The document proposes using neural networks to help an intelligent software agent called IDA learn to make high-quality decisions for assigning US Navy sailors to new jobs. Specifically, it evaluates using feedforward neural networks, multilayer perceptrons, and support vector machines to model the decision-making of human Navy personnel called detailers. The neural networks are trained on data from detailers involving sailors, jobs, and which jobs were offered to learn the constraints and preferences that guide human decisions. The goal is for the neural networks to help IDA's constraint satisfaction module make more human-like decisions over time as situations change.
![Learning High Quality Decisions with Neural Networks in
“Conscious” Software Agents
ARPAD KELEMEN1,2,3
YULAN LIANG1,2
STAN FRANKLIN1
1
Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Memphis
2
Department of Biostatistics, State University of New York at Buffalo
3
Department of Computer and Information Sciences, Niagara University
249 Farber Hall, 3435 Main Street, Buffalo, NY 14214
USA
akelemen@buffalo.edu purple.niagara.edu/akelemen
Abstract: Finding suitable jobs for US Navy sailors periodically is an important and ever-
changing process. An Intelligent Distribution Agent (IDA) and particularly its constraint
satisfaction module take up the challenge to automate the process. The constraint satisfaction
module's main task is to provide the bulk of the decision making process in assigning sailors to
new jobs in order to maximize Navy and sailor “happiness”. We propose Multilayer Perceptron
neural network with structural learning in combination with statistical criteria to aid IDA's
constraint satisfaction, which is also capable of learning high quality decision making over time.
Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) with different structures and algorithms, Feedforward Neural
Network (FFNN) with logistic regression and Support Vector Machine (SVM) with Radial Basis
Function (RBF) as network structure and Adatron learning algorithm are presented for
comparative analysis. Discussion of Operations Research and standard optimization techniques is
also provided. The subjective indeterminate nature of the detailer decisions make the optimization
problem nonstandard. Multilayer Perceptron neural network with structural learning and Support
Vector Machine produced highly accurate classification and encouraging prediction.
Key-Words: Decision making, Optimization, Multilayer perceptron, Structural learning,
Support vector machine
1 Introduction [7] and “consciousness”. The model
IDA [1], is a “conscious” [2], [3] software employed a linear functional approach to
agent [4], [5] that was built for the U.S. Navy assign fitness values to each candidate job for
by the Conscious Software Research Group each candidate sailor. The functional yielded
at the University of Memphis. IDA was a value in [0,1] with higher values
designed to play the role of Navy employees, representing higher degree of “match”
called detailers, who assign sailors to new between the sailor and the job. Some of the
jobs periodically. For this purpose IDA was constraints were soft, while others were hard.
equipped with thirteen large modules, each of Soft constraints can be violated without
which responsible for one main task. One of invalidating the job. Associated with the soft
them, the constraint satisfaction module, was constraints were functions which measured
responsible for satisfying constraints to how well the constraints were satisfied for
ensure the adherence to Navy policies, the sailor and the given job at the given time,
command requirements, and sailor and coefficients which measured how
preferences. To better model human behavior important the given constraint was relative to
IDA's constraint satisfaction was the others. The hard constraints cannot be
implemented through a behavior network [6], violated and were implemented as Boolean](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docdoc2696/85/Doc-doc-1-320.jpg)
![multipliers for the whole functional. A “current” sailor all over the time. Our goal in
violation of a hard constraint yields 0 value this paper is to use neural networks and
for the functional. statistical methods to learn from Navy
The process of using this method for detailers, and to enhance decisions made by
decision making involves periodic tuning of IDA's constraint satisfaction module. The
the coefficients and the functions. A number functions for the soft constraints were set up
of alternatives and modifications have been semi-heuristically in consultation with Navy
proposed, implemented and tested for large experts. We will assume that they are
size real Navy domains. A genetic algorithm optimal, though future efforts will be made to
approach was discussed by Kondadadi, verify this assumption.
