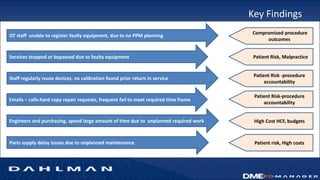
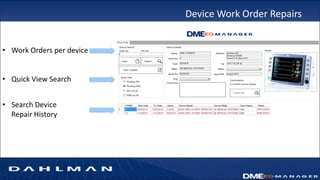
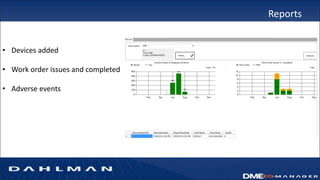
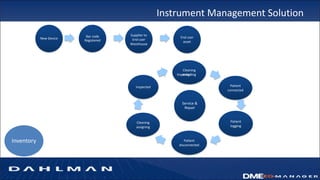
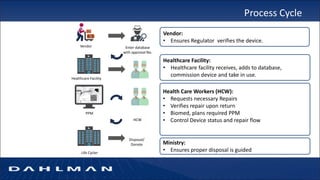
Many health care facilities do not adequately track medical devices and instruments, relying on paper logs or Excel spreadsheets. This leads to devices being misplaced, used improperly, or failing unexpectedly. A new digital device management system provides a solution, capturing comprehensive details on each device such as identification, maintenance needs, repair history, and location to ensure proper use and accountability. By digitizing device management, facilities can improve patient safety, quality of care, and reduce costs.