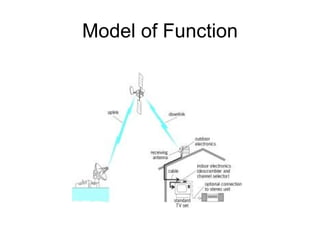
The document discusses the history and technology of digital satellite systems. It describes how DirectTV first launched in 1994 using the Thomson DSS system before DVB-S was standardized. DSS was functionally similar to DVB-S but used different information tables and transport streams. The document also outlines the basic components and positioning of communication satellites, frequency bands used, and compression standards involved in digital satellite television transmissions over time.