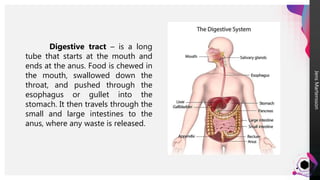
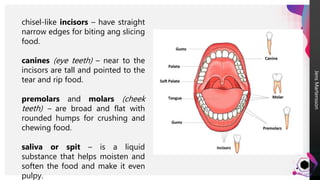
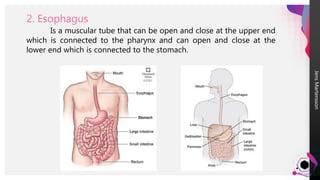
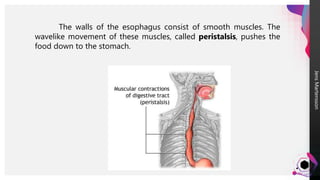
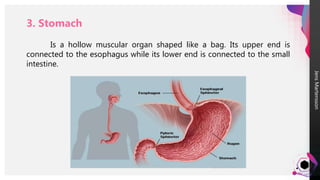
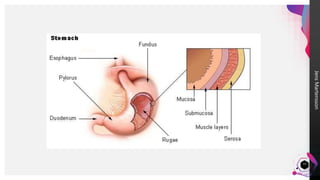
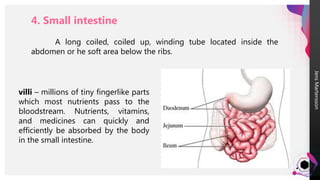
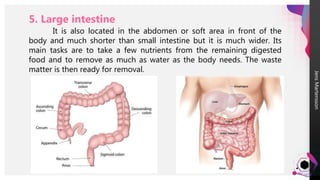
The digestive system breaks down food so that nutrients can be released and used for energy. Food travels through the digestive tract, which begins at the mouth and ends at the anus. The mouth contains teeth for breaking down food and saliva for softening it. Food then travels to the stomach through the esophagus and is further broken down by stomach acids and enzymes before moving to the small intestine, where most nutrient absorption occurs through villi. The large intestine then absorbs remaining nutrients and water before waste is excreted through the anus.