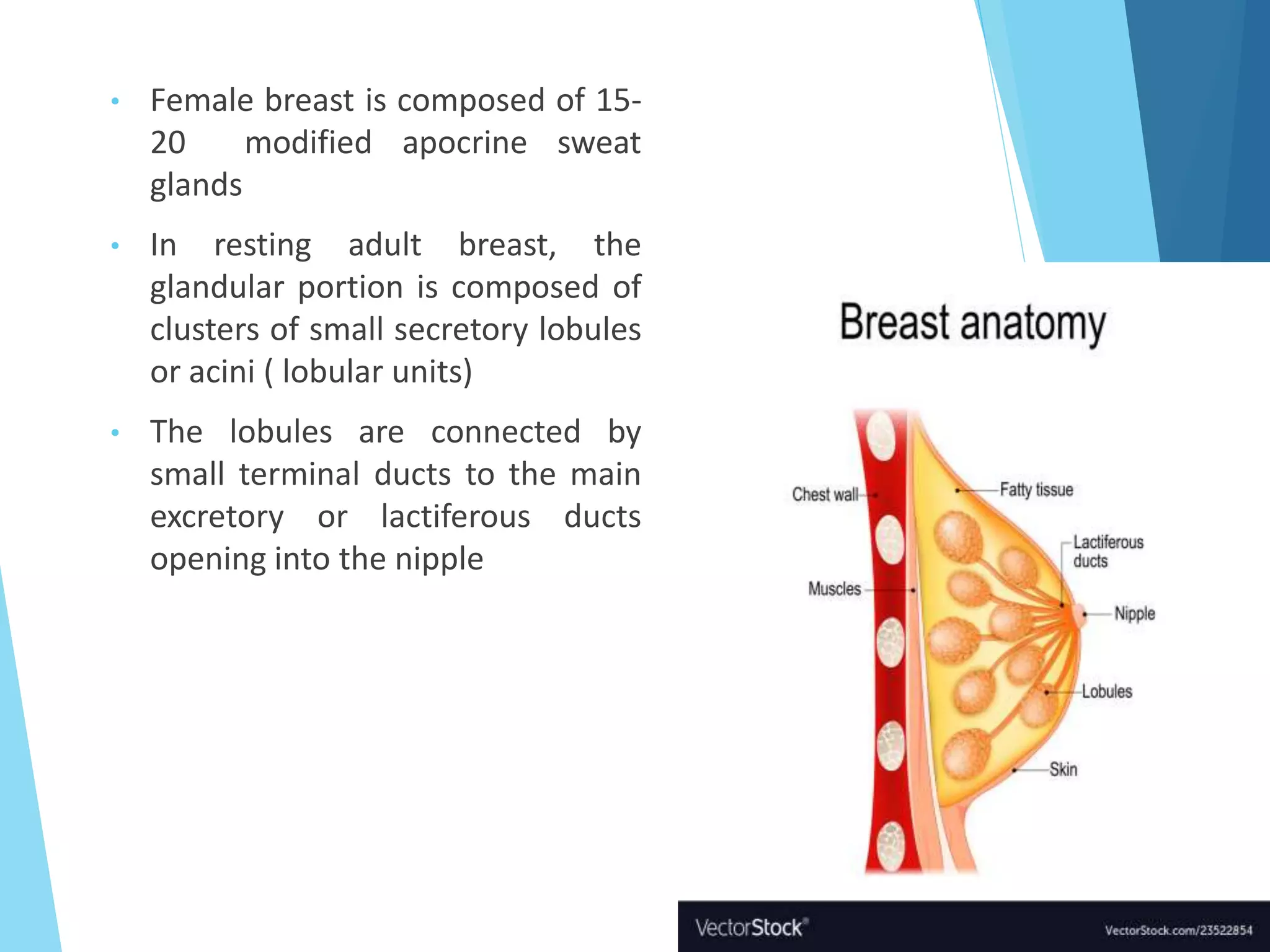
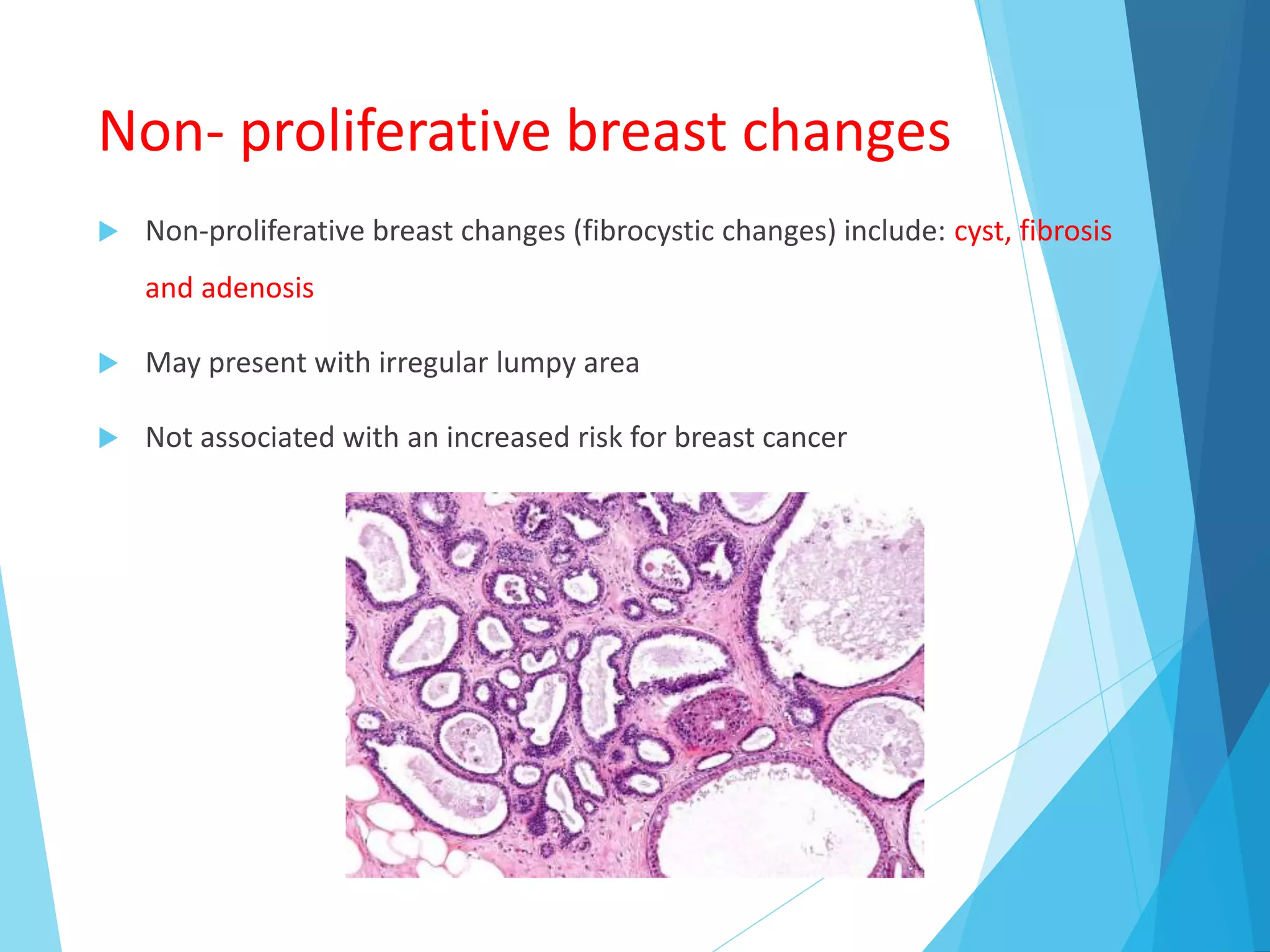
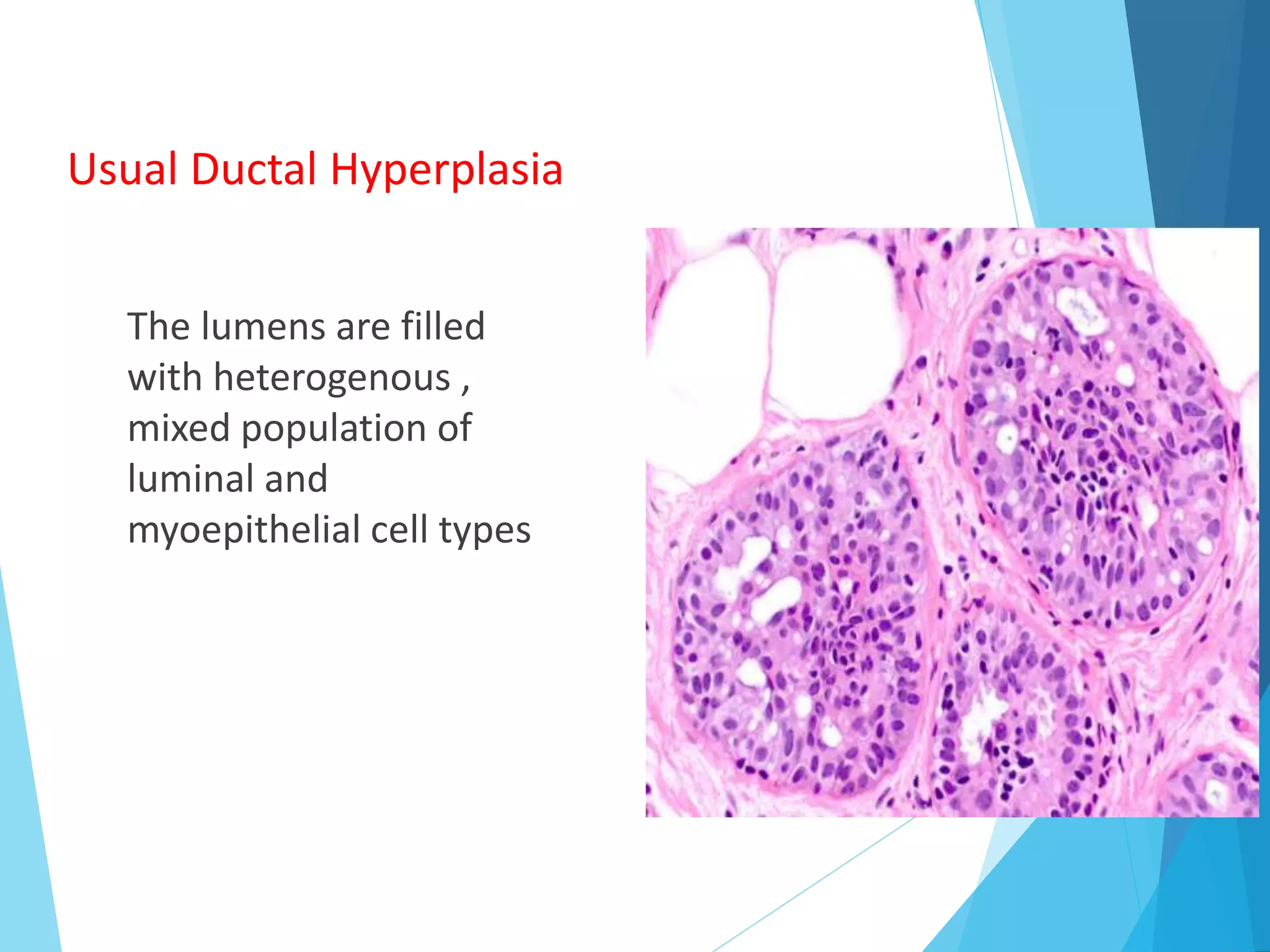