Dasgupta, and Franklin [8], and a large-scale While human detailers can make
network model was developed by Liang, judgments about job preferences for sailors,
Thompson and Buclatin [9], [10]. Other they are not always able to quantify such
operations research techniques were also judgments through functions and
explored, such as the Gale-Shapley model coefficients. Using data collected periodically
[11], simulated annealing, and Taboo search. from human detailers, a neural network
These techniques are optimization tools that learns to make human-like decisions for job
yield an optimal solution or one which is assignments. It is widely believed that
nearly optimal. Most of these different detailers may attach different
implementations were performed, by other importance to constraints, depending on the
researchers, years before the IDA project sailor community (a community is a
took shape and according to the Navy they collection of sailors with similar jobs and
often provided low rate of "match" between trained skills) they handle, and may change
sailors and jobs. This showed that standard from time to time as the environment
operation research techniques are not easily changes. It is important to set up the
applicable to this real life problem if we are functions and the coefficients in IDA to
to preserve the format of the available data reflect these characteristics of the human
and the way detailers currently make decision making process. A neural network
decisions. High quality decision making is an gives us more insight on what preferences are
important goal of the Navy but they need a important to a detailer and how much.
working model that is capable of making Moreover inevitable changes in the
decisions similarly to a human detailer under environment will result changes in the
time pressure, uncertainty, and is able to detailer's decisions, which could be learned
learn/evolve over time as new situations arise with a neural network although with some
and new standards are created. For such task, delay.
clearly, an intelligent agent and a learning In this paper, we propose several
neural network is better suited. Also, since approaches for learning optimal decisions in
IDA's modules are already in place (such as software agents. We elaborate on our
the functions in constraint satisfaction) we preliminary results reported in [1], [12], [13].
need other modules that integrate well with Feedforward Neural Networks with logistic
them. At this point we want to tune the regression, Multi Layer Perceptron with
functions and their coefficients in the structural learning and Support Vector
constraint satisfaction module as opposed to Machine with Radial Basis Function as
trying to find an optimal solution for the network structure were explored to model
decision making problem in general. Finally, decision making. Statistical criteria, like
detailers, as well as IDA, receive one Mean Squared Error, Minimum Description
problem at a time, and they try to find a job Length, etc. were employed to search for best
for one sailor as a time. Simultaneous job network structure and optimal performance.
search for multiple sailors is not a current We apply sensitivity analysis through
goal of the Navy or IDA. Instead, detailers choosing different algorithms to assess the
(and IDA) try to find the “best” job for the stability of the given approaches.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docdoc2696/85/Doc-doc-2-320.jpg)
![The job assignment problem of other The four hard constraints were applied to
military branches may show certain these attributes in compliance with Navy
similarities to that of the Navy, but the policies. 1277 matches passed the given hard
Navy's mandatory “Sea/Shore Rotation” constraints, which were inserted into a new
policy makes it unique and perhaps, more database.
challenging than other typical military, Table 1 shows the four soft constraints
civilian, or industry types of job assignment applied to the matches that satisfied the hard
problems. Unlike in most job assignments, constraints and the functions which
the Navy sends its sailors to short term sea implement them. These functions measure
and shore duties periodically, making the degrees of satisfaction of matches between
problem more constrained, time demanding, sailors and jobs, each subject to one soft
and challenging. This was one of the reasons constraint. Again, the policy definitions are
why we designed and implemented a simplified. All the fi functions are monotone
complex, computationally expensive, human- but not necessarily linear, although it turns
like “conscious” software. This software is out that linear functions are adequate in many
completely US Navy specific, but it can be cases. Note that monotonicity can be
easily modified to handle any other type of achieved in cases when we assign values to
job assignment. set elements (such as location codes) by
In Section 2 we describe how the data ordering. After preprocessing the function
were attained and formulated into the input values – which served as inputs to future
of the neural networks. In Section 3 we processing – were defined using information
discuss FFNNs with Logistic Regression, given by Navy detailers. Each of the
performance function and statistical criteria function's range is [0,1].
