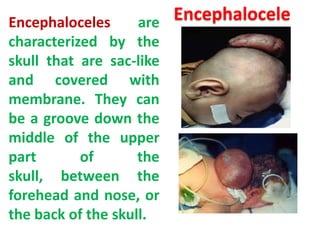
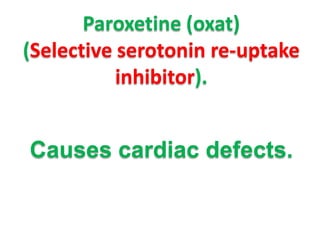
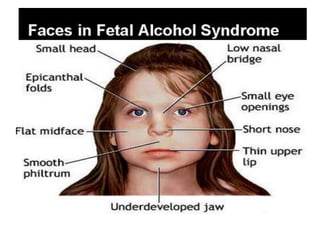
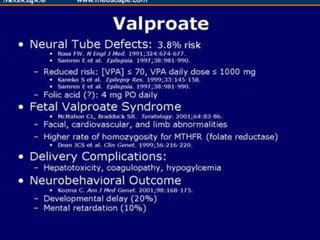
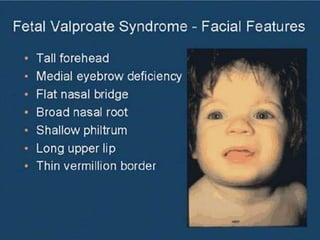
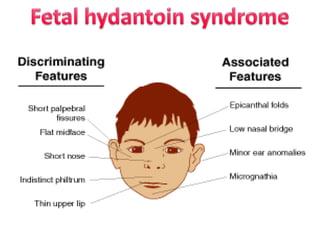
This document provides information on medication use during pregnancy. It discusses:
- The FDA pregnancy categories (A, B, C, D, X) which assess risk of fetal injury from drugs. Category A drugs are safest, while X should never be used.
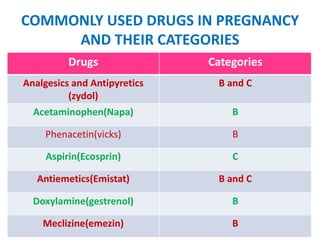
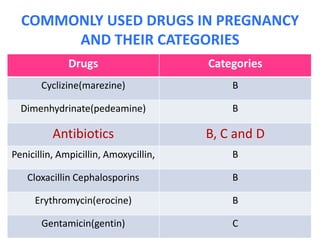
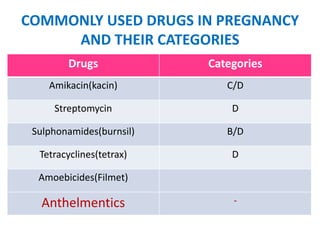
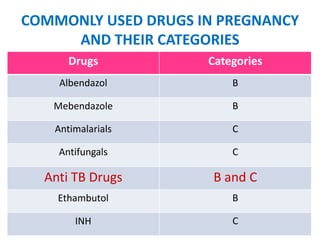
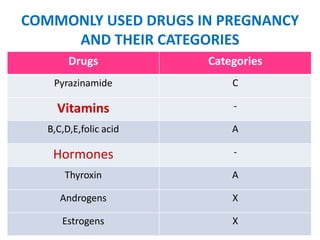
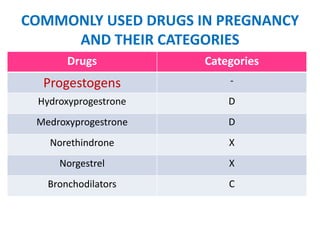
- Common drugs used in pregnancy and their categories, including analgesics, antibiotics, vitamins, and hormones.
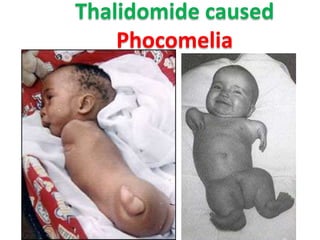
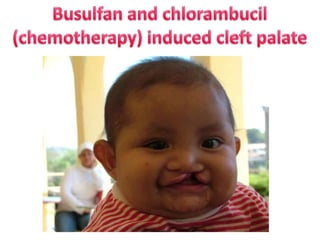
- Drugs that are contraindicated like thalidomide, Accutane, and warfarin due to known risks of birth defects.
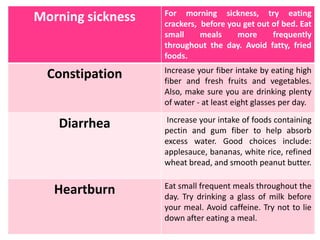
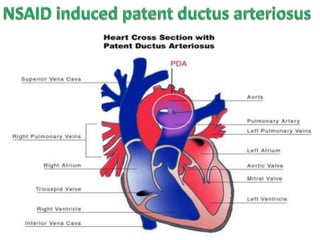
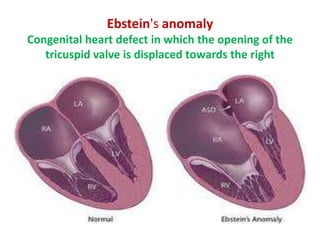
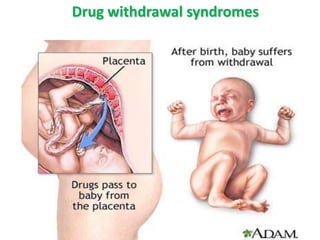
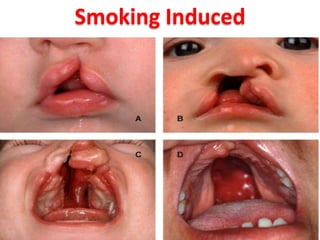
- Specific risks to the fetus from various drugs like NSAIDs causing PDA, lithium causing heart defects, and alcohol causing fetal alcohol syndrome.