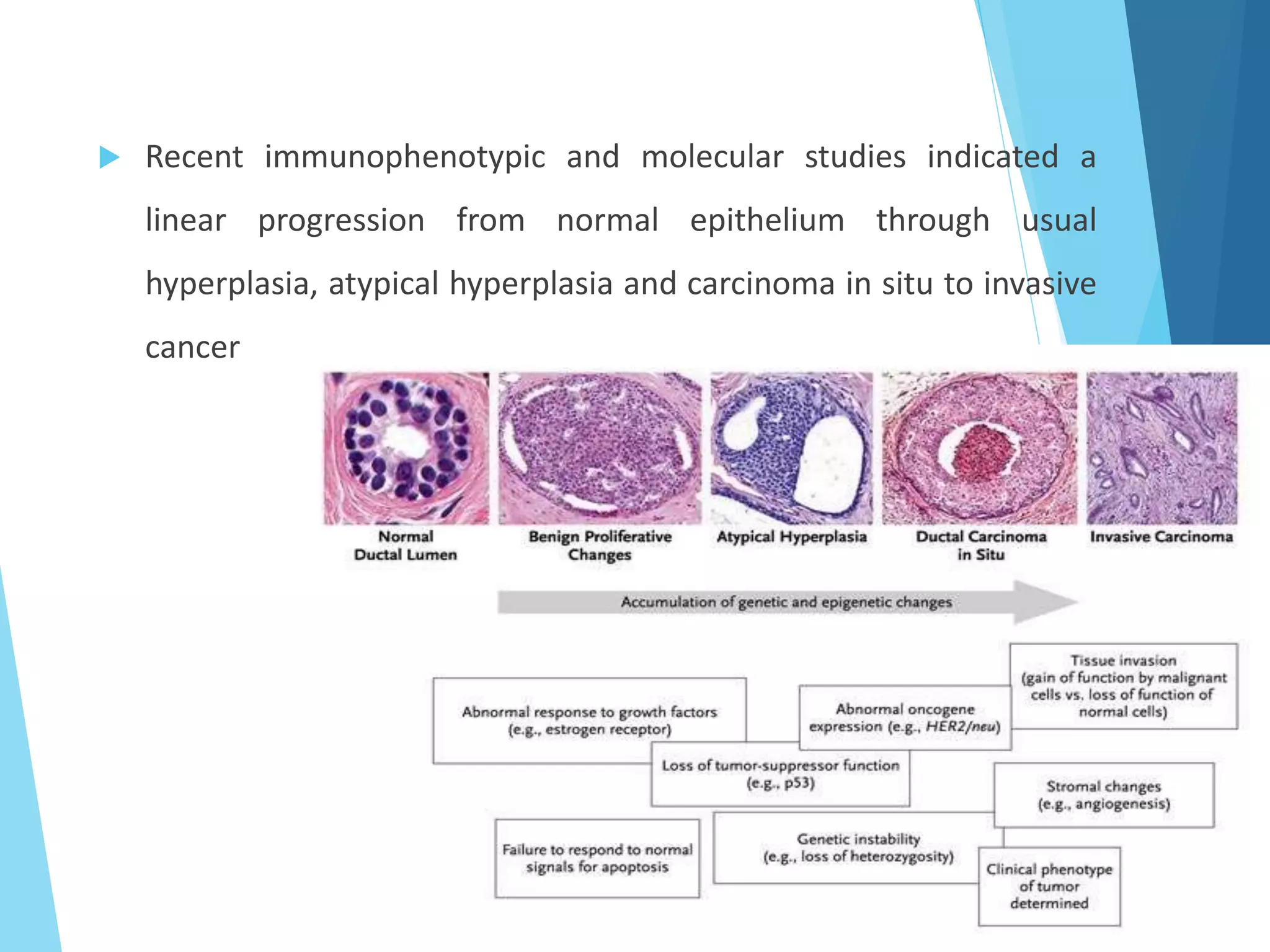
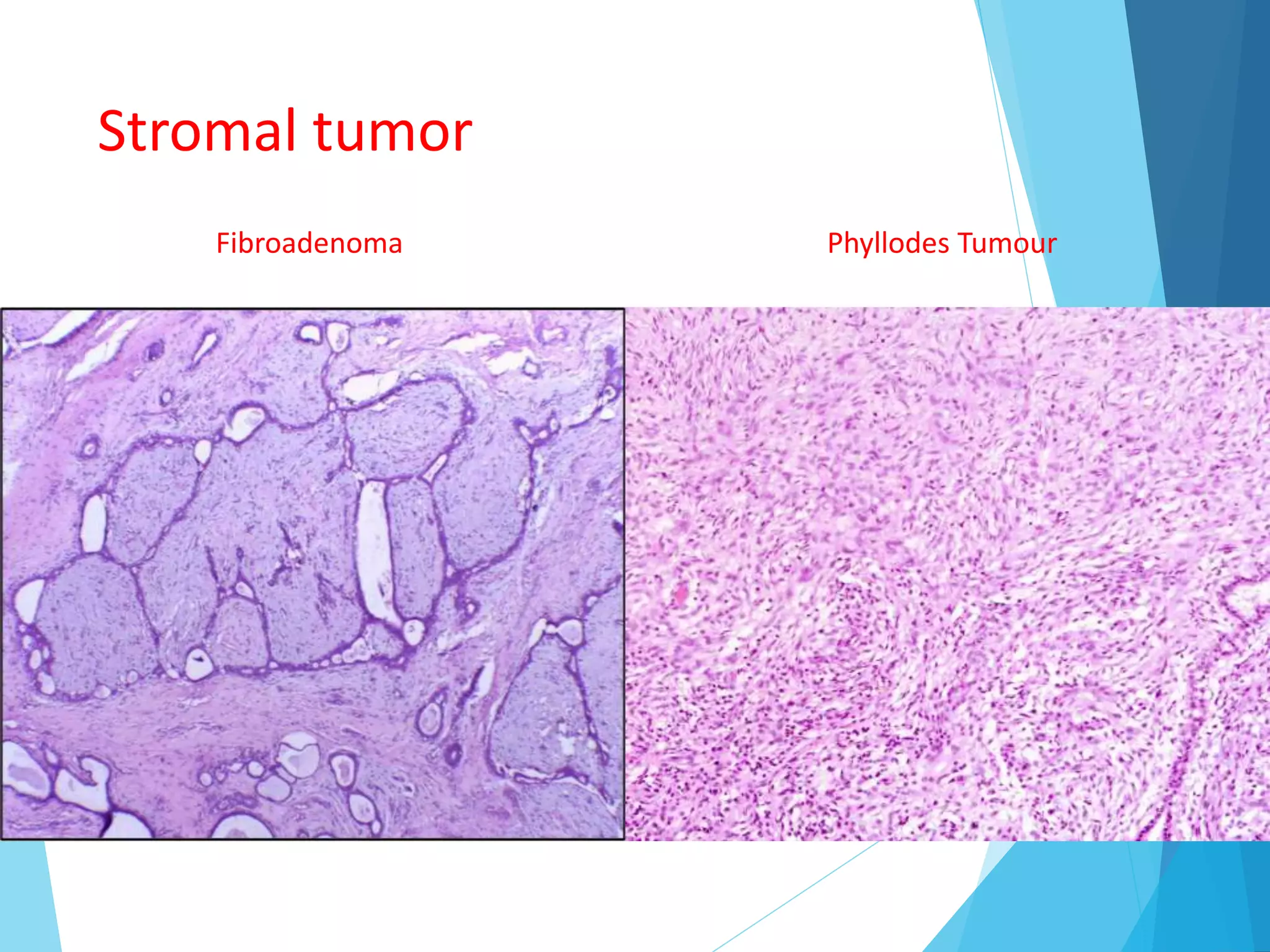