of MLP Selection for best performance
including learning algorithm selection. After Table 1. Soft constraints
this we turn our interest to Support Vector Policy name Policy
Machine since the data involved high level f1 Job Priority High priority jobs are more
noise. Section 4 presents some comparative important to be filled
analysis and numerical results of all the f2 Sailor It’s better to send a sailor
presented approaches along with the Location where he/she wants to go
sensitivity analysis. Preference
f3 Paygrade Sailor’s paygrade should
match the job’s paygrade
f Geographic Certain moves are more
2 Data Acquisition 4 Location preferable than others
The data was extracted from the Navy's
Assignment Policy Management System's job Output data (decisions) were acquired
and sailor databases. For the study one from an actual detailer in the form of
particular community, the Aviation Support Boolean answers for each possible match (1
Equipment Technicians (AS) community was for jobs to be offered, 0 for the rest). Each
chosen. Note that this is the community on sailor together with all his/her possible jobs
which the current IDA prototype is being that satisfied the hard constraints were
built [1]. The databases contained 467 sailors assigned to a unique group. The numbers of
and 167 possible jobs for the given jobs in each group were normalized into [0,1]
community. From the more than 100 by simply dividing them by the maximum
attributes in each database only those were value and included in the input as function f5.
selected which are important from the This is important because the outputs
viewpoint of the constraint satisfaction: (decisions given by detailers) were highly
Eighteen attributes from the sailor database correlated: there was typically one job
and six from the job database. For this study offered to each sailor.
we chose four hard and four soft constraints.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docdoc2696/85/Doc-doc-3-320.jpg)
![3 Design of Neural Network the changing of the combination of weights
One natural way the decision making with inputs f1,...,f4. The classification of
problem in IDA can be addressed is via the decision can be achieved through the best
tuning the coefficients for the soft threshold with the largest estimated
constraints. This will largely simplify the conditional probability from group data. The
agent's architecture, and it saves on both class prediction of an observation x from
running time and memory. Decision making group y was determined by
can also be viewed as a classification
problem, for which neural networks C ( x) = arg max k Pr( x | y = k ) ( 4)
demonstrated to be a very suitable tool. To find the best threshold we used
Neural networks can learn to make human- Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) to
like decisions, and would naturally follow provide the percentage of detections correctly
any changes in the data set as the classified and the non-detections incorrectly
environment changes, eliminating the task of classified. To do so we employed different
re-tuning the coefficients. thresholds with range in [0,1]. To improve
the generalization performance and achieve
3.1 Feedforward Neural Network the best classification, the MLP with
We use a logistic regression model to tune structural learning was employed [16], [17].
the coefficients for the functions f1,...,f4 for
the soft constraints and evaluate their relative 3.2 Neural Network Selection
importance. The corresponding conditional Since the data coming from human decisions
probability of the occurrence of the job to be inevitably include vague and noisy
offered is components, efficient regularization
techniques are necessary to improve the
y = P (decision = 1 | w) = g ( wT f )
ˆ (1) generalization performance of the FFNN.
a This involves network complexity adjustment
e
g (a ) = (2) and performance function modification.
1 + ea Network architectures with different degrees
of complexity can be obtained through
where g represents the logistic function adapting the number of hidden nodes and
evaluated at activation a. Let w denote partitioning the data into different sizes of
weight vector and f the column vector of the training, cross-validation and testing sets and
importance functions: f T = [ f1 ,..., f 5 ] . using different types of activation functions.
Then the “decision” is generated according to A performance function commonly used in
the logistic regression model. regularization, instead of the sum of squared
The weight vector w can be adapted using error (SSE) on the training set, is a loss
FFNN topology [14], [15]. In the simplest function (mostly SSE) plus a penalty term
case there is one input layer and one output [18]-[21]:
logistic layer. This is equivalent to the
generalized linear regression model with J = SSE + λ ∑ w 2 (5)
logistic function. The estimated weights From another point of view, for achieving the
satisfy Eq.(3): optimal neural network structure for noisy
data, structural learning has better
∑w i = 1, 0 ≤ wi ≤ 1 (3) generalization properties and usually use the
i following modified performance function
The linear combination of weights with [16], [17]:
inputs f1,...,f4 is a monotone function of J = SSE + λ ∑ | w | (6)
conditional probability, as shown in Eq.(1)
and Eq.(2), so the conditional probability of
job to be offered can be monitored through](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docdoc2696/85/Doc-doc-4-320.jpg)
![Yet in this paper we propose an alternative • Correlation Coefficient (r) can show the
cost function, which includes a penalty term agreement between the input and the
as follows: output or the desired output and the
predicted output. In our computation, we
J = SSE + λn / N (7 ) use the latter.
