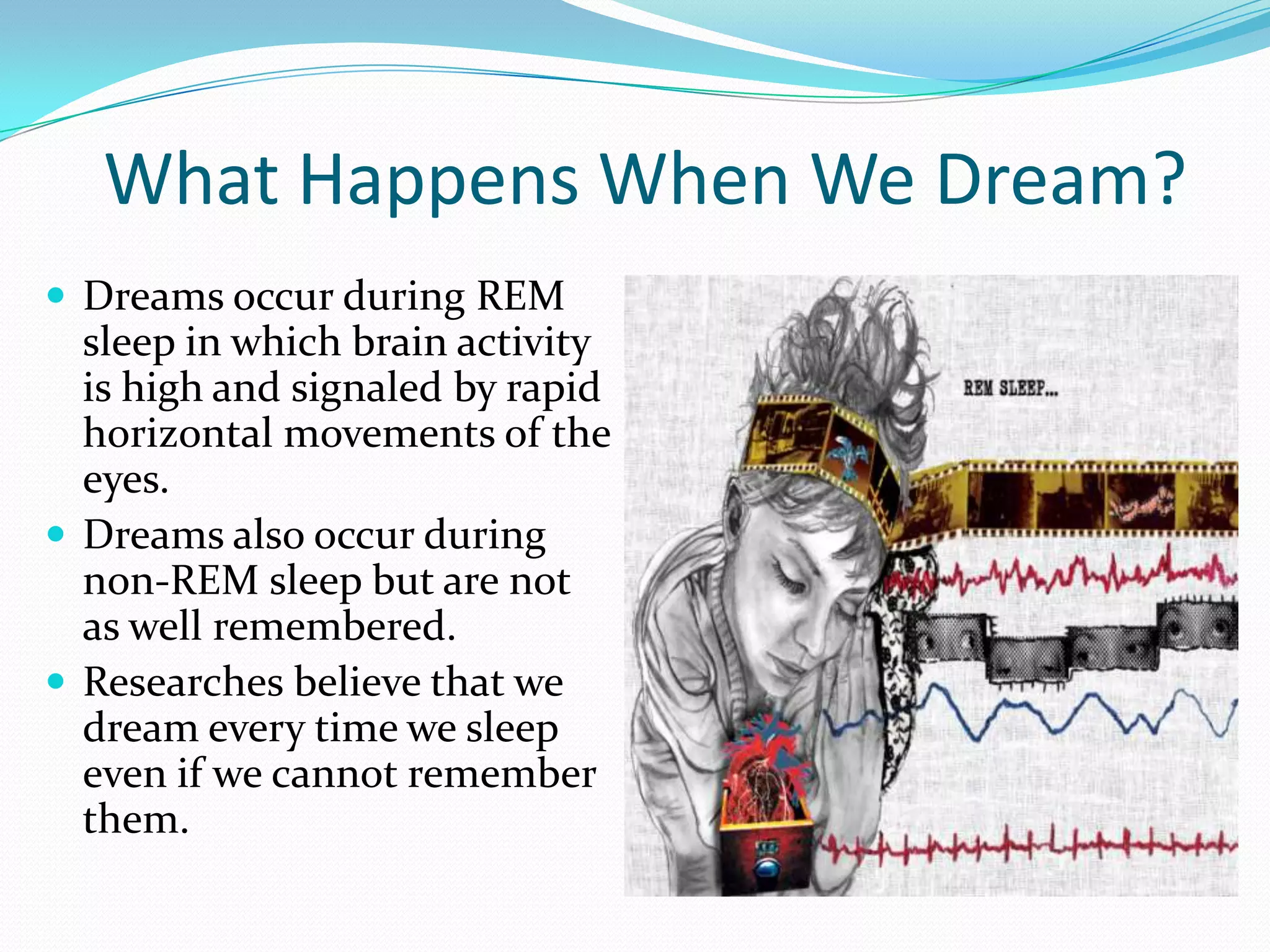
Dreams occur during REM sleep and involve vivid images, sounds, thoughts and sensations. They are believed to be manifestations of unconscious thoughts and emotions. Sigmund Freud theorized that dreams represent unconscious desires, especially sexual ones. More recent theories suggest dreams help process daily experiences and reinforce learning. Evolutionary theories posit dreams enhanced ancestral survival. Different types of dreams include normal, lucid, nightmares and reoccurring dreams. Daydreams also involve semi-conscious thoughts and can represent unconscious wishes.