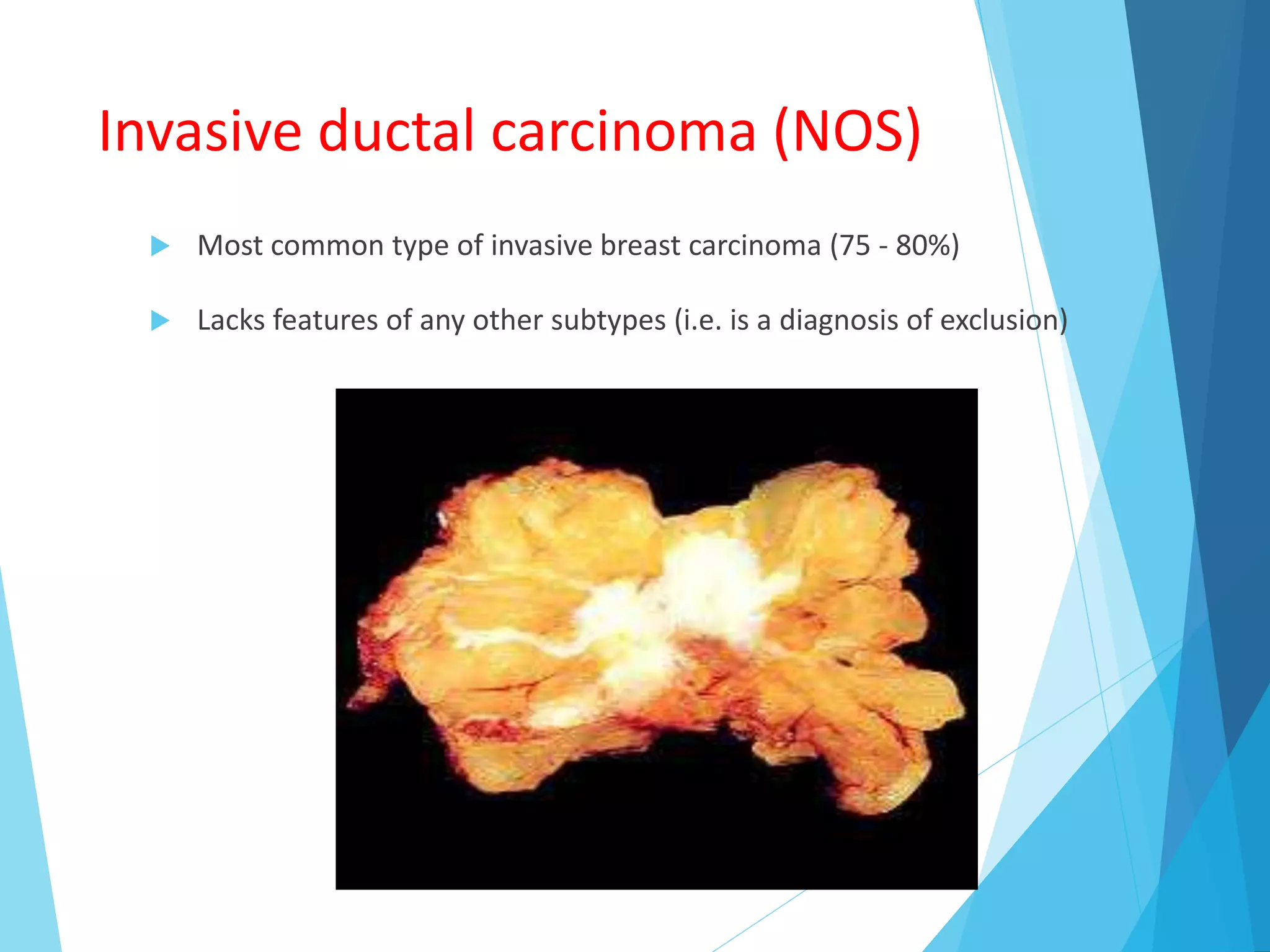
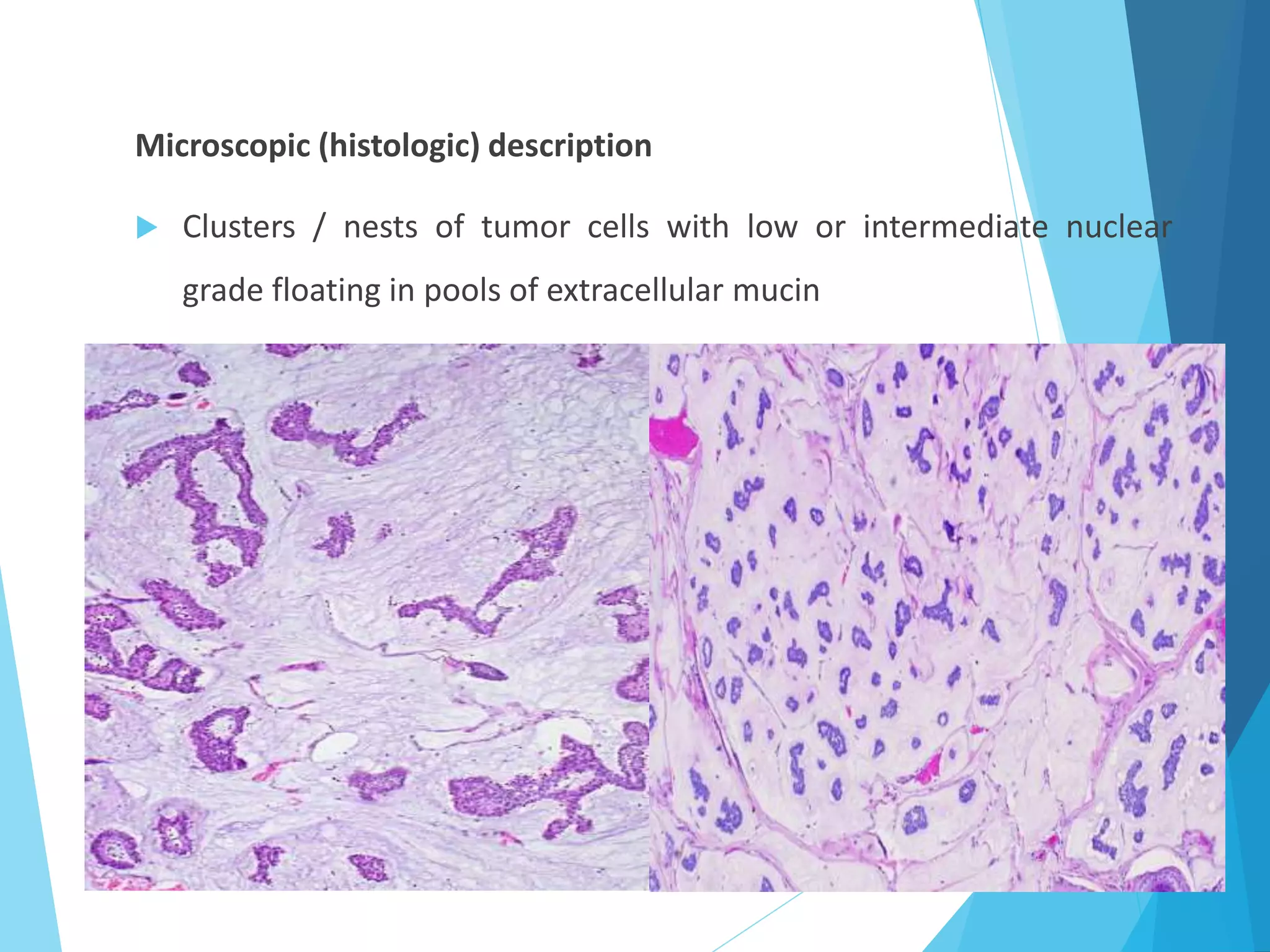
The document provides an overview of breast anatomy, common breast diseases, and associated clinical presentations, including benign and malignant lesions. It highlights the role of mammography in early detection, classification of benign and malignant tumors, and the importance of risk factors and prognostic indicators in breast cancer. Additionally, it discusses male breast pathologies, including gynecomastia and carcinoma, emphasizing the need for awareness and diagnosis in both genders.