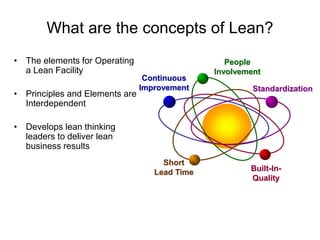
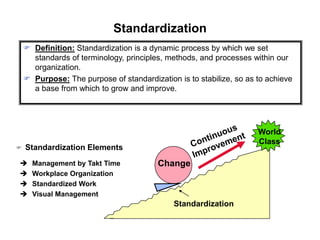
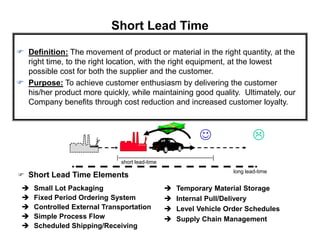
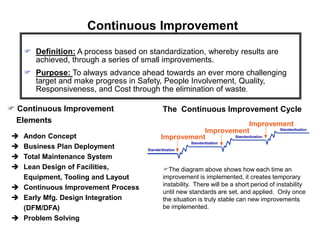
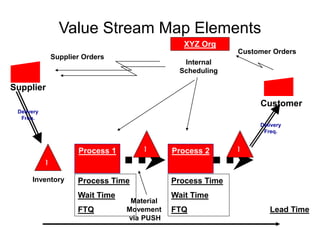
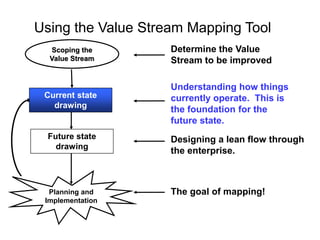
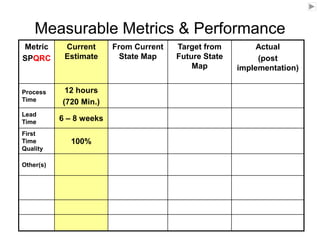
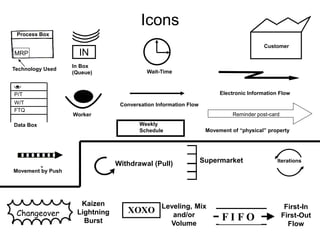
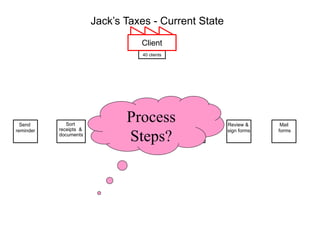
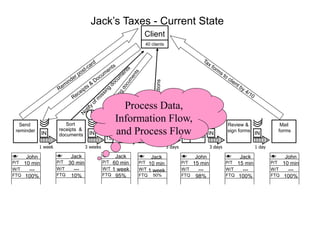
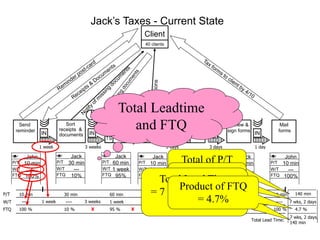
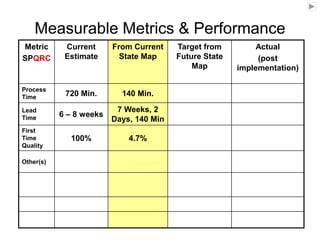
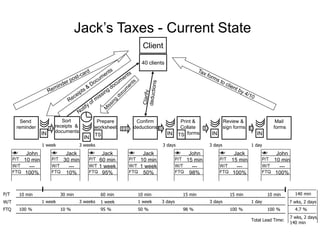
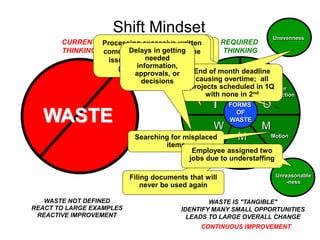
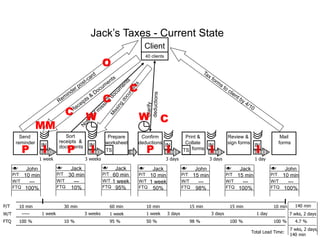
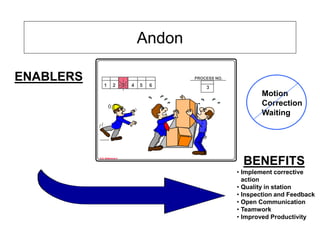
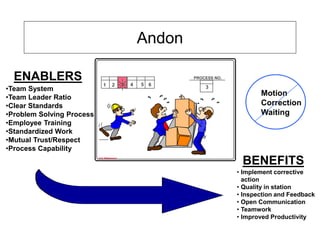
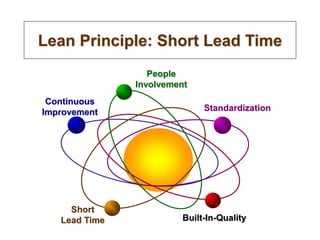
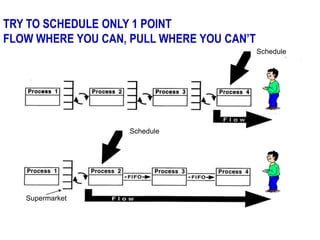
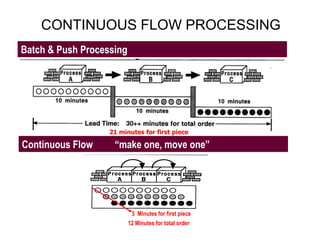
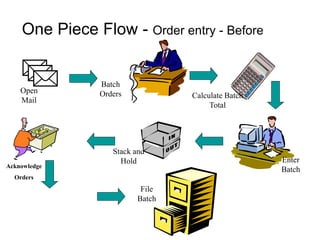
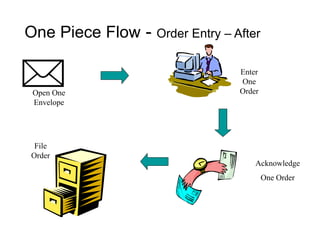
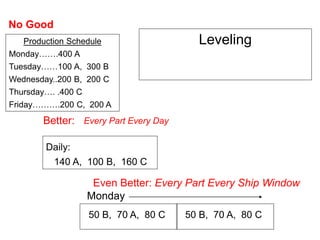
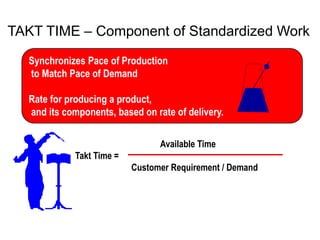
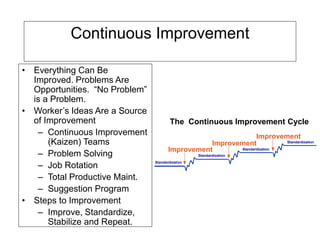
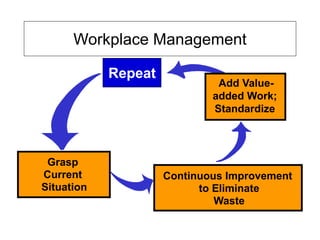
