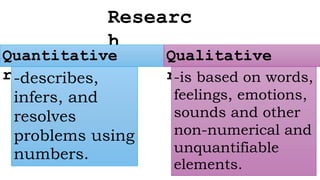
This document defines and distinguishes key technical terms used in research such as quantitative and qualitative research, variables, hypotheses, and sampling. It provides examples of different types of research including action research, thesis, and case studies. Concepts are defined as terms that describe objects, phenomena, or ideas, while a theory is an organized body of concepts and principles meant to explain a particular phenomenon. The document also discusses how to narrow a research topic through demographics, issues, location, timeframe, and causes.