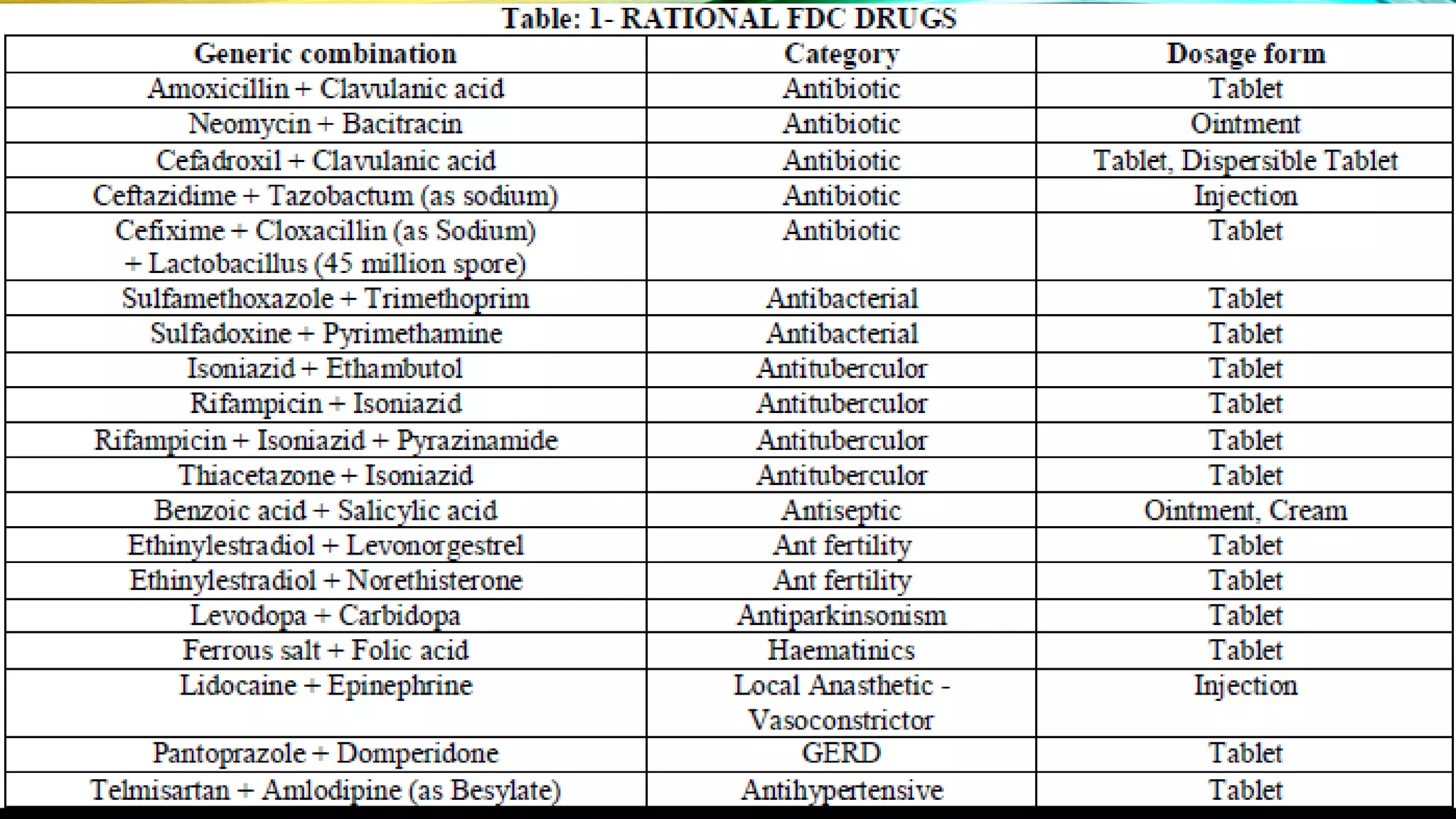
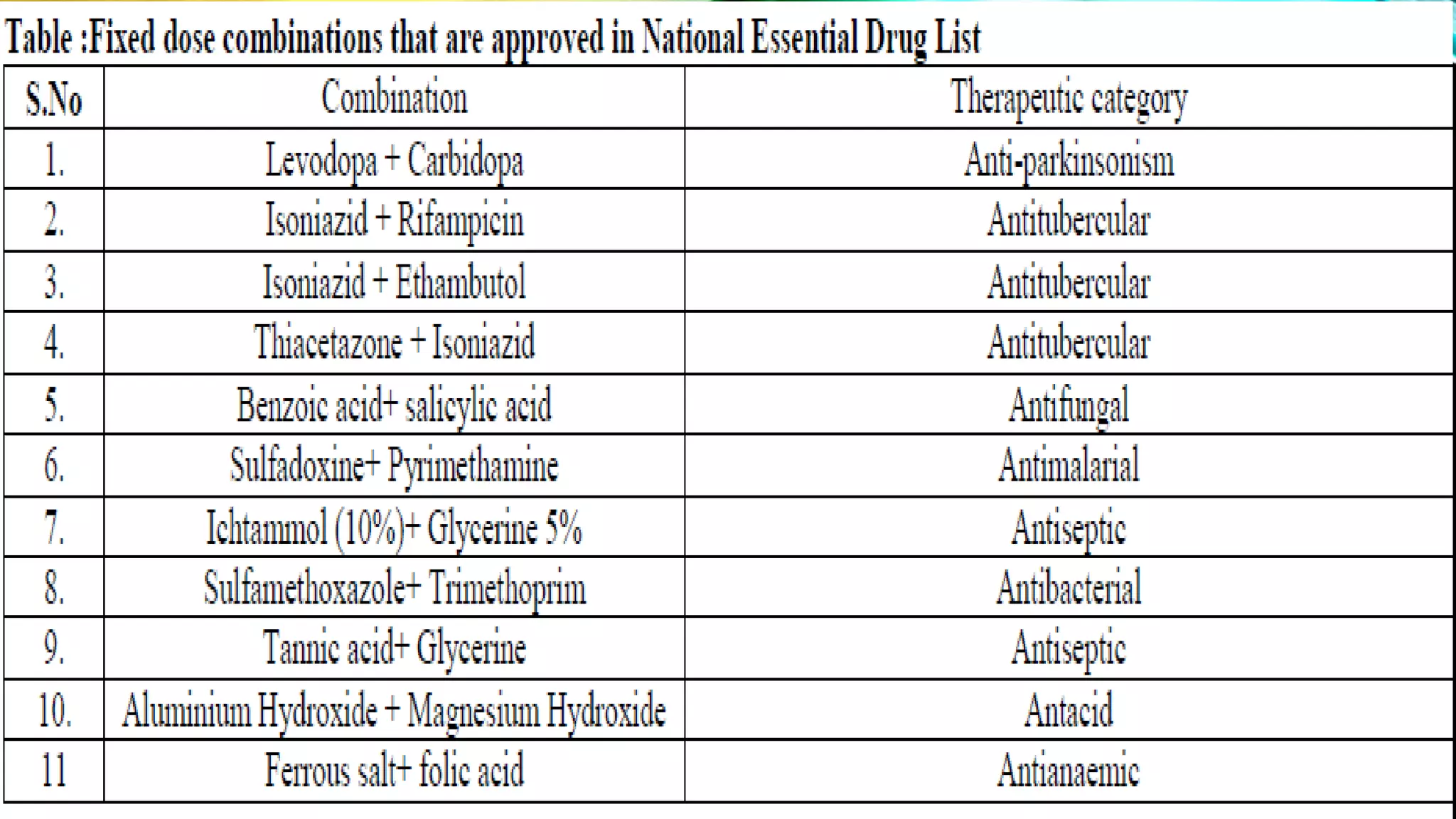
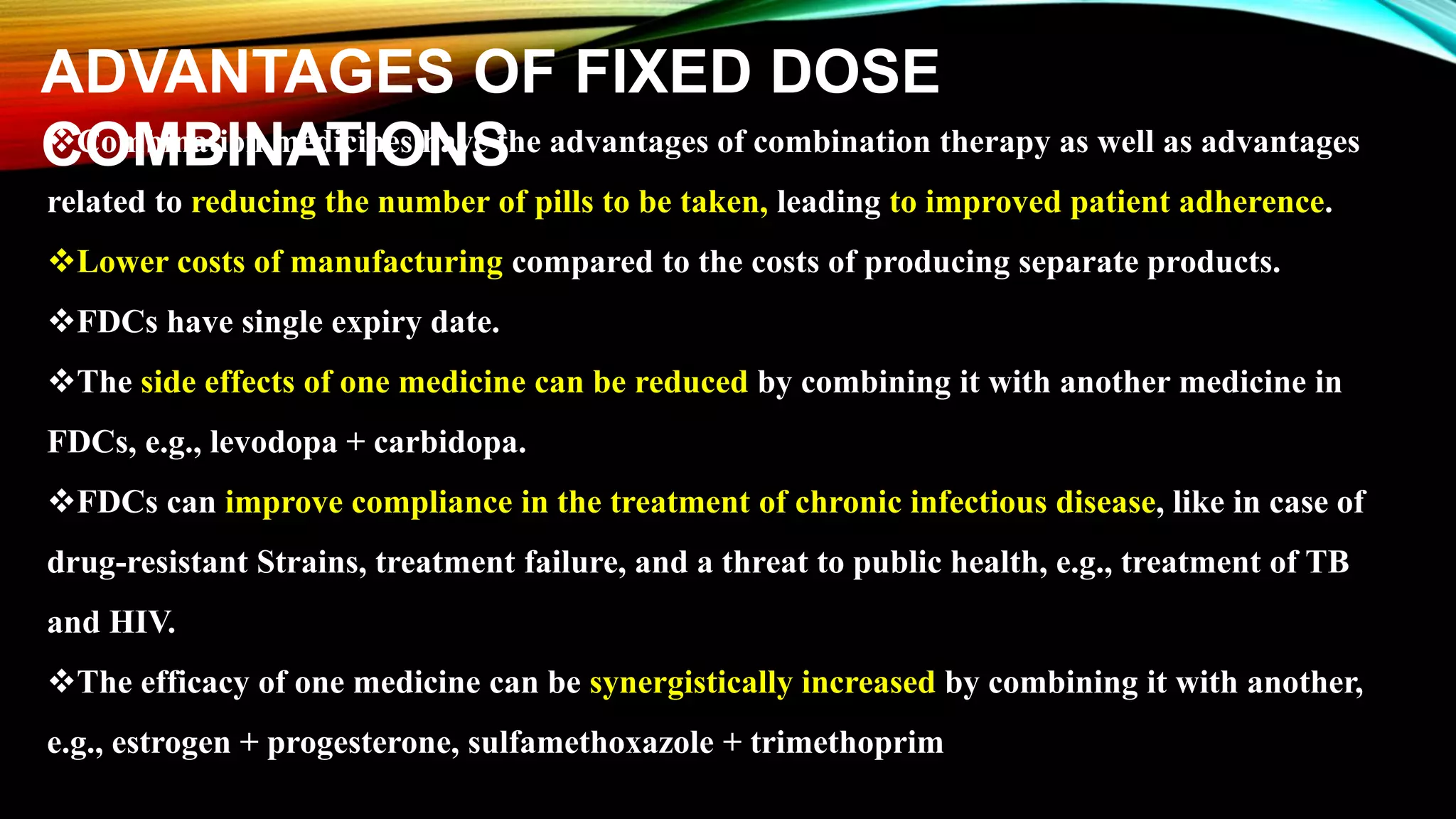
This document discusses fixed dose drug combinations (FDDCs), including their definitions, types, rationality, advantages, and disadvantages. It defines FDDCs as combinations of two or more active pharmaceutical ingredients formulated as a single medicine. FDDCs can be rational if they have complementary mechanisms of action, decrease resistance, and increase efficacy and compliance while decreasing adverse effects. However, irrational FDDCs lack pharmacological justification and may increase side effects and costs without additional benefit. The document also notes issues with overpromotion of irrational FDDCs in India and efforts to better regulate these combinations.