where SSE is the sum of squared error, λ is a • Akaike Information Criteria [22]:
penalty factor, n is the number of parameters AIC ( K a ) = − 2 log( Lml ) + 2 K a (8)
in the network decided by the number of
hidden nodes and N is the size of the input • Minimum Description Length [23]:
example set. This helps to minimize the MDL( K a ) = − log( Lml ) + 0.5K a log N (9)
number of parameters (optimize network where Lml is the maximum value of the
structure) and improve the generalization likelihood function and Ka is the number of
performance. adjustable parameters. N is the size of the
In our study the value of λ in Eq.(7) input examples' set.
ranged from 0.01 to 1.0. Note that λ=0 The MSE can be used to determine how
represents a case where we don't consider well the predicted output fits the desired
structural learning, and the cost function output. More epochs generally provide higher
reduces into the sum of squared error. correlation coefficient and smaller MSE for
Normally the size of input samples should be training in our study. To avoid overfitting
chosen as large as possible in order to keep and to improve generalization performance,
the residual as small as possible. Due to the training was stopped when the MSE of the
cost of the large size samples, the input may cross-validation set started to increase
not be chosen as large as desired. However, if significantly. Sensitivity analyses were
the sample size is fixed then the penalty performed through multiple test runs from
factor combined with the number of hidden random starting points to decrease the chance
nodes should be adjusted to minimize Eq.(7). of getting trapped in a local minimum and to
Since n and N are discrete, they can not be find stable results.
optimized by taking partial derivatives of the The network with the lowest AIC or MDL
Lagrange multiplier equation. For achieving is considered to be the preferred network
the balance between data-fitting and model structure. An advantage of using AIC is that
complexity from the proposed performance we can avoid a sequence of hypothesis
function in Eq.(7), we would also like to find testing when selecting the network. Note that
the effective size of training samples the difference between AIC and MDL is that
included in the network and also the best MDL includes the size of the input examples
number of hidden nodes for the one hidden which can guide us to choose appropriate
layer case. Several statistical criteria were partition of the data into training and testing
carried out for this model selection in order sets. Another merit of using MDL/AIC
to find the best FFNN and for better versus MSE/Correlation Coefficient is that
generalization performance. We designed a MDL/AIC use likelihood which has a
two-factorial array to dynamically retrieve probability basis. The choice of the best
the best partition of the data into training, network structure is based on the
cross-validation and testing sets with maximization of predictive capability, which
adapting the number of hidden nodes given is defined as the correct classification rate
the value of λ: and the lowest cost given in Eq.(7).
• Mean Squared Error (MSE) defined as
the Sum of Squared Error divided by the 3.3 Learning Algorithms for FFNN
degree of freedom. For this model, the Various learning algorithms have been tested
degree of freedom is the sample size for comparison study [18], [21]:
minus the number of parameters included • Back propagation with momentum
in the network. • Conjugate gradient](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docdoc2696/85/Doc-doc-5-320.jpg)
![• Quickprop discriminant functions. RBF has good
• Delta-delta properties for function approximation but
The back-propagation with momentum poor generalization performance. To improve
algorithm has the major advantage of speed this we employed Adatron learning algorithm
and is less susceptible to trapping in a local [28], [29]. Adatron replaces the inner product
minimum. Back-propagation adjusts the of patterns in the input space by the kernel
weights in the steepest descent direction in function of the RBF network. It uses only
which the performance function is decreasing those inputs for training that are near the
most rapidly but it does not necessarily decision surface since they provide the most
produce the fastest convergence. The search information about the classification. It is
of the conjugate gradient is performed along robust to noise and generally yields no
conjugate directions, which produces overfitting problems, so we do not need to
generally faster convergence than steepest cross-validate to stop training early. The used
descent directions. The Quickprop algorithm performance function is the following:
uses information about the second order
N
derivative of the performance surface to
accelerate the search. Delta-delta is an J ( xi ) = λi (∑ λ j w j G ( xi − x j 2σ 2 ) + b) (10)
j =1
adaptive step-size procedure for searching a
performance surface [21]. The performance M = min J ( xi ) (11)
i
of best MLP with one hidden layer network where λi is multiplier, wj is weight, G is
obtained from above was compared with Gaussian distribution and b is bias.