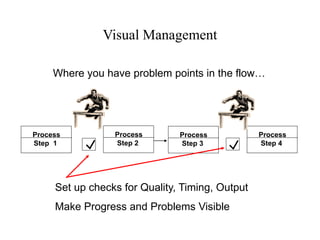
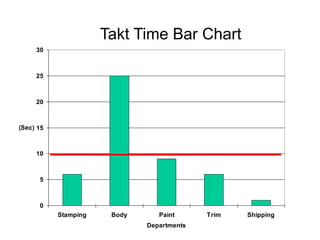
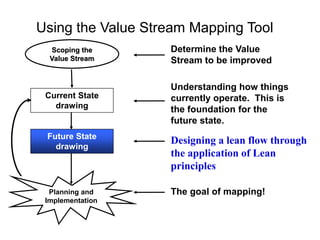
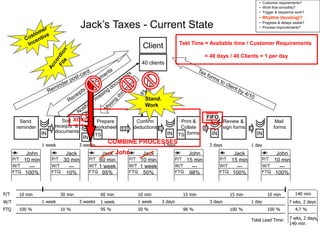
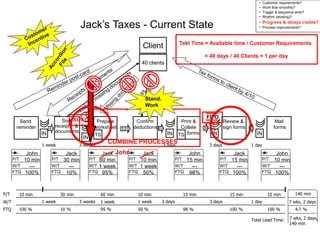
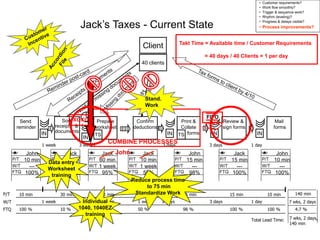
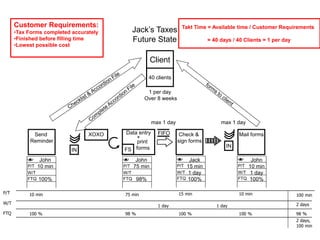
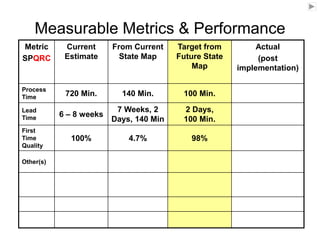
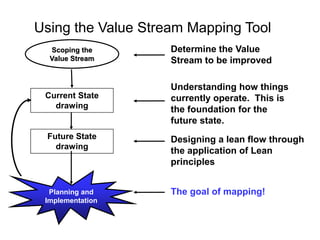
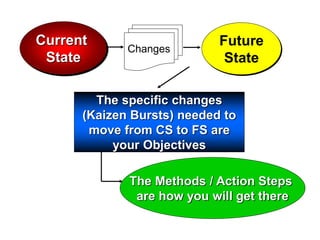
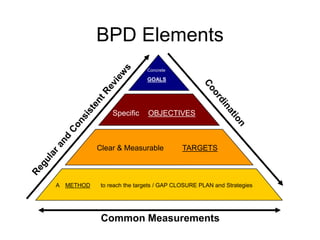
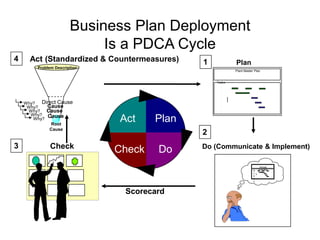
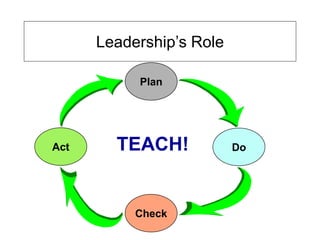
The document outlines the goals and principles of value stream mapping (VSM) as a tool to enhance lean implementation by standardizing processes and improving quality. It emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement, built-in quality, short lead times, and employee involvement, while illustrating current state mapping through a case study of a CPA's tax preparation process. The document also highlights the significance of identifying and eliminating waste to achieve better performance and customer satisfaction.