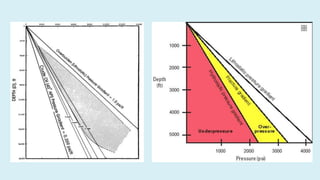
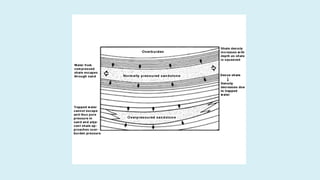
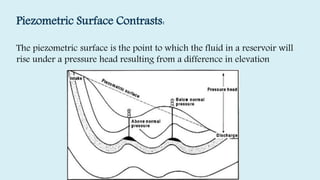
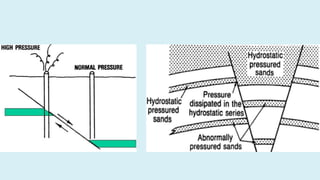
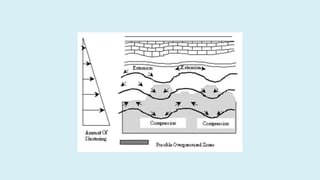
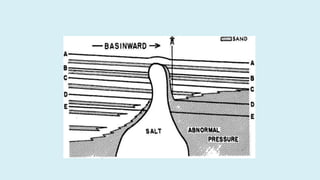
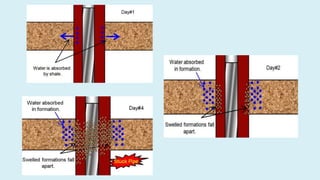
This document summarizes several potential problems that can occur while drilling beds, including abnormal pressure, unconsolidated formations, shale instability, key seats, and ledges. Abnormal pressure can result from rapid sedimentation, evaporite deposition, piezometric surface contrasts, diagenesis processes, tectonic activity like folding and faulting, salt diapirism, and uplift. Unconsolidated formations can cause particles to separate and fall downhole. Shale instability can occur through mechanical or chemical mechanisms involving swelling and weakening. Key seats refer to wear points where the drill string changes direction. Ledges form from sequential soft, hard, and fractured formations wearing differently and potentially sticking the drill string.