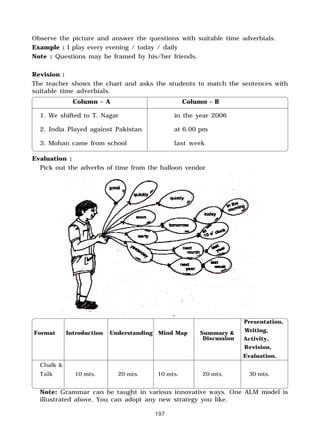
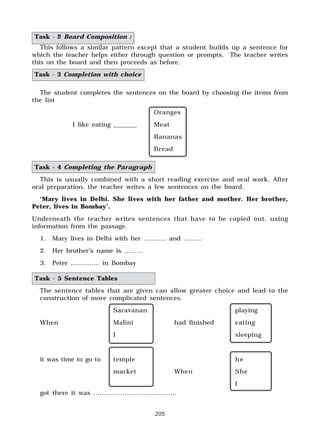
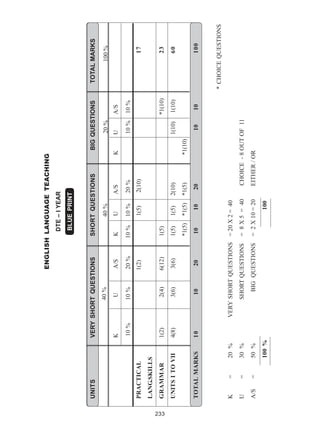
This document outlines the syllabus for English Language Teaching for the first year of the Diploma in Teacher Education course. It discusses the objectives of developing the necessary skills for trainees to listen, speak, read and write effectively in English as well as increase their vocabulary and strengthen their knowledge of grammar. It emphasizes adopting effective teaching-learning strategies and organizing language activities. It covers content areas like practical language skills, grammar and usage as well as methodology topics like objectives of learning English, oral skills, listening and speaking, teaching methods and approaches, teaching vocabulary, prose and poetry. The syllabus aims to equip trainees with skills to teach English effectively and make learning enjoyable for students.


































































































































































![158
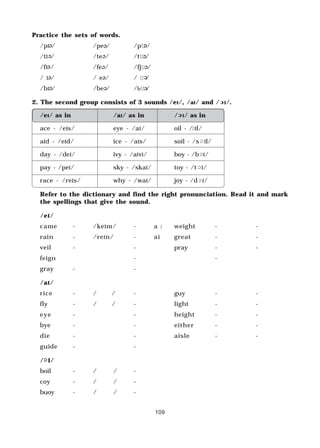
b) All structural words.
c) Words which are useful because other words can be built from them
e.g. Spot-spotted, spotless, spotty and unspotted.
2. In the first year we should have vocabulary referring to concrete things –
things that can be seen, touched and gradually we should proceed from
concrete to abstract.
Mr. Billow’s four concentric circles can make a basis for this
i) the class room.
ii) the home environment.
iii) vocabulary from outside the classroom and home environment which can
be introduced with the help of the pictures and
iv) similar vocabulary but which cannot be introduced in this way.
In the first year, when the students have fully grasped the vocabulary and
structures concerning class room objects, they should go on to structures and
vocabulary concerning the home environment. Similarly in the second year, they
should be introduced to structures dealing with things outside their environment
with the help of pictures and other audio-visual aids, proceeding from the known
to the unknown. As and when the children move on grasping sufficient vocabulary
concerning concrete objects, we have to introduce vocabulary and structure relating
to abstract things outside their own experience.
The first verb introduced should be am / are / is (this is a book). Afterwards the
idea of continuous tenses should be taken up. Later on in the coming years, the
tenses introduced should include the definite and perfect ones.
The need for controlled composition with the pictures and other visual aids must
also influence the grading of vocabulary and structures.
3. How to decide – in later stages - which word is simple and which is difficult.
Look at this sentence:
I’m not going to put up with this behaviour any longer.
All the words in this sentence link with one another and help to make up the
sense of the sentence; but three words in particular, “put up with” are firmly
linked together: they operate as a unit – and have one meaning (roughly ‘tolerate’
or ‘endure’) so here we have three words for one lexical item (Refer to ‘phrasal
verbs’ in the unit on CONTENT – SECOND YEAR. The concept of lexical item as
one kind of unit of meaning is useful to the teacher, as it helps to make clear
what is being taught. It reveals one reason why a difficult word like ‘helicopter’
which has only one meaning may be easier to teach them a so called ‘simple’
word like ‘head’ which may be in several different lexical items:
- a hat on my head.
- at the head [ = top ] of the page.
- the head [ = boss ] of the business.
- to head [ = lead] a team etc.
However one may feel in the end that there is no such thing as ‘the perfect’
order or grading. We teach many new words nowadays as children are picking
up a large number of vocabulary items outside the school through the electronic
and print media. They are growing linguistically too. They come to school with
a precious wealth of vocabulary. So we need not restrict them to a limited](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dted1-english-140519001813-phpapp02/85/Dted1-english-170-320.jpg)