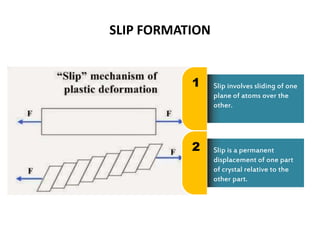
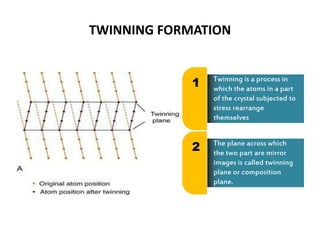
Dislocations are defects in crystal structures caused by stress and strain. There are different types of dislocations including edge dislocations and screw dislocations. Dislocations cause plastic deformation in metals by allowing slip and twinning to occur when stress is applied. Slip involves the sliding of crystal planes over one another, resulting in a permanent displacement, while twinning involves the rearrangement of atoms across a twinning plane. Dislocations are classified into types and influence many material properties, such as making metals able to undergo shaping processes that involve plastic deformation.