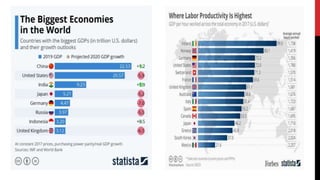
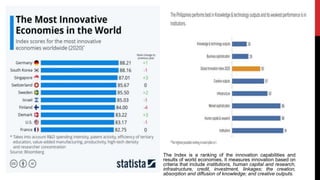
The document discusses the challenges and strategies surrounding productivity and innovation, particularly in the context of the economic downturn caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. It identifies factors contributing to productivity slowdown, including demographic shifts and adverse shocks, while emphasizing the need for clear vision, employee motivation, and enhanced communication as recipes for success. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of adapting organizational design and integrating technology to support productivity and innovation goals.