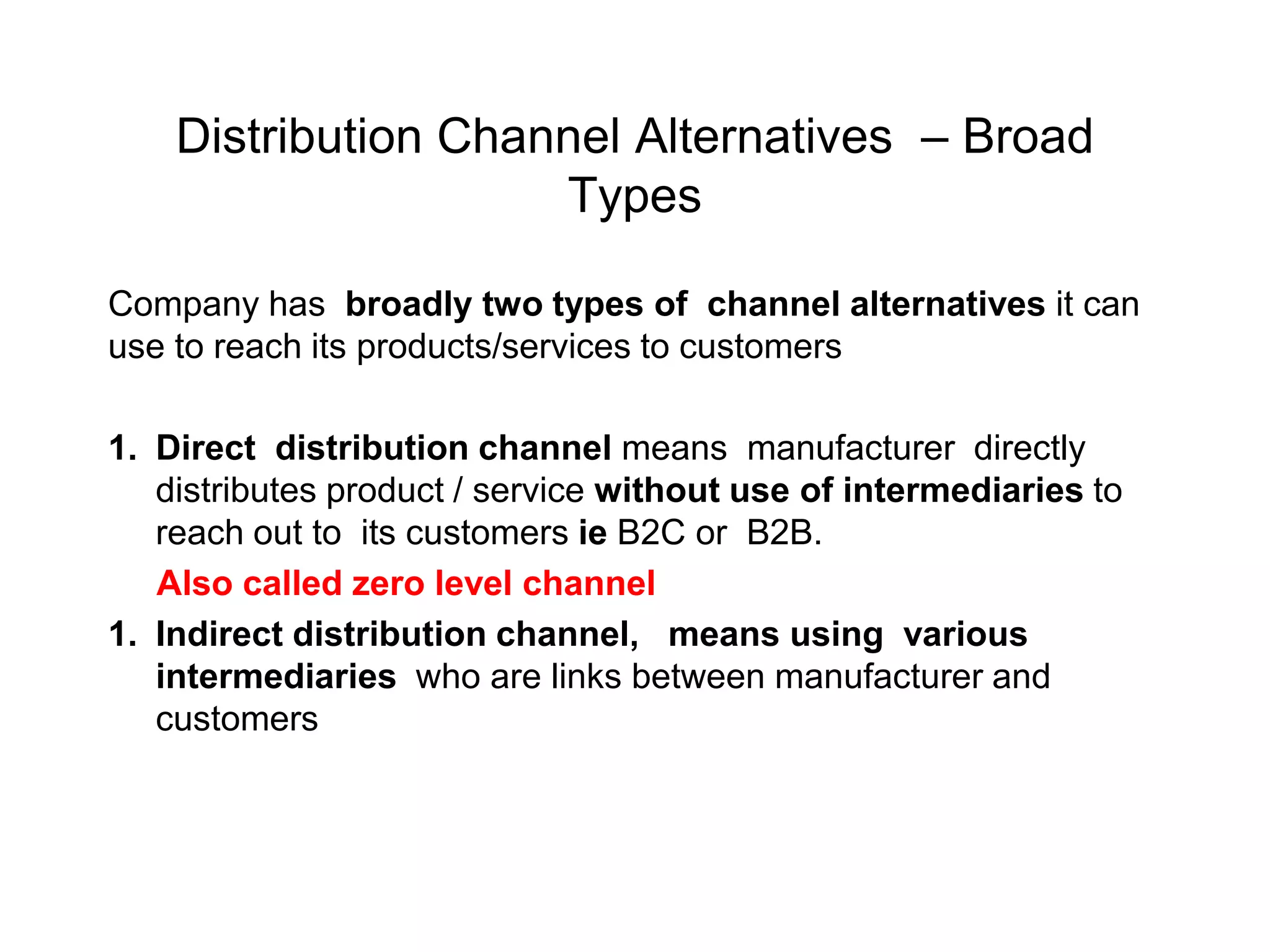
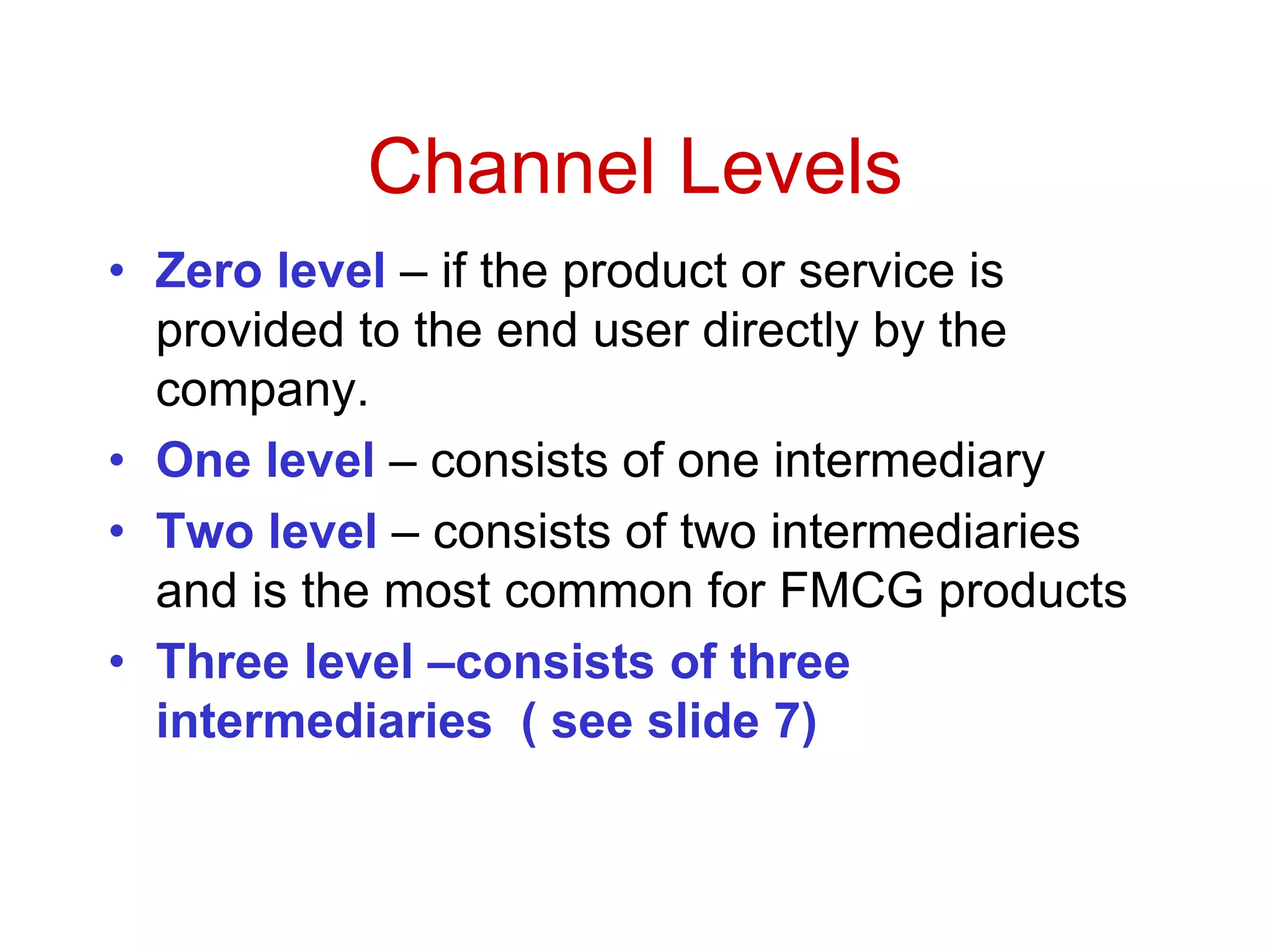
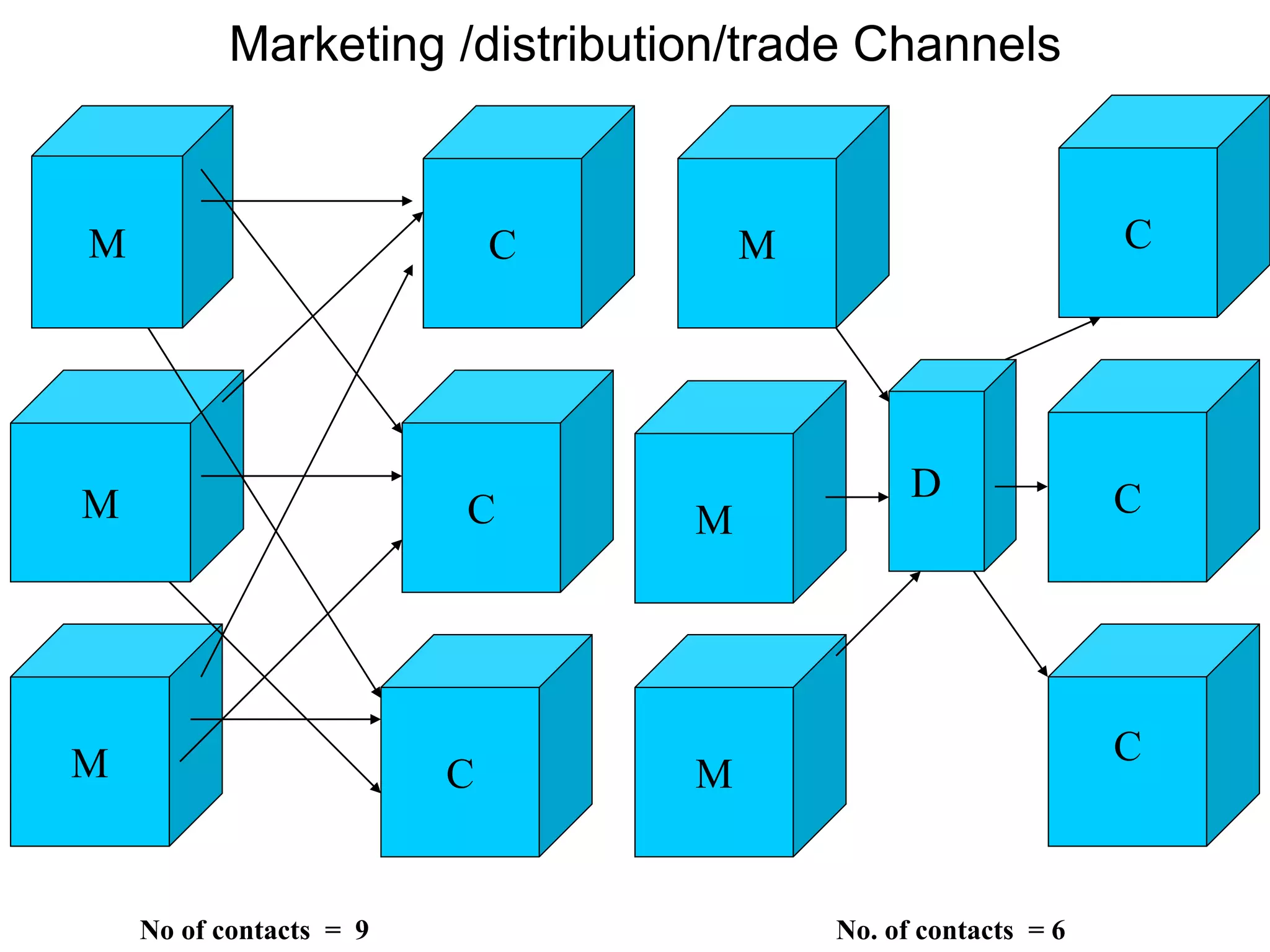
