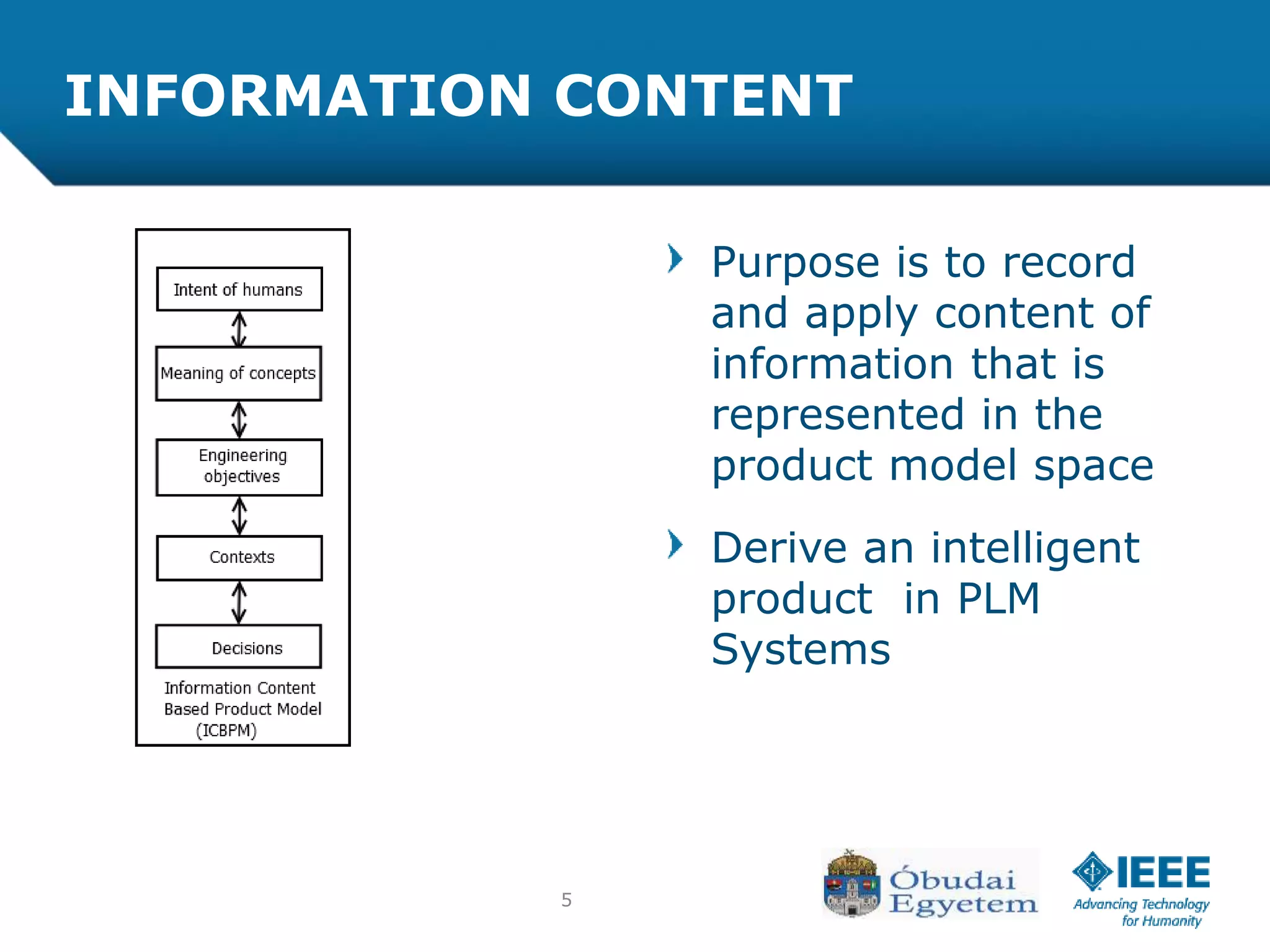
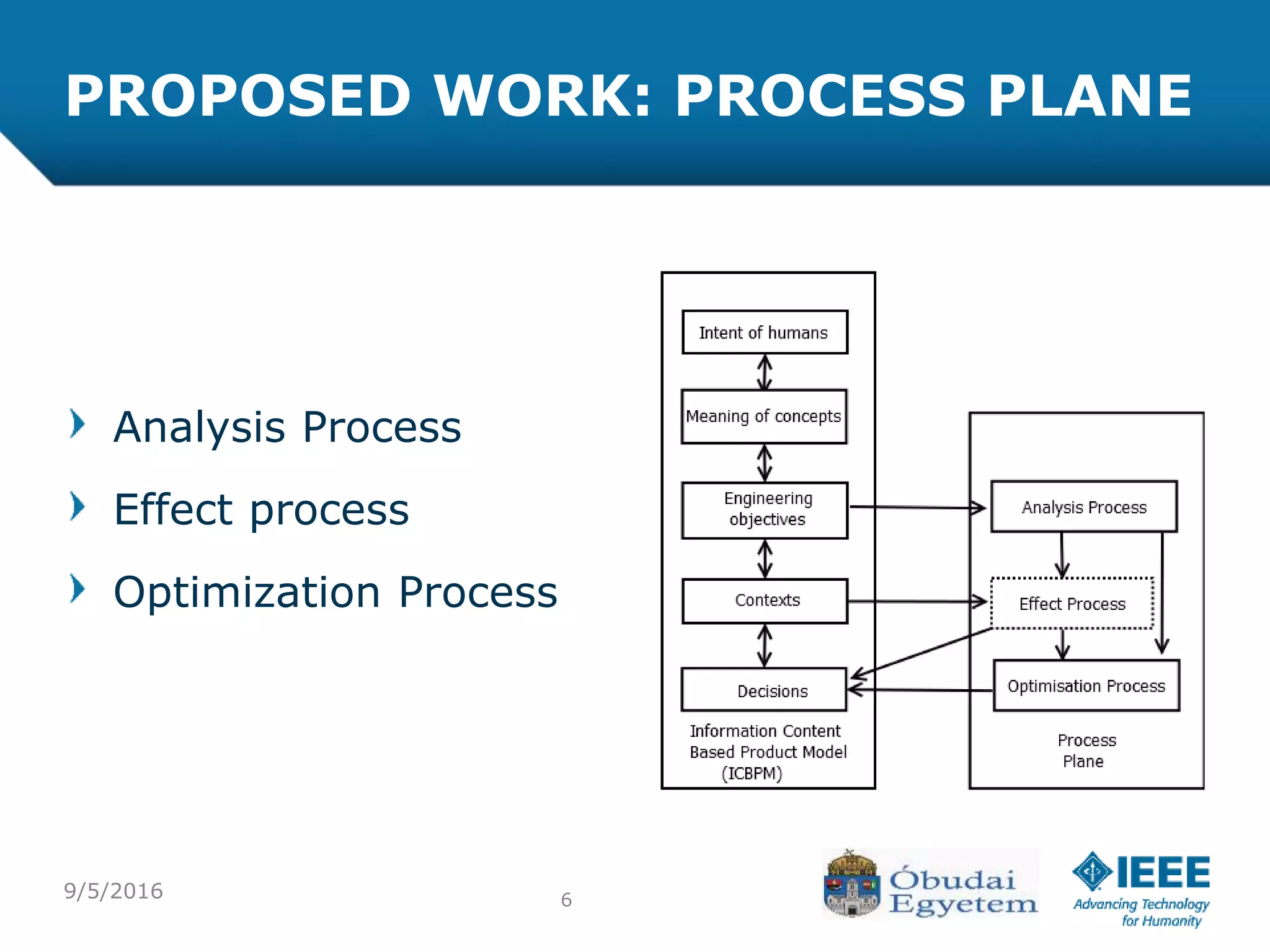
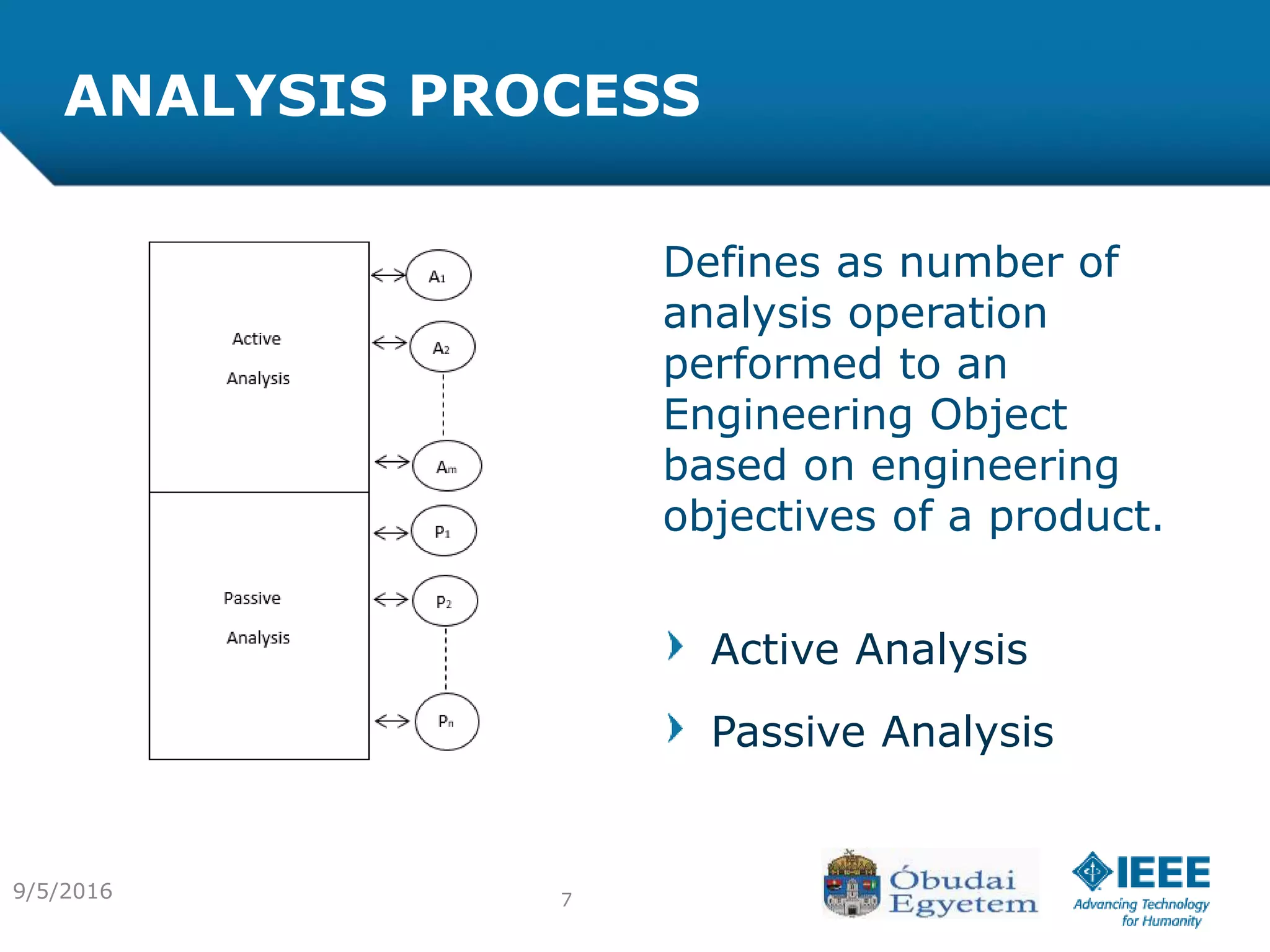
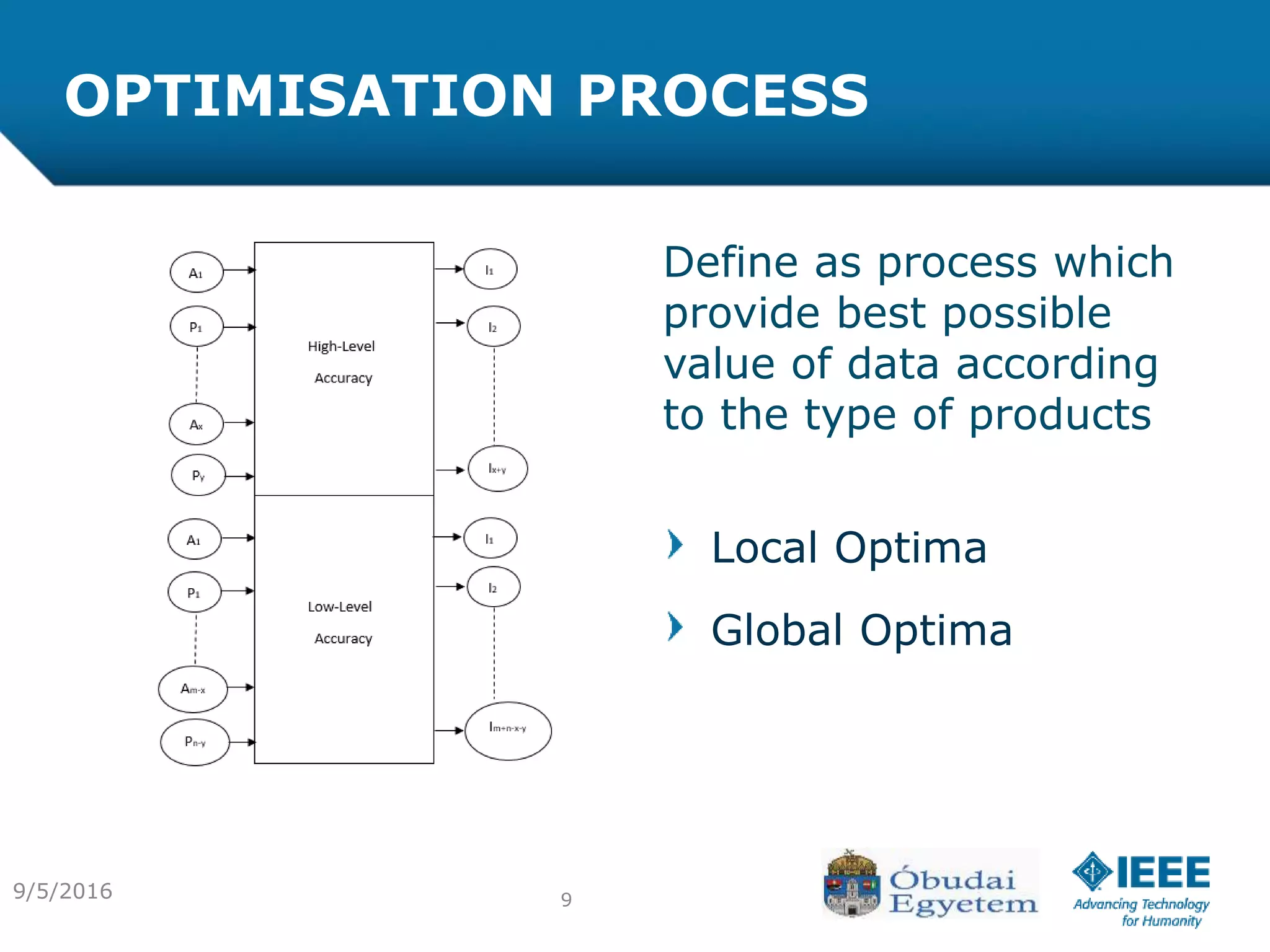
