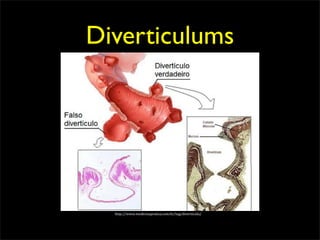
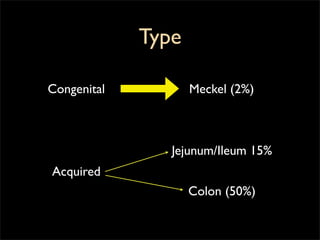
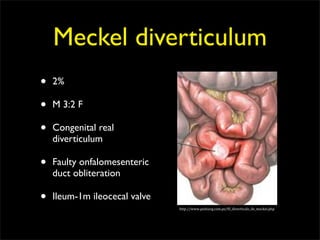
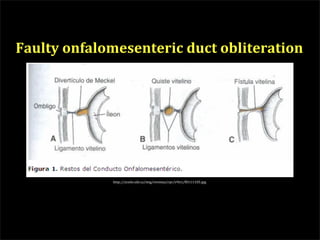
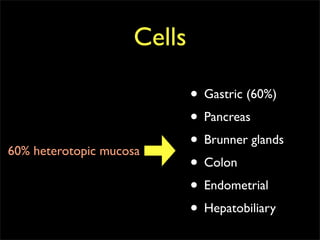
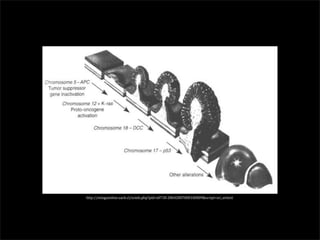
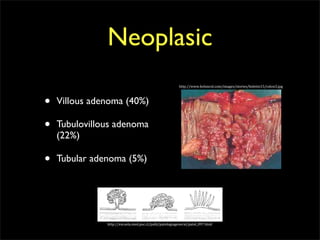
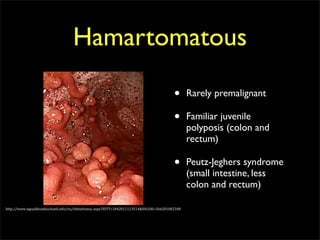
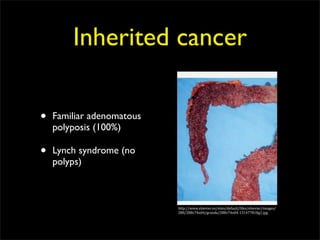
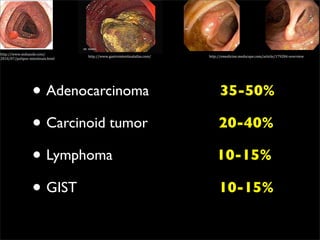
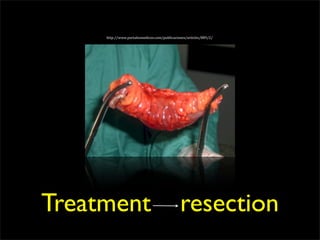
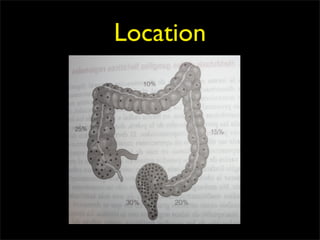
This document discusses diverticulums (diverticula), which are pouches that form in the lining of the gastrointestinal tract. It describes different types of diverticula including Meckel's diverticulum, colonic diverticula, and jejunal/ileal diverticula. It discusses potential complications like hemorrhage, diverticulitis, obstruction, and perforation. The document also provides information on diagnosis and treatment of diverticula including enteroclysis, endoscopy, and surgery.