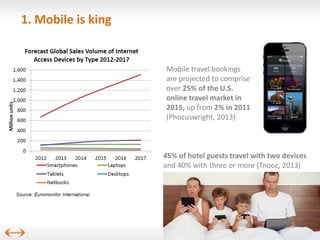
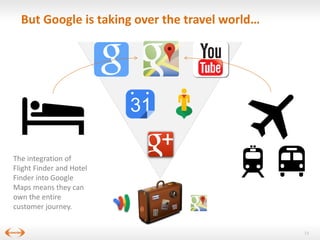
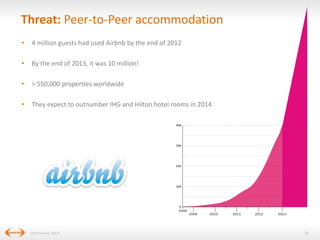
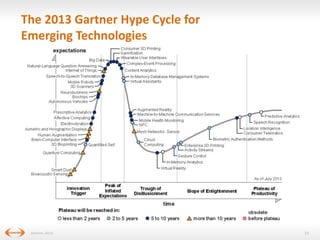
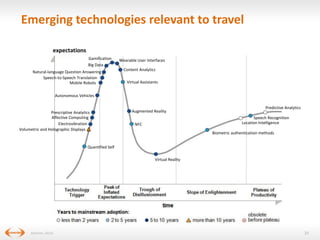
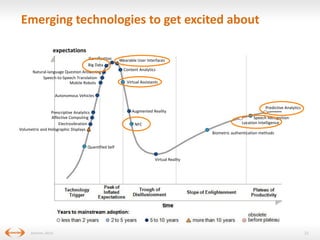
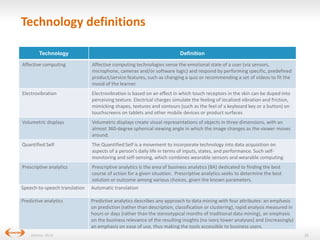
The document discusses digital disruption in the travel industry, highlighting the significant impact of technology on value creation and business models. Key trends include the rise of mobile bookings, metasearch, and the growth of peer-to-peer accommodation services like Airbnb. It emphasizes the need for the industry to adapt to these changes, which also present new revenue opportunities.