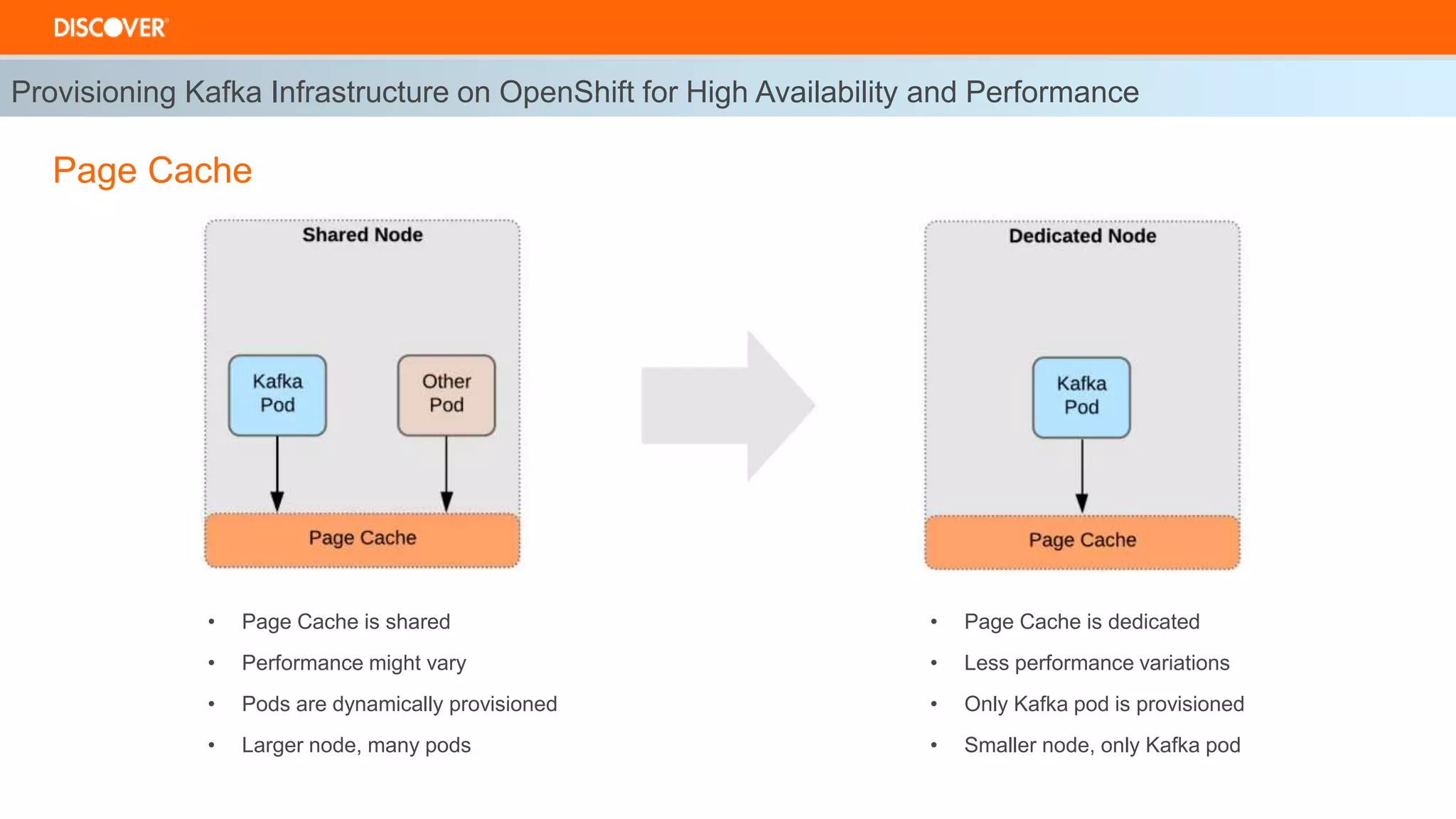
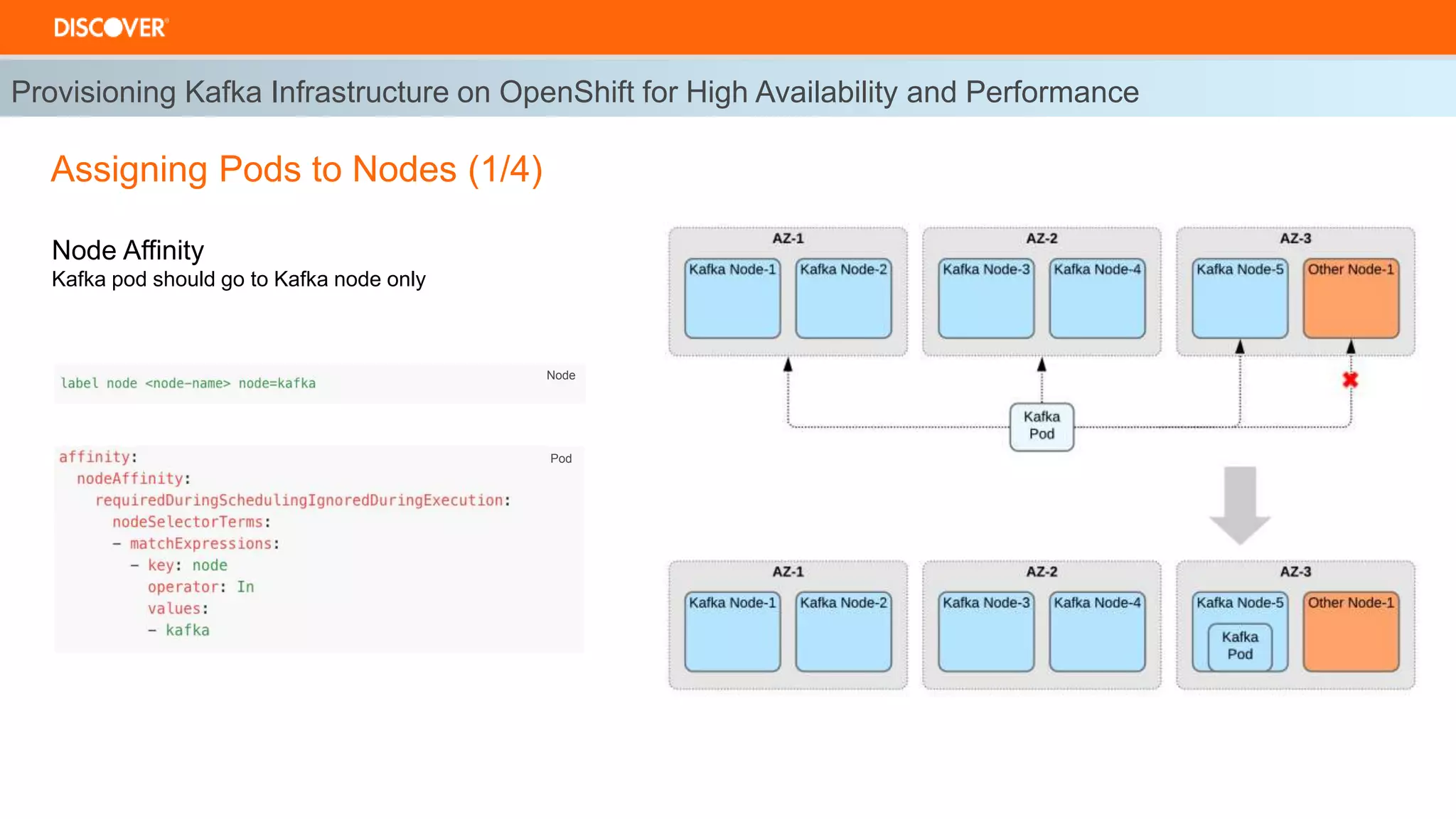
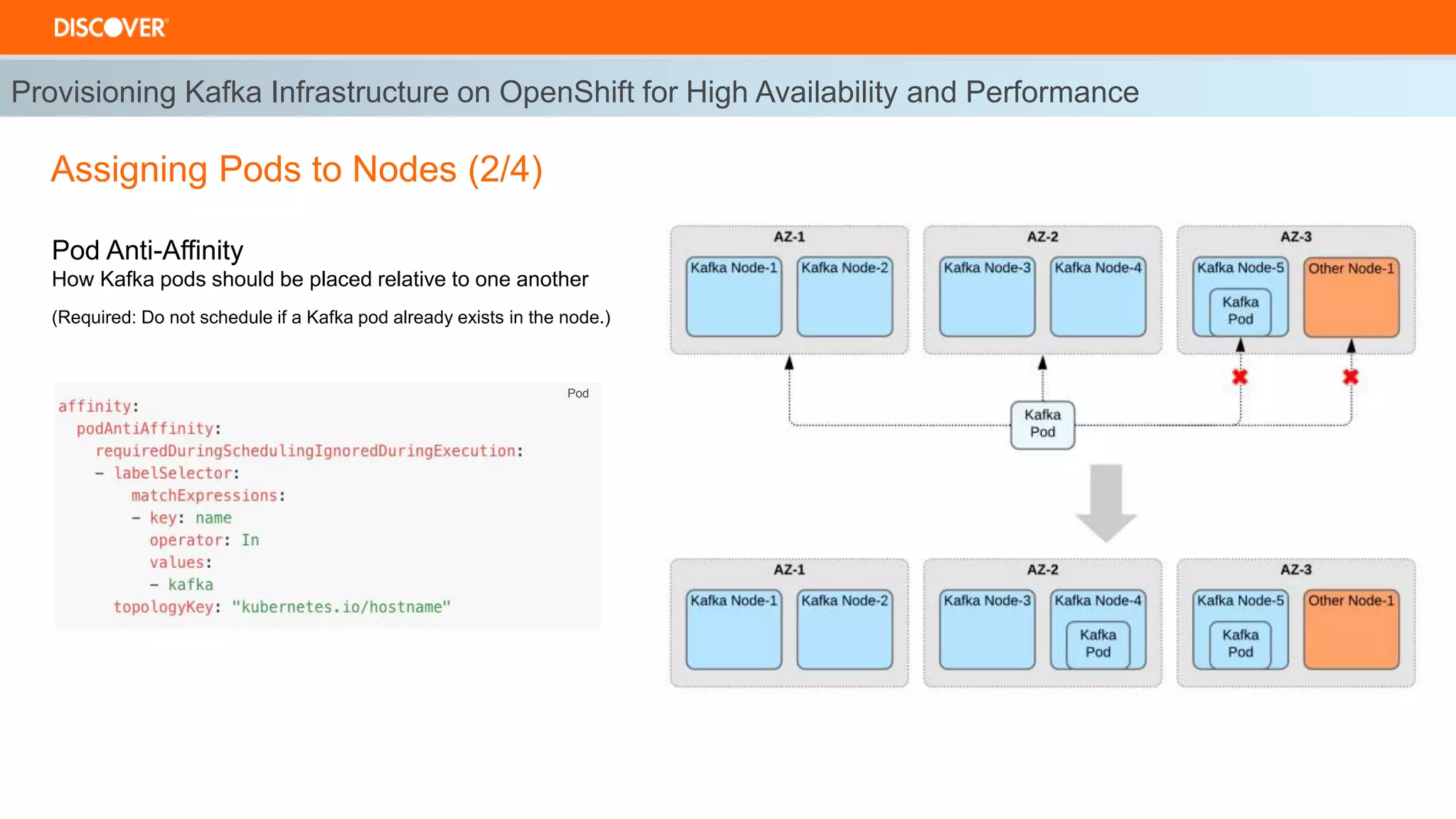
