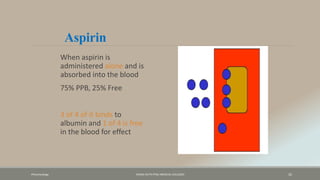
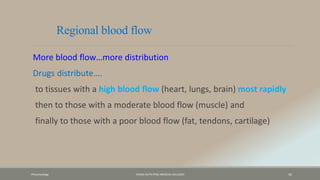
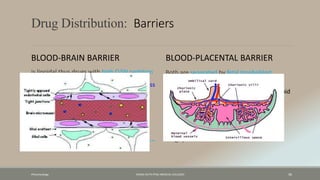
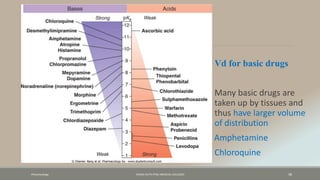
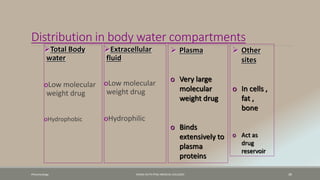
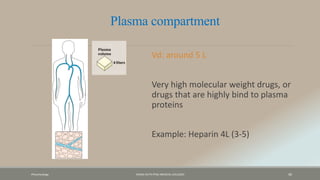
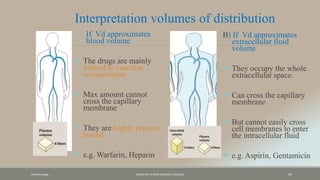
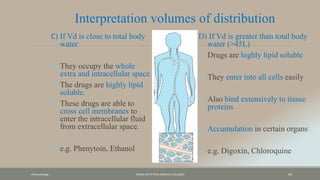
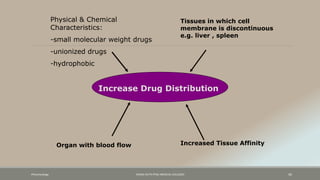
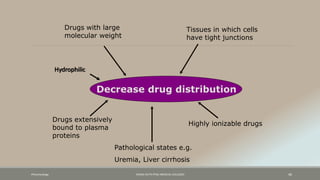
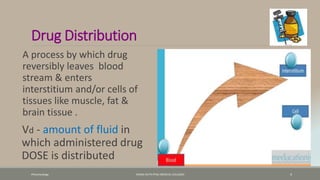
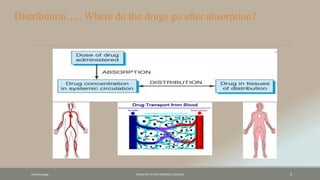
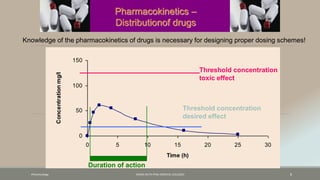
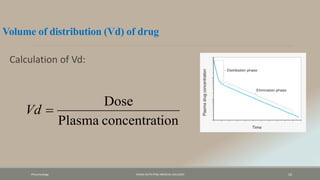
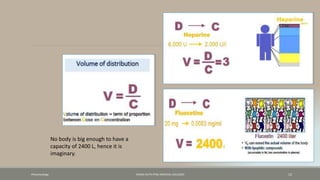
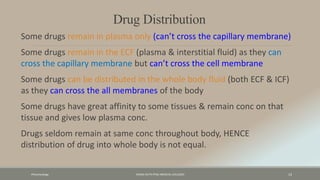
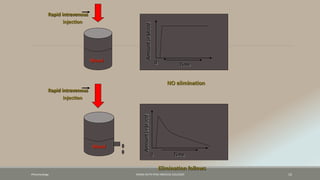
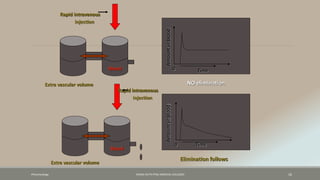
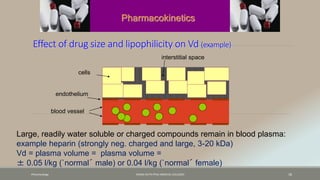
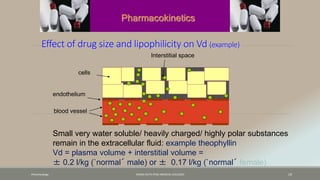
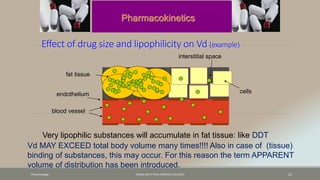
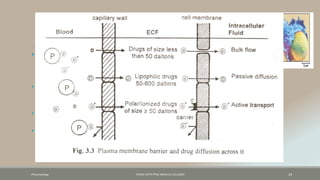
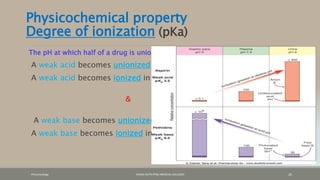
The document discusses drug distribution, defining it as the process by which drugs leave the bloodstream and enter body tissues. It covers factors affecting distribution, such as drug size, lipophilicity, and protein binding, as well as the concept of volume of distribution and its significance for dosing. Key insights include that distribution is uneven across body compartments and demonstrates how various physiological and pathological conditions can influence the pharmacokinetics of drugs.















![Plasma Protein Binding [PPB]
ACIDIC DRUGS
High affinity & low capacity
Two particular sites of the albumin molecule
bind acidic drugs with high affinity (strongly)
BASIC DRUG
Low affinity & high capacity
Basic drugs bind with alpha1-acid
glycoprotein & Lipo protein
Pharamcology FAZAIA RUTH PFAU MEDICAL COLLEGES 29
CLASS I DRUGS
o Low dose/capacity
ratio e.g.
Tolbutamide
CLASS II DRUGS
o High dose/capacity
ratio e.g.
Sulphonamide](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugdistribution-230302165320-1161b6c7/85/Drug-Distribution-pptx-29-320.jpg)