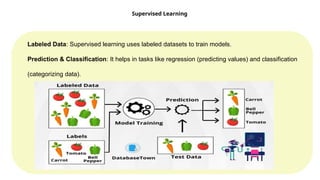
UNIT II SUPERVISED LEARNING
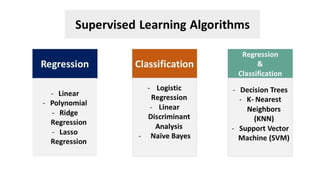
Linear Regression Models: Least squares, single & multiple variables, Bayesian linear regression(Predicts a range instead of one value, considering uncertainty.), gradient descent(Step-by-step improvement to find the best solution.), Linear Classification Models: Discriminant function - Perceptron algorithm, Probabilistic discriminative model - Logistic regression, Probabilistic generative model - Naive Bayes, Maximum margin classifier - Support vector machine, Decision Tree, Random Forests.




























![Linear Regression Models
.
Python code for Single Linear Regression, Multiple Linear Regression, and Least Squares Calculation:
print(f"Equation: Price = {model.intercept_:.2f} + {model.coef_[0]:.4f}(Size) + {model.coef_[1]:.2f}(Bedrooms)")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2-250711083438-7c579aa8/85/UNIT-II-SUPERVISED-LEARNING-Introduction-32-320.jpg)















