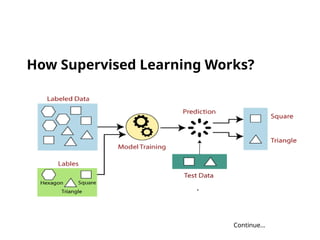
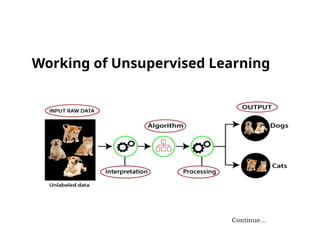
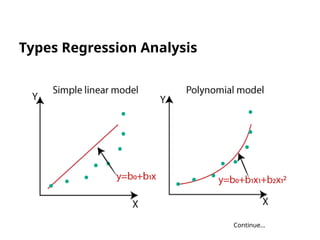
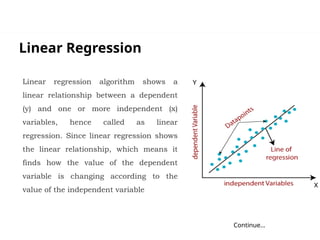
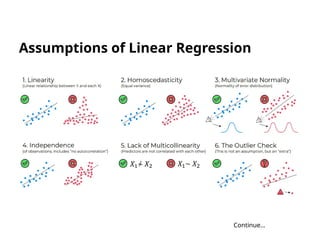
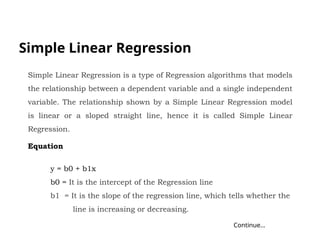
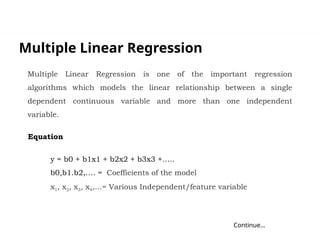
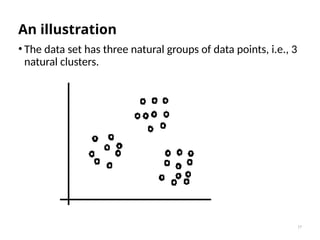
The document discusses machine learning, highlighting its ability to enable computers to learn from past data using algorithms. It covers two main types of machine learning: supervised, where models are trained with labeled data, and unsupervised, where models work with unlabeled data to identify underlying patterns. Additionally, it describes various techniques within these types, such as regression and clustering, showcasing their applications in real-world scenarios.