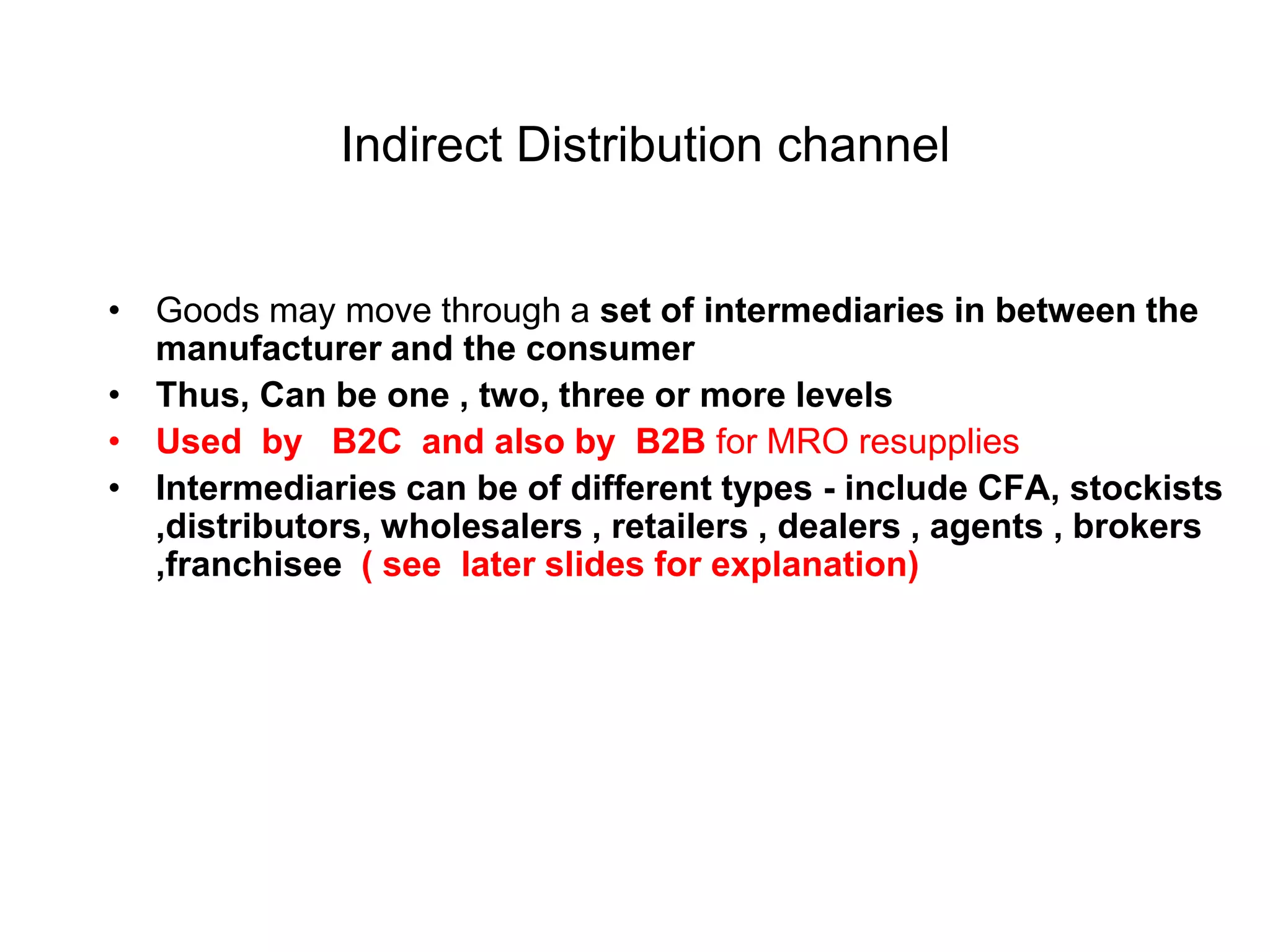
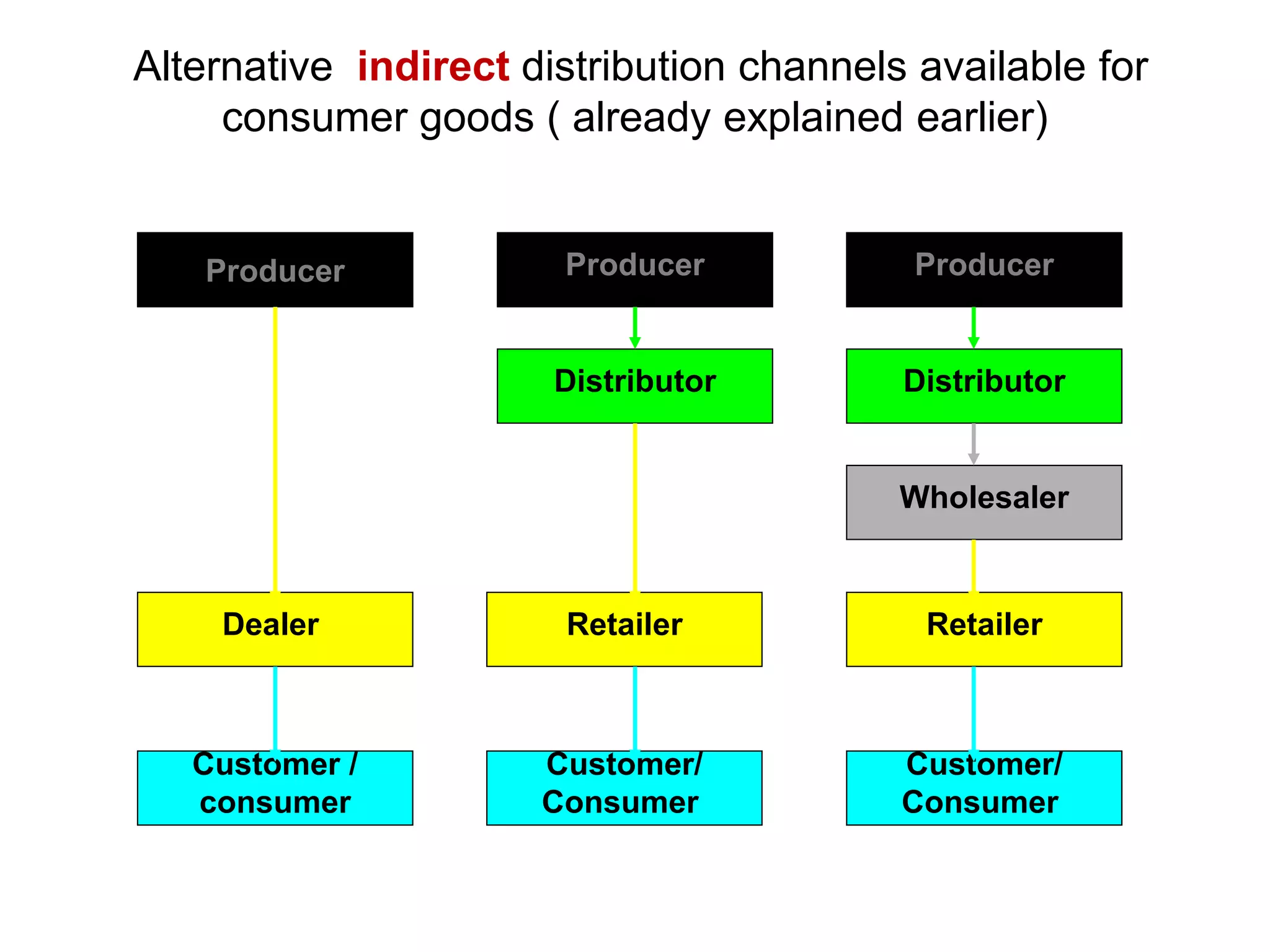
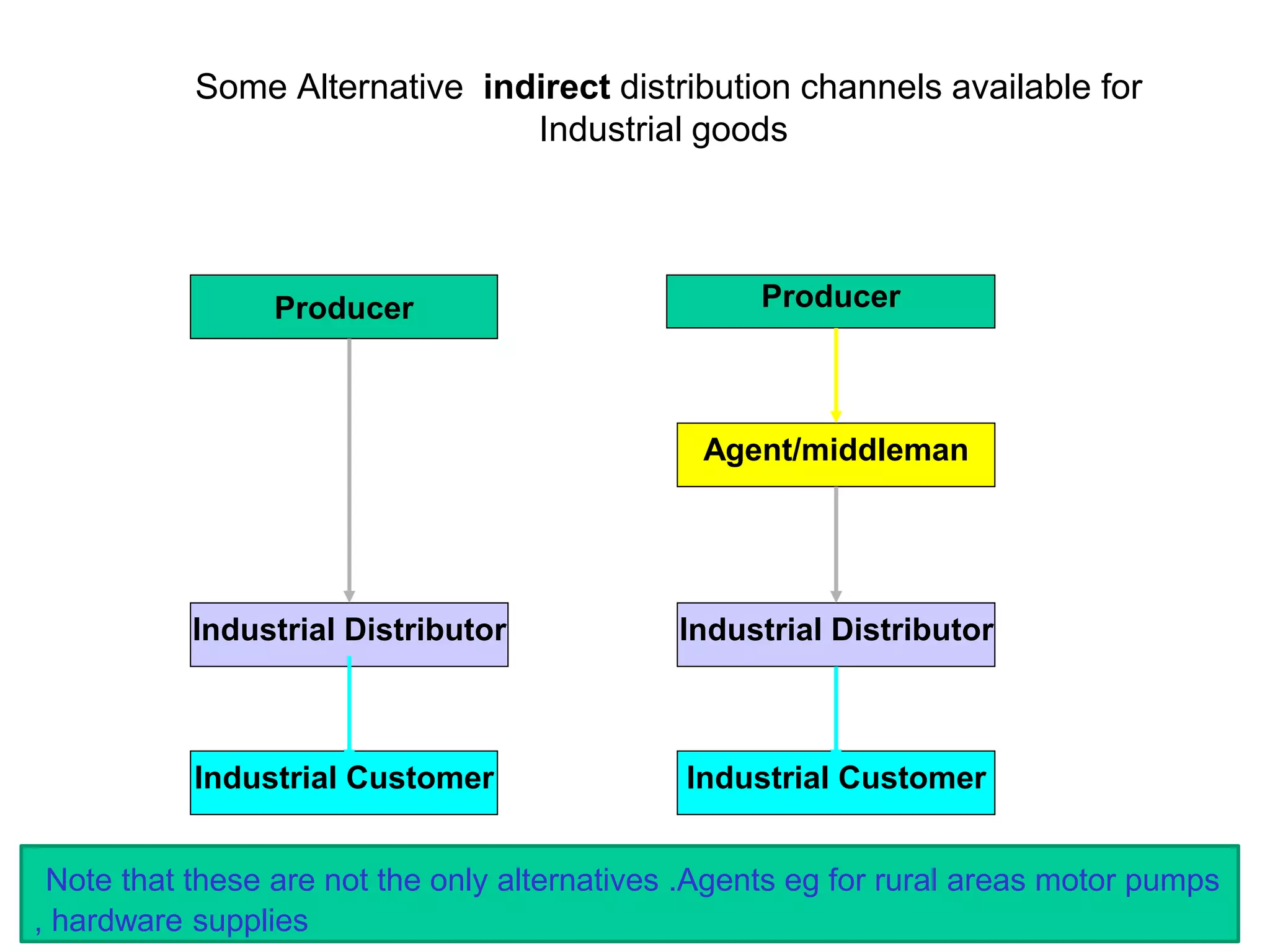