popular classification method Support Vector We chose a common starting multiplier
Machine and FFNN with logistic regression. (0.15), learning rate (0.70), and a small
threshold (0.01). While M is greater than the
3.4 Support Vector Machine threshold, we choose a pattern xi to perform
Support Vector Machine is a method for the update. After update only a few of the
finding a hyperplane in a high dimensional weights are different from zero (called the
space that separates training samples of each support vectors), they correspond to the
class while maximizes the minimum distance samples that are closest to the boundary
between the hyperplane and any training between classes. Adatron algorithm can
samples [24]-[27]. SVM has properties to prune the RBF network so that its output for
deal with high noise level and flexibly testing is given by
applies different network architectures and
optimization functions. Our used data
involves relatively high level noise. To deal
g ( x) = sgn( ∑ λ w G( x − x ,2σ
i i
i∈Support Vectors
i
2
) − b) (12)
with this the interpolating function for
so it can adapt an RBF to have an optimal
mapping the input vector with the target
margin. Various versions of RBF networks
vector should be modified such a way that it
(spread, error rate, etc.) were also applied but
averages over the noise on the data. This
the results were far less encouraging for
motivates using Radial Basis Function neural
generalization than with SVM with the above
network structure in SVM. RBF neural
method.
network provides a smooth interpolating
function, in which the number of basis
functions are decided by the complexity of
mapping to be represented rather than the
size of data. RBF can be considered as an
extension of finite mixture models. The
4 Data Analysis and Results
For implementation we used a Matlab 6.1
advantage of RBF is that it can model each
[30] environment with at least a 1GHz
data sample with Gaussian distribution so as
Pentium IV processor. For data acquisition
to transform the complex decision surface
into a simpler surface and then use linear](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docdoc2696/85/Doc-doc-6-320.jpg)
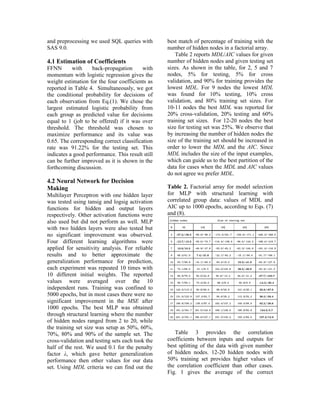

![700 for future models. Fig. 4 shows the size enabling more accurate learning. All
sensitivity analysis and the performance these together mean that different Navy
comparison of back-propagation with enlisted communities are handled very
momentum, conjugate gradient descent, differently by different detailers, but IDA and
quickprop, and delta-delta learning its constraint satisfaction are well equipped to
algorithms for MLP with different number of learn how to make decisions similarly to the
hidden nodes and best cutting of the sample detailers, even in a parallel fashion.
set. As it can be seen their performance were
relatively close for our data set, and delta-
delta performed the best. MLP with back-
propagation with momentum also performed
well around 15 hidden nodes. MLP with 15
hidden nodes and 25% testing set size gave
approximately 6% error rate, which is a very
good generalization performance for
predicting jobs to be offered for sailors. Even
though SVM provided slightly higher correct
classification rate than MLP, it has a
significant time complexity.
4.4 Result Validation
To further test our method and to verify the Fig. 3: Typical MSE of training (dotted line)
robustness and the efficiency of our methods, and cross-validation (solid line) with the best
a different community, the Aviation MLP with one hidden layer (H=15, training
Machinist (AD) community was chosen. set size=50%).
2390 matches for 562 sailors have passed
preprocessing and the hard constraints.
Before the survey was actually done a minor
semi-heuristic tuning of the functions was
performed to comfort the AD community.