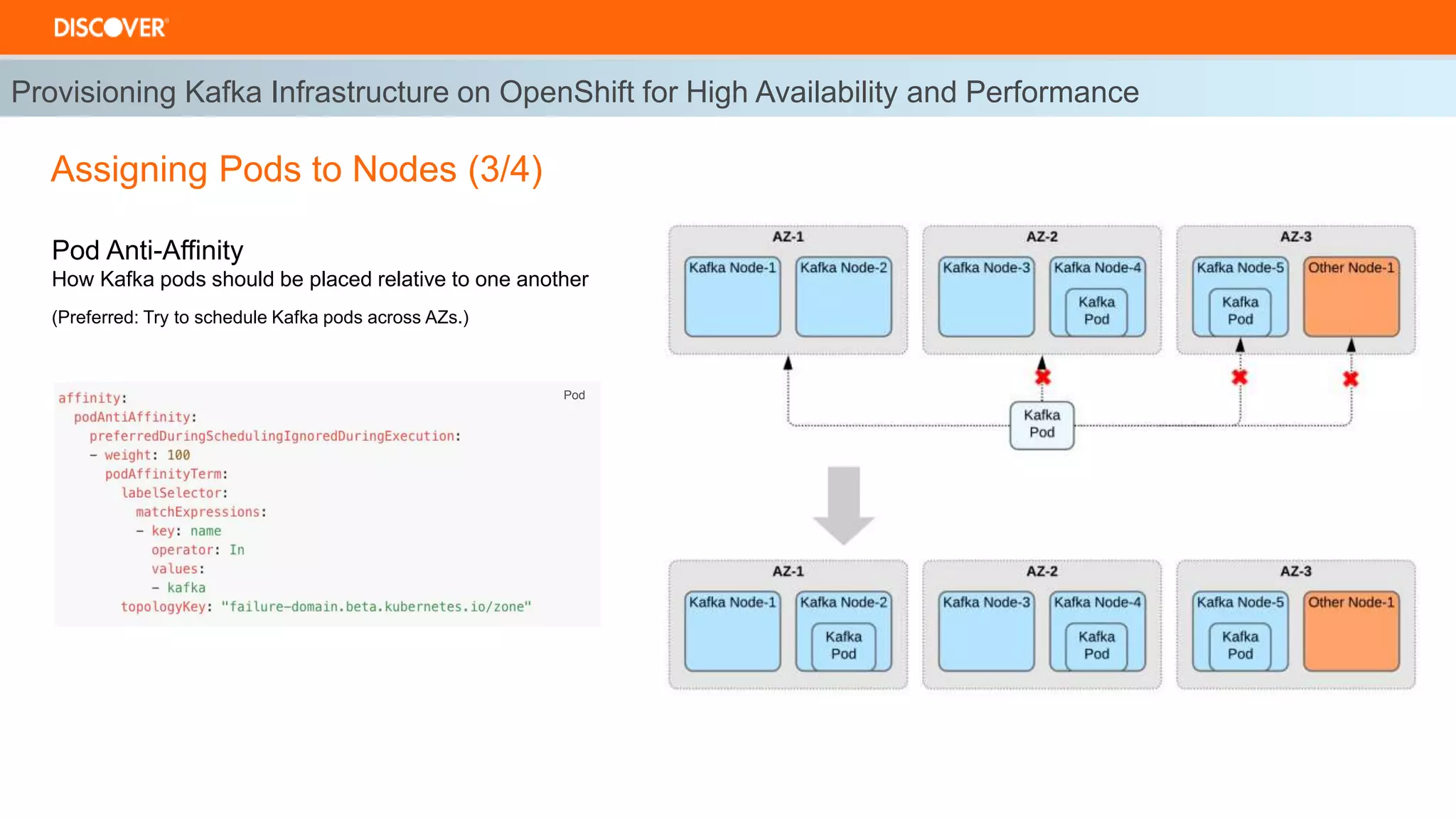
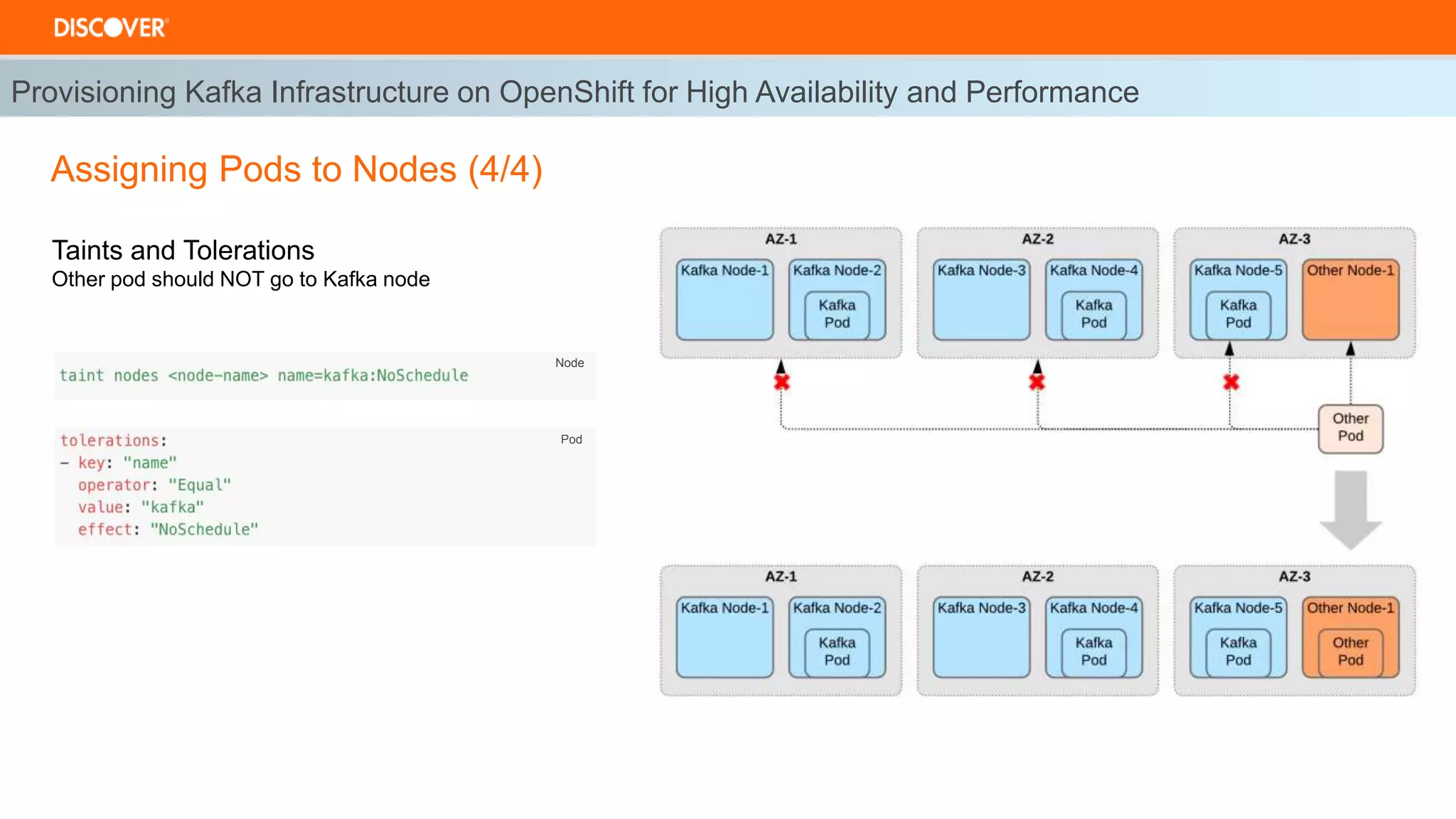
