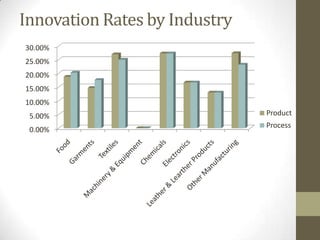
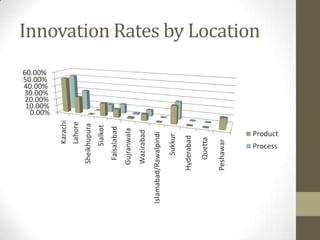
3) Uses panel data from Pakistani manufacturing firms to estimate innovation rates based on firm characteristics like size, location, and industry. The highest innovation rates are in Karachi, large firms, and textile/food/garment industries.
4) Employs a probit model to estimate the effects of internal