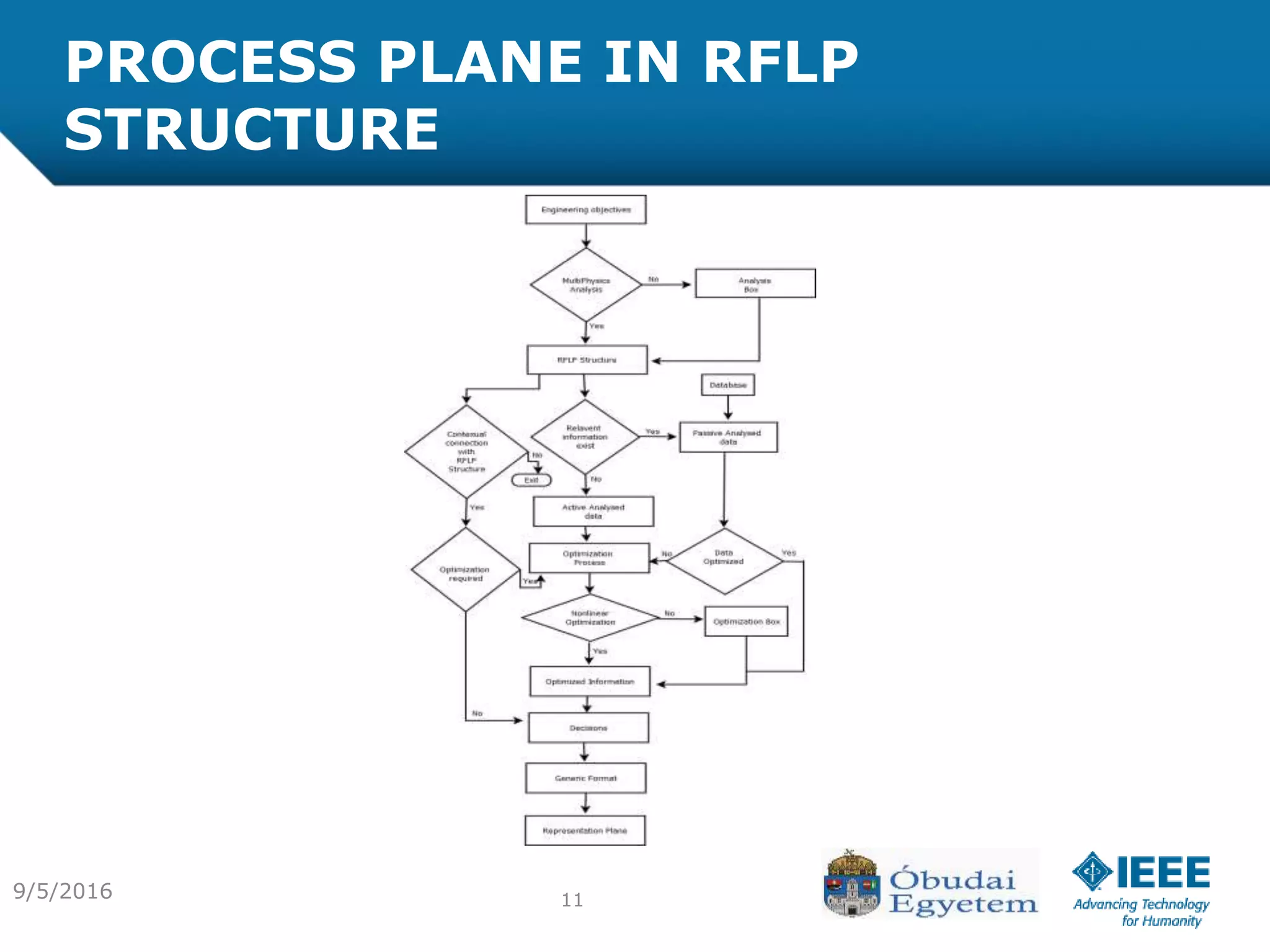
The document discusses the various processes involved in the Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) information content model, highlighting the analysis process, effect process, and optimization process. It introduces the RFLP structure as a new method for product definition, emphasizing its ability to manage engineering objects more effectively. The conclusion suggests the need for extending theoretical insights into practical applications while exploring the integration of fuzzy concepts for decision-making.