1) Drug interactions can occur when two drugs are taken together and one drug modifies the effects of the other. This can increase therapeutic effects in some planned cases, but can also cause toxicity or therapeutic failure in unplanned cases.
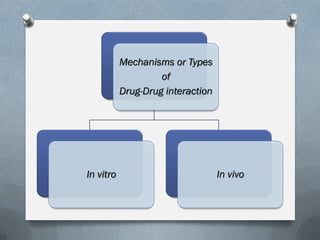
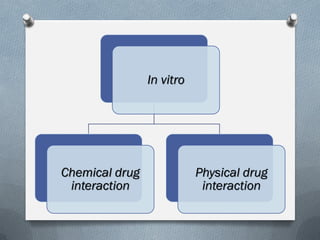
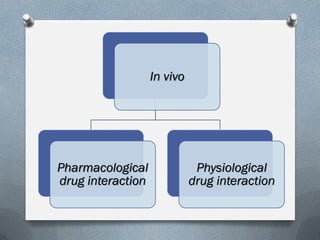
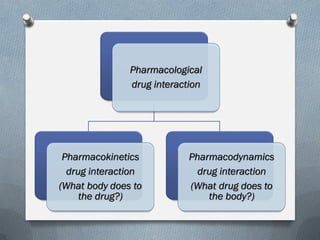
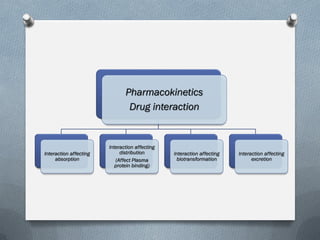
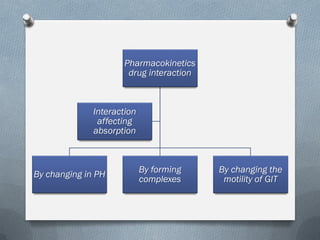
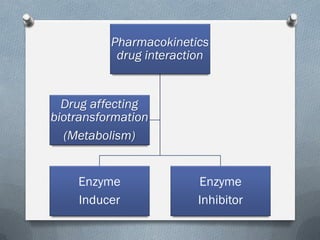
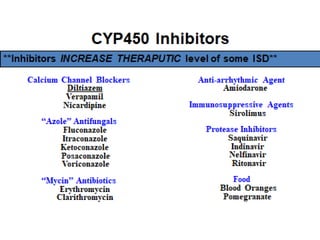
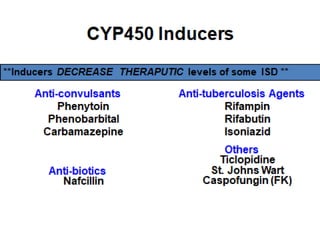
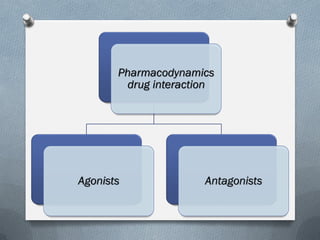
2) Mechanisms of drug interactions include changes in absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of one or both drugs. They can occur through pharmacological or physiological pathways such as enzymatic induction or inhibition.
3) Several case studies are presented involving patients taking multiple drugs where evaluating for potential drug interactions is important for optimizing treatment and avoiding adverse effects.