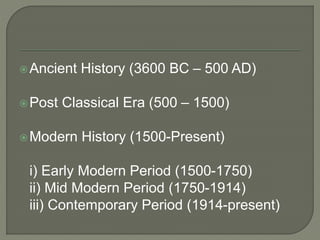
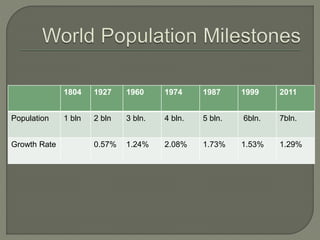
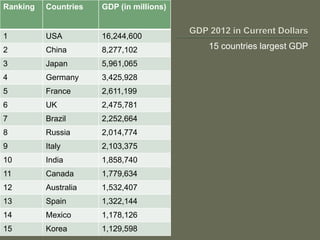
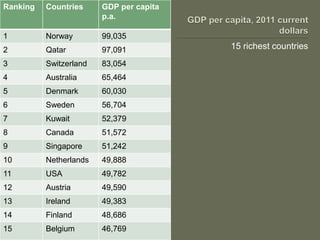
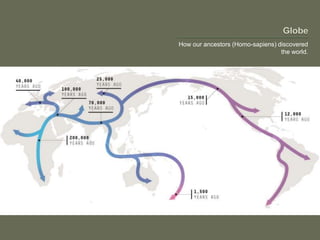
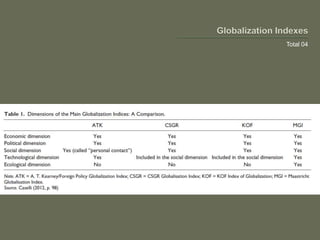
The document explores globalization through a political economy and civilization approach, outlining historical timelines and the evolution of civilizations from the Paleolithic era to modern history. It presents demographic data, including population rankings and GDP statistics of various countries, alongside the significance of trade and economic relationships among BRICS nations. The discussion raises concerns about future geopolitical tensions and the potential for global conflicts.