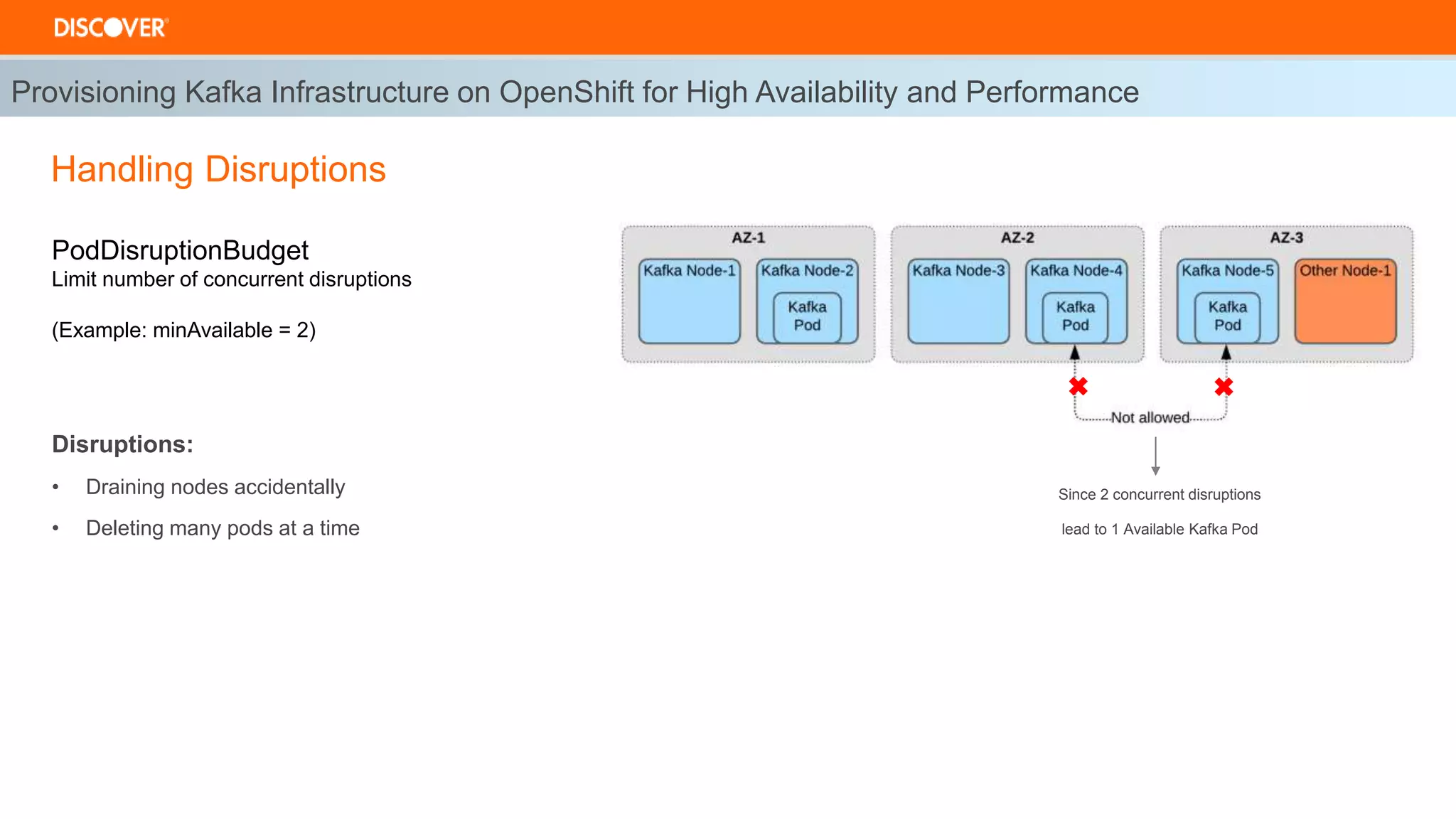
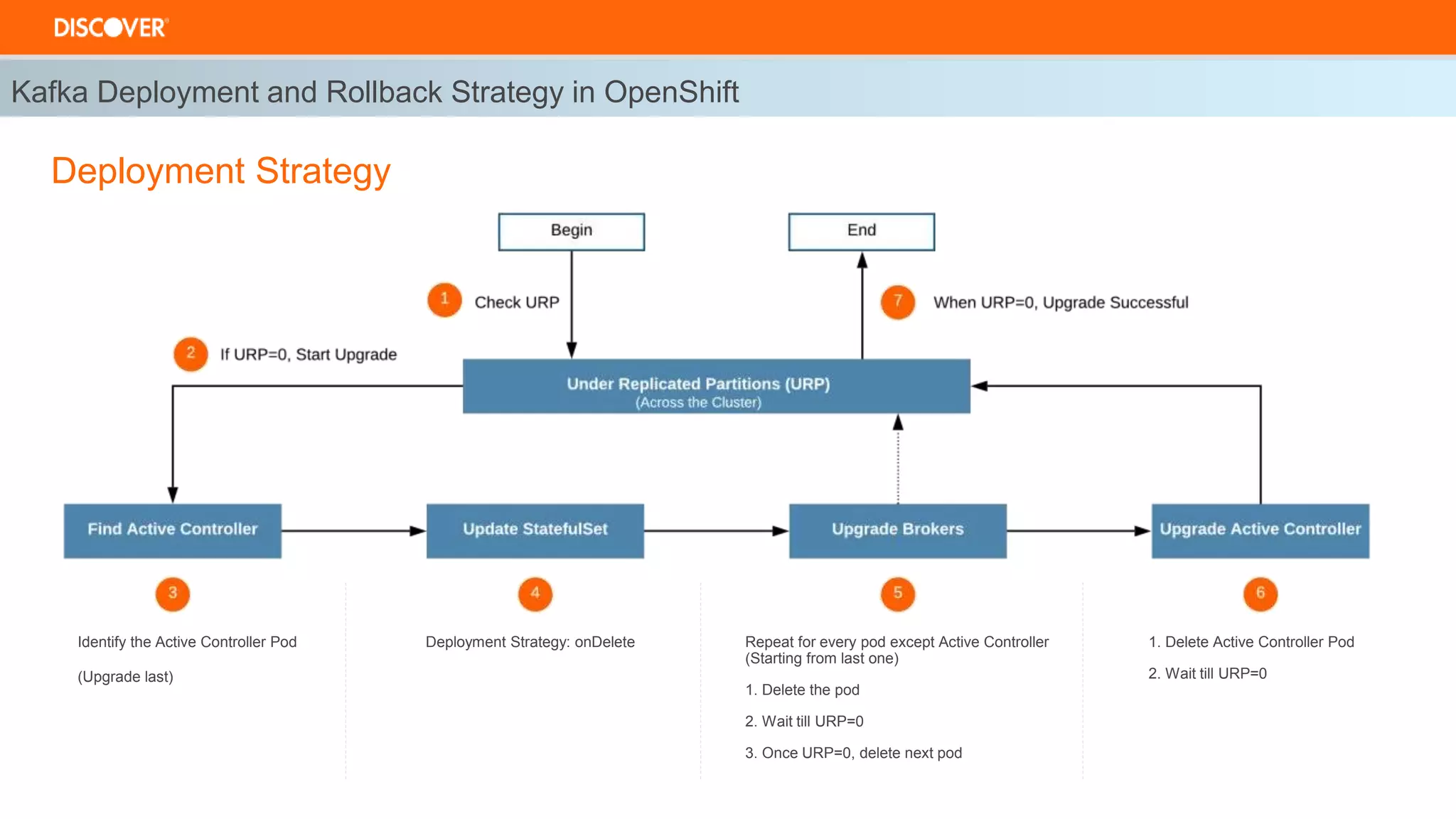
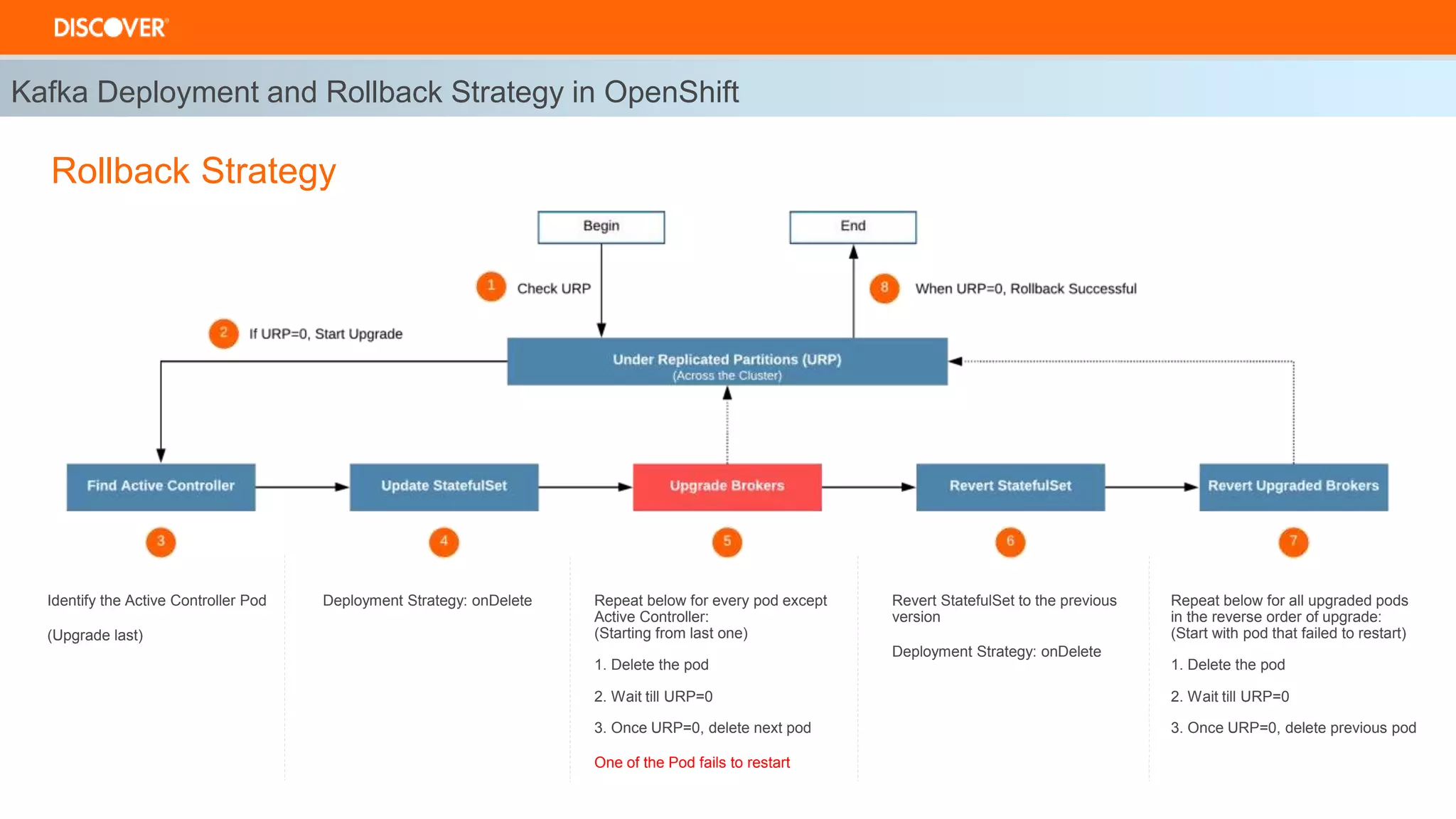
