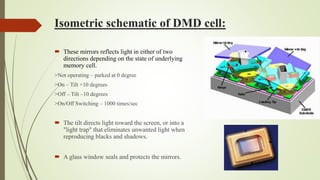
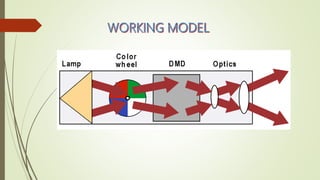
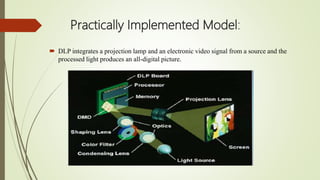
This document discusses digital light processing (DLP) technology. DLP uses thousands of tiny mirrors on a digital micromirror device (DMD) chip to reflect light and produce high-quality images. It provides advantages like brightness, sharpness, and versatility. The document outlines the history and components of DLP, how DLP works by converting signals and creating color and grayscale images, and applications like DLP televisions. Potential disadvantages include the "rainbow effect" seen by some users. The future of DLP is promising as the technology is used in more business and high-definition projection applications.