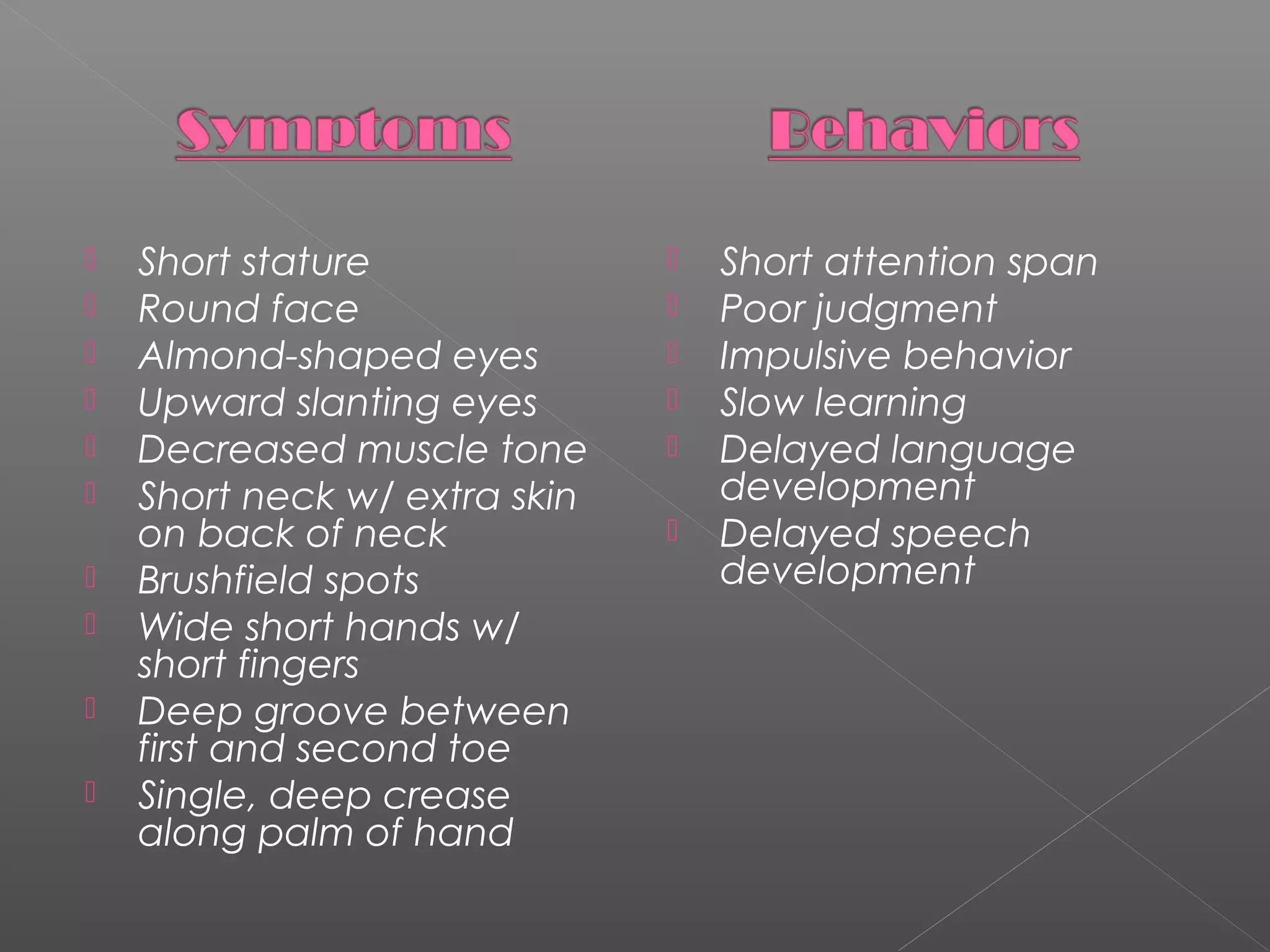
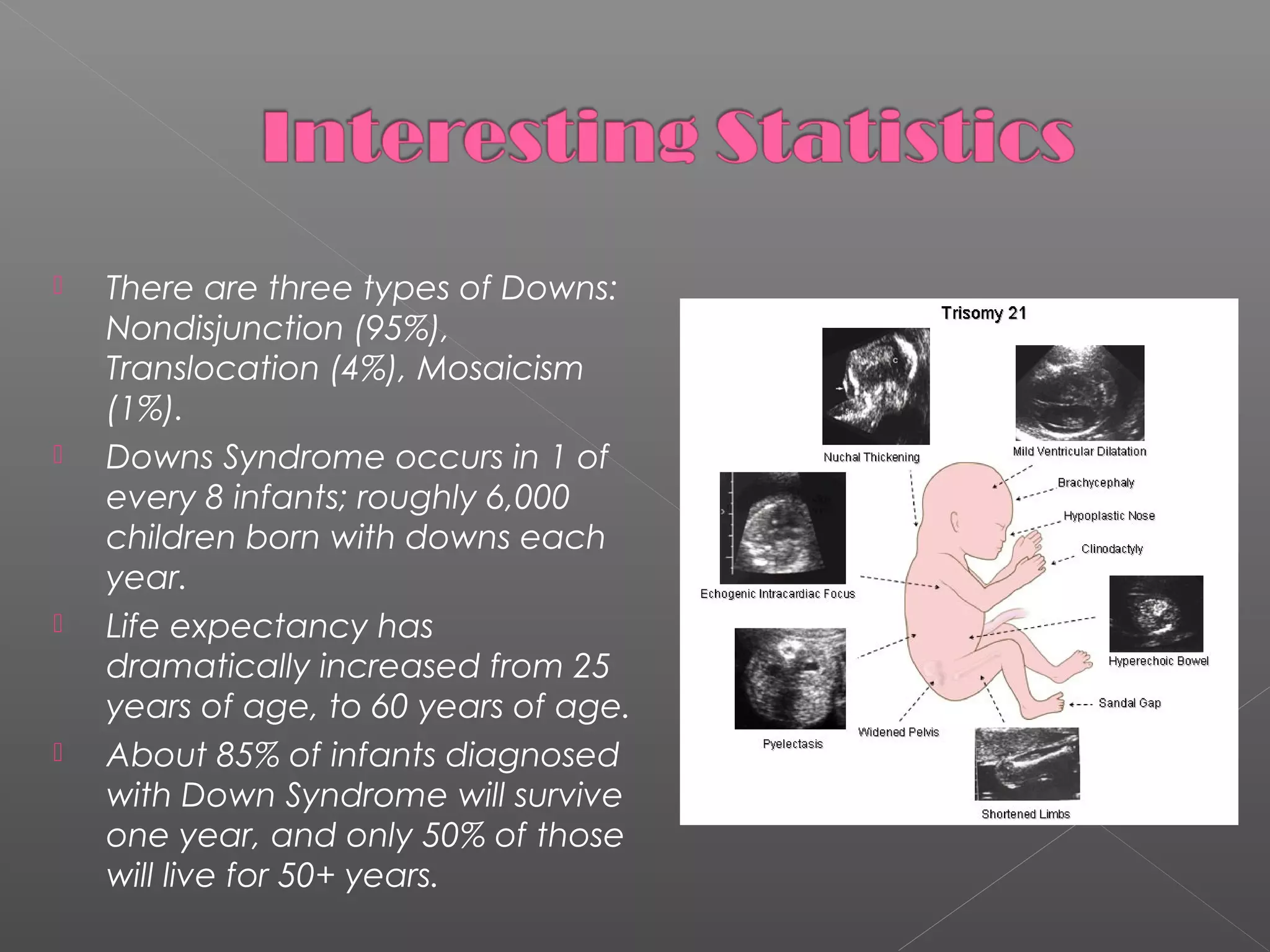
This document provides information about Down Syndrome through defining what it is, possible causes, identifying characteristics, teaching strategies, statistics, and family resources. Down Syndrome is a chromosomal disorder where chromosome 21 is abnormal, causing mental and physical impairments. It can be caused by factors like advanced maternal age or genetics. People with Down Syndrome often have distinctive physical traits and experience delays in areas like language and speech development. The document discusses individualized education approaches like speech therapy, technology use, small group instruction, and praise-based behavior management as effective strategies. It provides statistics on Down Syndrome occurrences and life expectancy increases. Finally, it lists local family support resources.