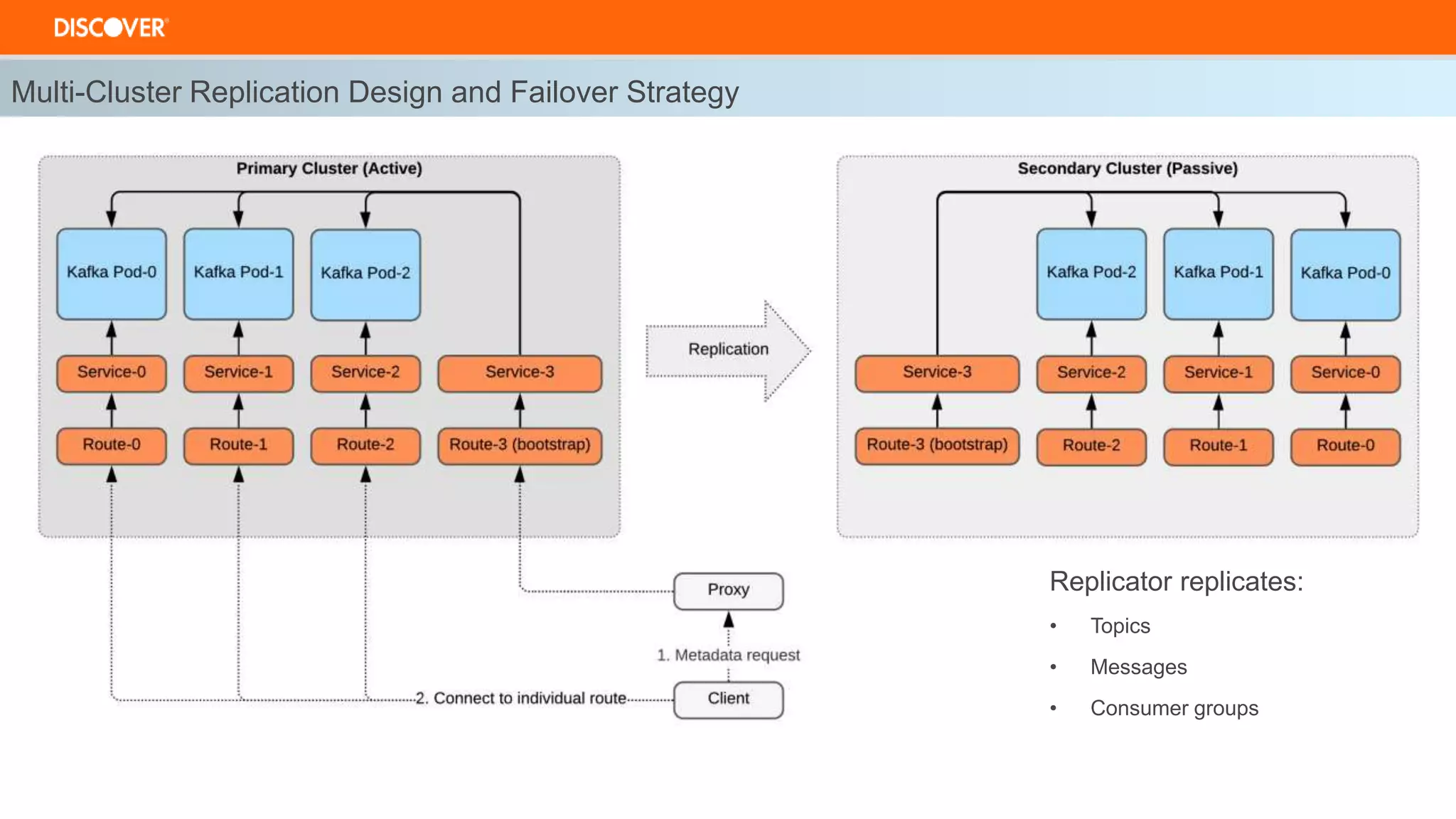
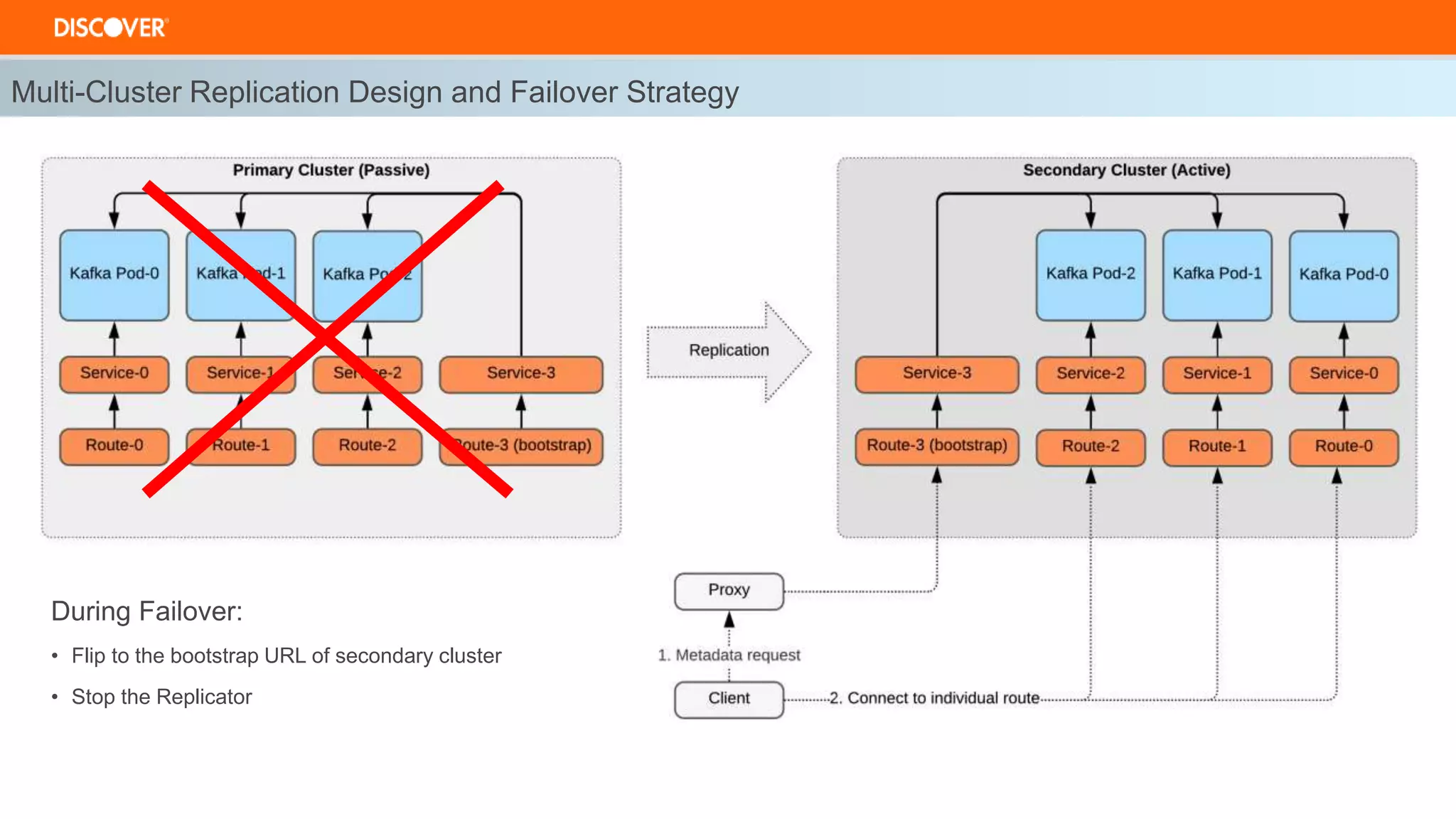
The document discusses the deployment of Kafka on OpenShift, highlighting infrastructure provisioning for high availability, performance strategies, and disruption management. It details pod affinity and anti-affinity scheduling, deployment and rollback strategies, and the importance of multi-cluster replication and failover processes. Key components include managing disruptions, utilizing pod disruption budgets, and ensuring seamless transitions during failures.