The aim of such tuning was to make sure that
the soft constraint functions yield values on
the [0,1] interval for the AD data. This tuning
was very straightforward and could be done
automatically for future applications. The
data then was presented to an expert AD
detailer who was asked to offer jobs to the
sailors considering only the same four soft
constraints as we have used before: Job
Priority, Sailor Location Preference, Fig. 4: Correct classification rates for MLP
Paygrade, Geographic Location. The with different number of hidden nodes using
acquired data then was used the same way as 50% training set size for four different
it was discussed earlier and classifications algorithms. Dotted line: Back-propagation
were obtained. Table 4 reports learned with Momentum algorithm. Dash-dotted line:
coefficients for the same soft constraints. As Conjugate Gradient Descent algorithm.
it can be seen in the table the coefficients Dashed line: Quickprop algorithm. Solid line:
were very different from those reported for Delta-Delta algorithm.
the AS community. However, the obtained Table 4. Estimated coefficients for soft
mean correct classification rate was 94.6%, constraints for the AS and AD communities
even higher than that of the AS community. Coefficient Corresponding Estimated wi
This may be partly due to the larger sample](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docdoc2696/85/Doc-doc-9-320.jpg)
![Function Value that the coefficients have to be updated from
AS AD time to time as well as online neural network
w1 f1 0.316 0.010 trainings are necessary to comply with
w2 f2 0.064 0.091 changing Navy policies and other
w3 f3 0.358 0.786 environmental challenges.
w4 f4 0.262 0.113
References:
Some noise is naturally present when [1] S. Franklin, A. Kelemen, and L.
humans make decisions in a limited time McCauley, IDA: A cognitive agent
frame. According to one detailer's estimation architecture Proceedings of IEEE
a 20% difference would occur in the International Conference on Systems, Man,
decisions even if the same data would be and Cybernetics '98, IEEE Press, pp. 2646,
presented to the same detailer at a different 1998.
time. Also, it is widely believed that different [2] B. J. Baars, Cognitive Theory of
detailers are likely to make different Consciousness Cambridge University Press,
decisions even under the same circumstances. Cambridge, 1988.
Moreover environmental changes might [3] B. J. Baars, In the Theater of
further bias decisions. Consciousness, Oxford University Press,
Oxford, 1997.
[4] S. Franklin and A. Graesser, Intelligent
5 Conclusion Agents III: Is it an Agent or just a program?:
High-quality decision making using optimum A Taxonomy for Autonomous Agents,
constraint satisfaction is an important goal of Proceedings of the Third International
IDA, to aid the NAVY to achieve the best Workshop on Agent Theories, Architectures,
possible sailor and NAVY satisfaction and Languages, Springer-Verlag, pp. 21-35,
performance. A number of neural networks 1997.
with statistical criteria were applied to either [5] S. Franklin, Artificial Minds, Cambridge,
improve the performance of the current way Mass, MIT Press, 1995.
IDA handles constraint satisfaction or to [6] P. Maes, “How to Do the Right Thing,
come up with alternatives. IDA's constraint Connection Science, 1:3, 1990.
satisfaction module, neural networks and [7] H. Song and S. Franklin, A Behavior
traditional statistical methods are Instantiation Agent Architecture, Connection
complementary with one another. In this Science, Vol. 12, pp. 21-44, 2000.
work we proposed and combined MLP with [8] R. Kondadadi, D. Dasgupta, and S.
structural learning and a novel cost function, Franklin, An Evolutionary Approach For Job
statistical criteria, which provided us with the Assignment,Proceedings of International
best MLP with one hidden layer. 15 hidden Conference on Intelligent Systems,
nodes and 25% testing set size using back- Louisville, Kentucky, 2000.
propagation with momentum and delta-delta [9] T. T. Liang and T. J. Thompson,
learning algorithms provided good Applications and Implementation - A large-
generalization performance for our data set. scale personnel assignment model for the
SVM with RBF network architecture and Navy, The Journal For The Decisions
Adatron learning algorithm gave the best Sciences Institute, Volume 18, No. 2 Spring,
classification performance for decision 1987.
making with an error rate below 6%, [10] T. T. Liang and B. B. Buclatin,
although with significant computational cost. Improving the utilization of training
In comparison to human detailers such a resources through optimal personnel
performance is remarkable. Coefficients for assignment in the U.S. Navy, European
the existing IDA constraint satisfaction Journal of Operational Research 33, pp.
module were adapted via FFNN with logistic 183-190, North-Holland, 1988.
regression. It is important to keep in mind](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docdoc2696/85/Doc-doc-10-320.jpg)
![[11] D. Gale and L. S. Shapley, College Processing Systems 2 (Morgan Kaufmann),
Admissions and stability of marriage, The pp. 598-606, 1990.
