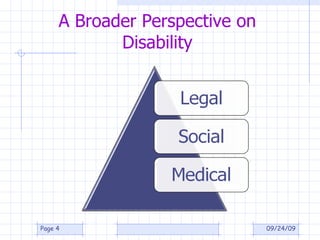
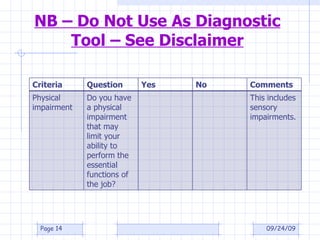
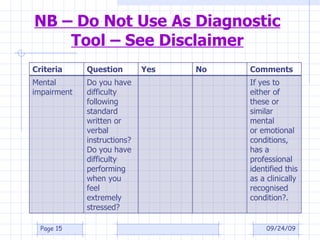
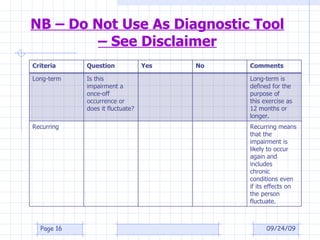
The document discusses what constitutes a disability according to South African law, specifically the Employment Equity Act of 1998. It provides definitions for disability, including having a long-term or recurring physical or mental impairment that substantially limits prospects for employment. It also discusses considerations for determining if an impairment is substantially limiting and exclusions. Employers are instructed to focus on fair treatment and qualifications for a job rather than an applicant's incapacity.