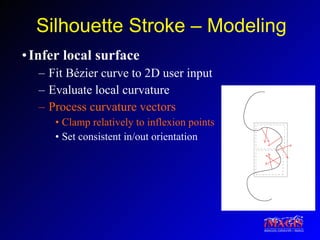
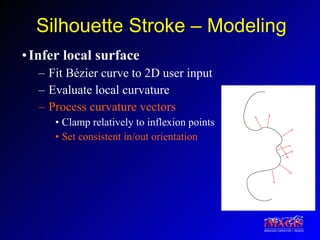
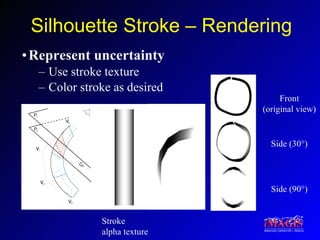
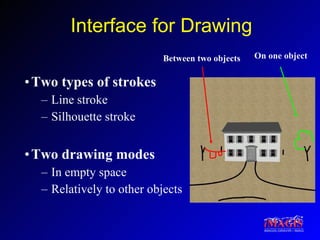
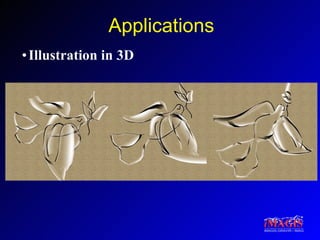
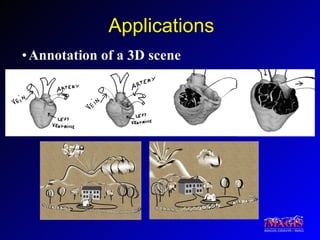
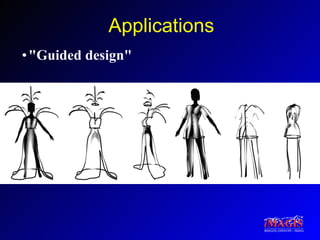
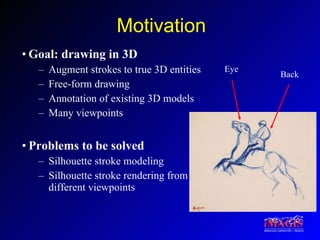
This document proposes a method for drawing in 3D using view-dependent silhouette strokes that can represent uncertainty and occlusion. It discusses previous work on 3D drawing that was limited to specific interfaces or primitives. The proposed approach models silhouette strokes as 3D curves with associated surfaces, and renders them from different viewpoints while managing occlusion. An interface allows drawing lines and silhouettes in empty space or on objects. Applications include illustration, annotation, and guided 3D design. Future work includes handling tubular objects and real-world testing in teaching anatomy.


![Previous Work [Akeo et al., 1994] [Pugh, 1992] 2D drawing is converted to 3D Specify hidden parts by hand](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drawing-for-illustration-and-annotation-in-3d-091213145423-phpapp02/85/Drawing-For-Illustration-And-Annotation-In-3D-5-320.jpg)
![Previous Work [Lipson and Shpitalni, 1996] [Eggli et al., 1997] No free-form drawing Limited number of primitives](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drawing-for-illustration-and-annotation-in-3d-091213145423-phpapp02/85/Drawing-For-Illustration-And-Annotation-In-3D-6-320.jpg)
![Previous Work [Cohen et al., 1999] [Tolba et al., 1999] 3D curves design, no drawing 2D drawings reprojected, no visibility changes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drawing-for-illustration-and-annotation-in-3d-091213145423-phpapp02/85/Drawing-For-Illustration-And-Annotation-In-3D-7-320.jpg)
![Previous Work [Igarashi et al., 1999] [Zeleznik et al., 1996] Limited to a given gestural interface Closed strokes only](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drawing-for-illustration-and-annotation-in-3d-091213145423-phpapp02/85/Drawing-For-Illustration-And-Annotation-In-3D-8-320.jpg)
![Previous Work [Cohen et al., 2000] Drawing modes adapted to landscaping only, no 3D model reconstruction in billboard mode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drawing-for-illustration-and-annotation-in-3d-091213145423-phpapp02/85/Drawing-For-Illustration-And-Annotation-In-3D-9-320.jpg)