American Mathematical Monthly, Vol 60, No [21] C. M. Bishop, Neural Networks for
1, pp. 9-15, 1962. Pattern Recognition Oxford University Press,
[12] A. Kelemen, Y. Liang, R. Kozma, and S. 1995.
Franklin, Optimizing Intelligent Agent's [22] H. Akaike, A new look at the statistical
Constraint Satisfaction with Neural model identification, IEEE Trans. Automatic
Networks, Innovations in Intelligent Systems Control, Vol. 19, No. 6, pp. 716-723, 1974.
(A. Abraham, B. Nath, Eds.), in the Series [23] J. Rissanen, Modeling by shortest data
“Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing”, description, Automat., Vol. 14, pp. 465-471,
Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, Germany, pp. 1978.
255-272, 2002. [24] C. Cortes and V. Vapnik, Support vector
[13] A. Kelemen, S. Franklin, and Y. Liang, machines, Machine Learning, 20, pp.
Constraint Satisfaction in Conscious 273-297, 1995.
Software Software Agents - A Practical [25] N. Cristianini and J. Shawe-Taylor, An
Application, Journal of Applied Artificial Introduction to Support Vector Machines
Intelligence, Vol. 19: No. 5, pp. 491-514, (and other kernel-based learning methods)},
2005. Cambridge University Press, 2000.
[14] M. Schumacher, R. Rossner, and W. [26] B. Scholkopf, K. Sung, C. Burges, F.
Vach, Neural networks and logistic Girosi, P. Niyogi, T. Poggio, and V. Vapnik,
regression: Part I', Computational Statistics Comparing support vector machines with
and Data Analysis, 21, pp. 661-682, 1996. Gaussian kernels to radial basis function
[15] E. Biganzoli, P. Boracchi, L. Mariani, classifiers, IEEE Trans. Sign. Processing,
and E. Marubini, Feed Forward Neural 45:2758 -- 2765, AI Memo No. 1599, MIT,
Networks for the Analysis of Censored Cambridge, 1997.
Survival Data: A Partial Logistic Regression [27] K.-R. Muller, S. Mika, G. Ratsch, and
Approach, Statistics in Medicine, 17, pp. K. Tsuda, An introduction to kernel-based
1169-1186, 1998. learning algorithms, IEEE Transactions on
[16] R. Kozma, M. Sakuma, Y. Yokoyama, Neural Networks}, 12(2):181-201, 2001.
and M. Kitamura, On the Accuracy of [28] T. T. Friess, N. Cristianini, and C.
Mapping by Neural Networks Trained by Campbell, The kernel adatron algorithm: a
Backporpagation with Forgetting, fast and simple learning procedure for
Neurocomputing, Vol. 13, No. 2-4, pp. support vector machine, Proc. 15th
295-311, 1996. International Conference on Machine
[17] M. Ishikawa, Structural learning with Learning, Morgan Kaufman, 1998.
forgetting, Neural Networks, Vol. 9, pp. [29] J. K. Anlauf and M. Biehl, The Adatron:
509-521, 1996. an adaptive perceptron algorithm,
[18] S. Haykin, Neural Networks Prentice Europhysics Letters, 10(7), pp. 687--692,
Hall Upper Saddle River, NJ, 1999. 1989.
[19] F. Girosi, M. Jones, and T. Poggio, [30] Matlab2004 Matlab User Manual,
Regularization theory and neural networks Release 6.0, Natick, MA: MathWorks, Inc,
architectures, Neural Computation, 2004.
7:219--269, 1995.
[20] Y. Le Cun, J. S. Denker, and S. A. Solla,
Optimal brain damage, in D. S. Toureczky,
ed. Adavnces in Neural Information](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docdoc2696/85/Doc-doc-11-320.jpg)