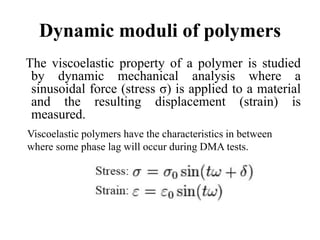
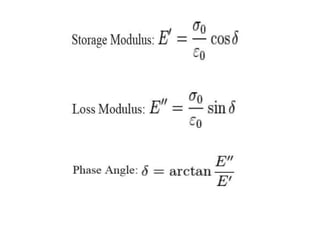
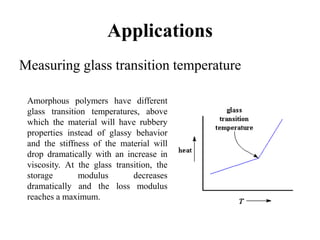
Dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) is a technique used to characterize materials, especially polymers, by applying a sinusoidal stress and measuring the strain. DMA can identify transitions like the glass transition temperature by varying temperature or stress frequency. Materials with viscoelastic behavior between solid and liquid, like polymers and glasses, are candidates for DMA. DMA is used for molecular structure analysis, quality control testing of materials, food and biomedical applications, and obtaining engineering property data of polymers over a range of temperatures and frequencies.