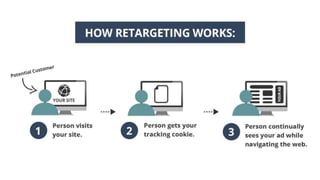
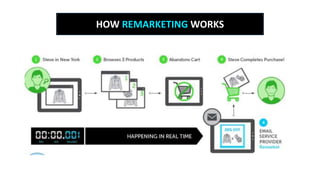
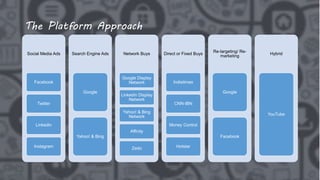
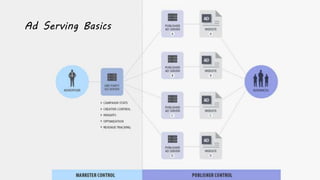
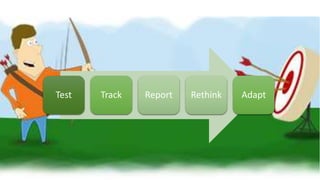
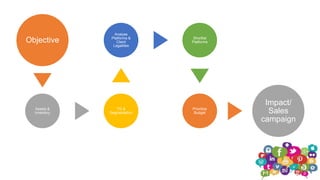
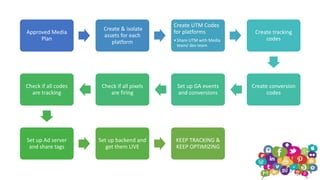
The document outlines the roles and responsibilities of a digital media expert, detailing key concepts such as impressions, click-through rates, and different advertising payment structures like CPM and CPC. It emphasizes the importance of understanding client needs, setting clear campaign objectives, defining target audiences, and utilizing various advertising platforms including social media and search engines. Additionally, it highlights the process of creating and managing effective media plans while addressing the pros and cons of different advertising approaches.