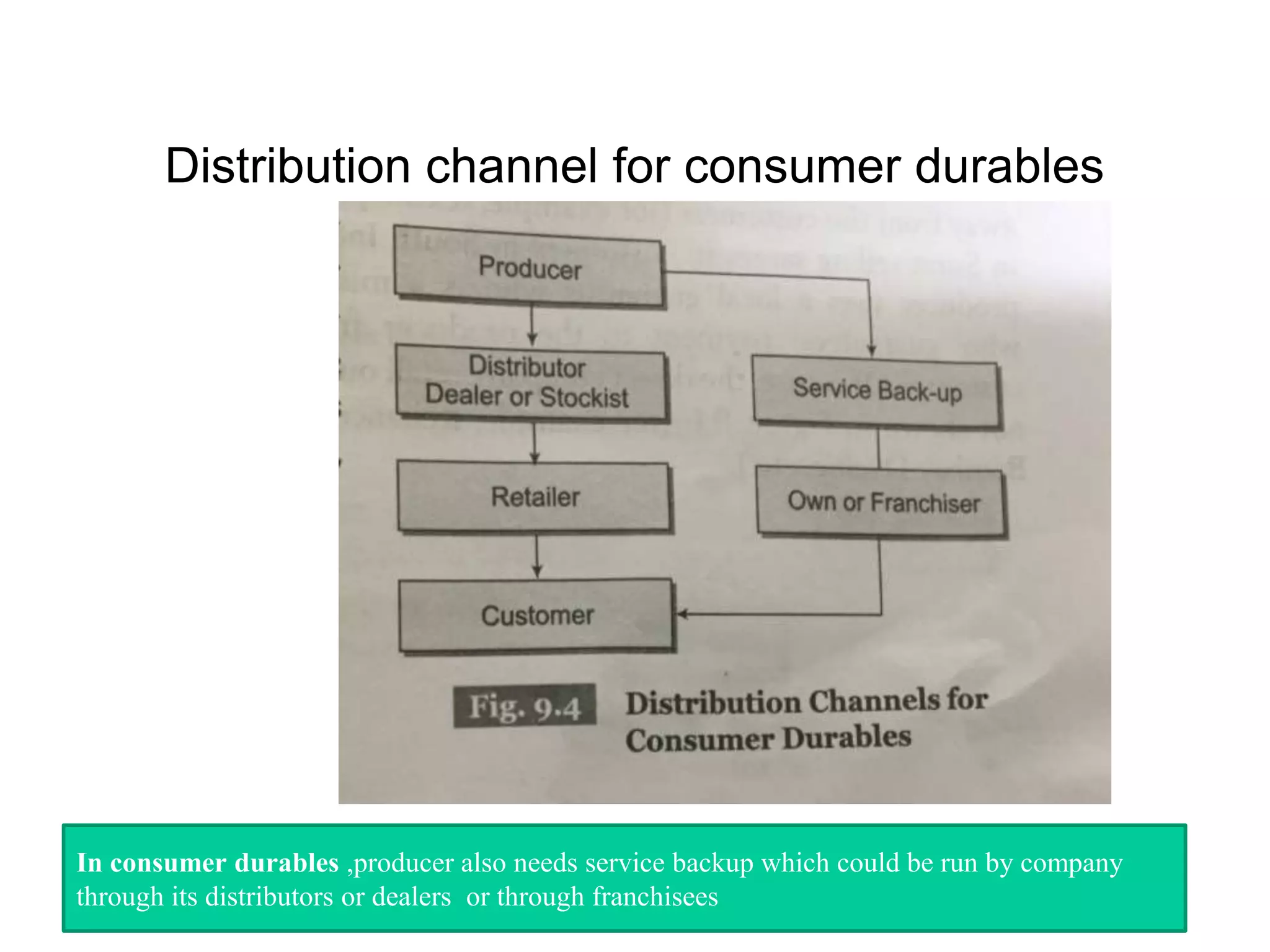
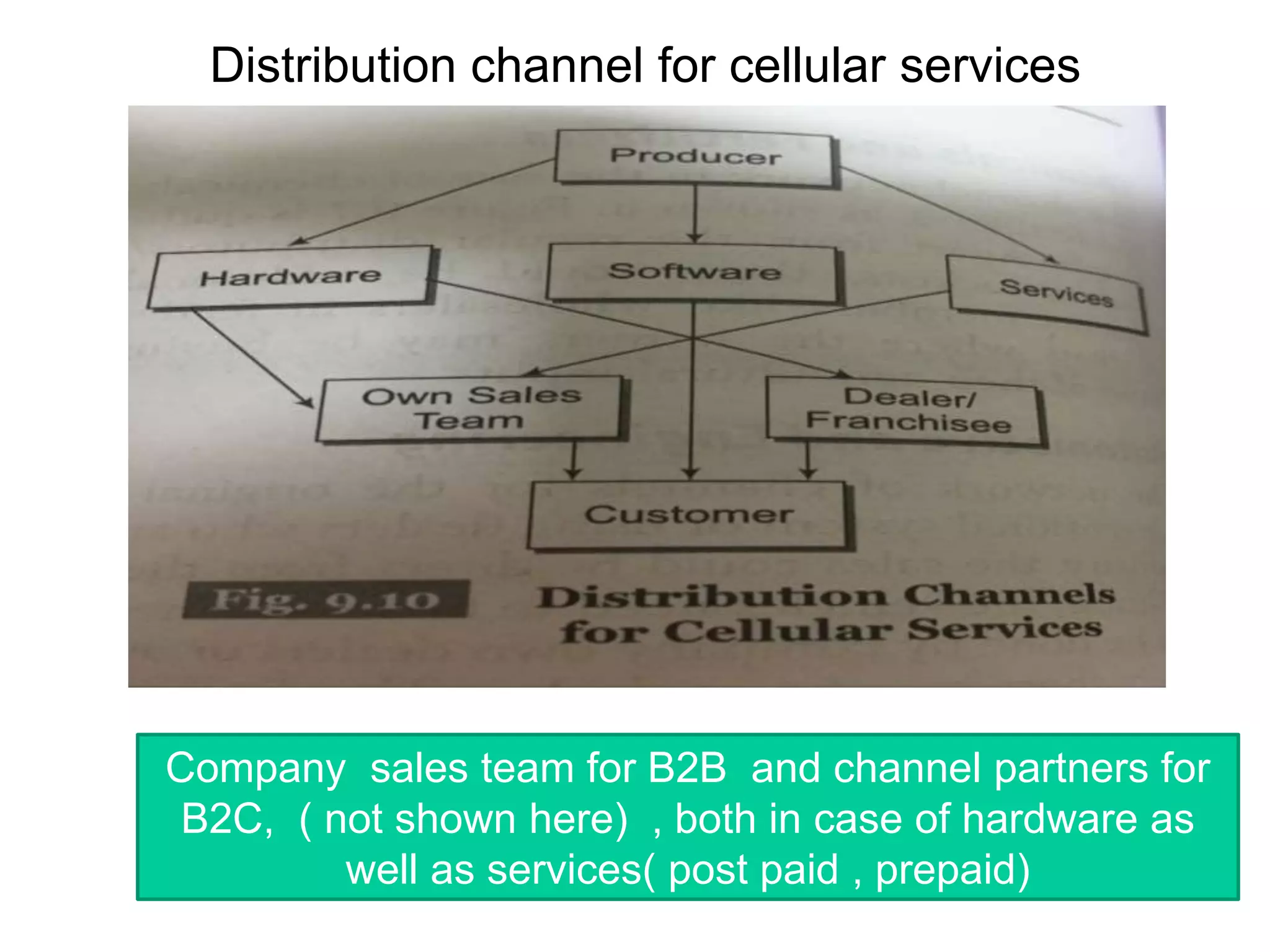
Distribution management involves coordinating all activities to efficiently move finished goods from production to consumers. It provides utilities like place, time, form, assortment, and possession to bridge discrepancies between supply and demand. Distribution channels can be direct or indirect, involving various intermediaries. Companies may choose direct distribution for some products and indirect channels using distributors, wholesalers and retailers for others depending on factors like product characteristics, buyer needs, and company objectives. Channel members take on functions like physical distribution, marketing support, inventory management, and after-sales service.