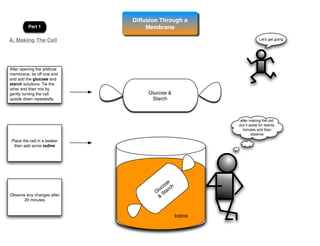
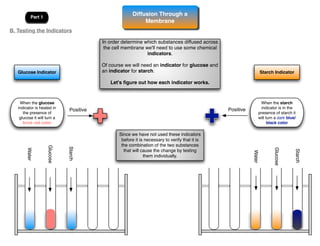
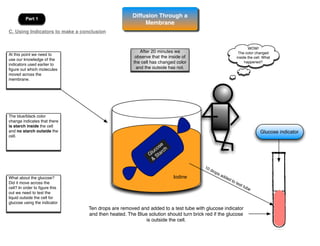
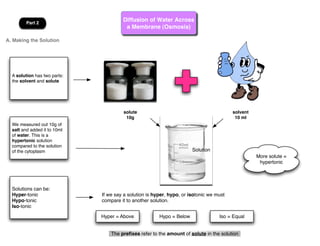
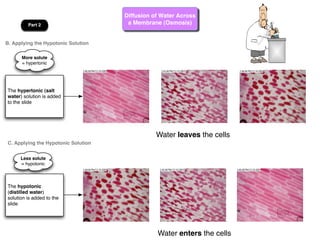
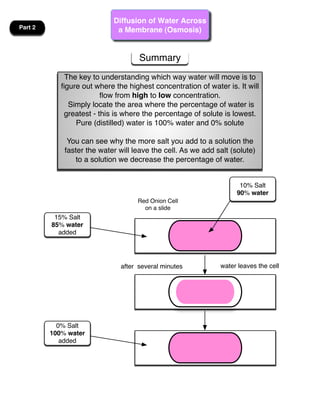
This lab involves modeling diffusion and osmosis using artificial cells. In part one, an artificial cell containing glucose and starch is placed in iodine solution. Indicators show that starch remains inside the cell while glucose diffuses out. Part two examines osmosis in red onion cells, with solutions of varying salt concentrations causing water to move into or out of the cells depending on their relative concentrations.