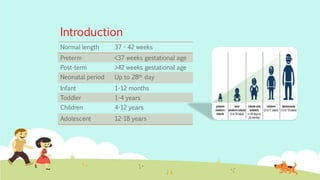
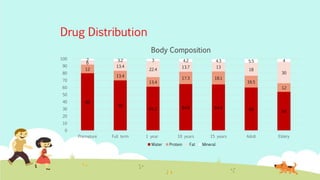
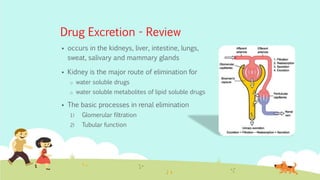
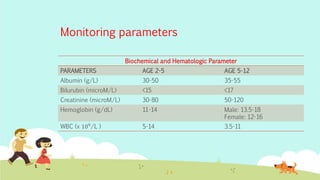
This document provides an overview of principles of neonatal and pediatric pharmacology. It discusses pediatric ages and developmental stages. It then covers topics of pediatric pharmacokinetics including absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion. Factors such as organ maturation, body composition and plasma protein binding affect how drugs are processed in pediatric patients compared to adults. The document also reviews monitoring parameters and considerations for pediatric drug therapy including dose calculations, choice of formulations, disease conditions, adverse reactions and counseling.