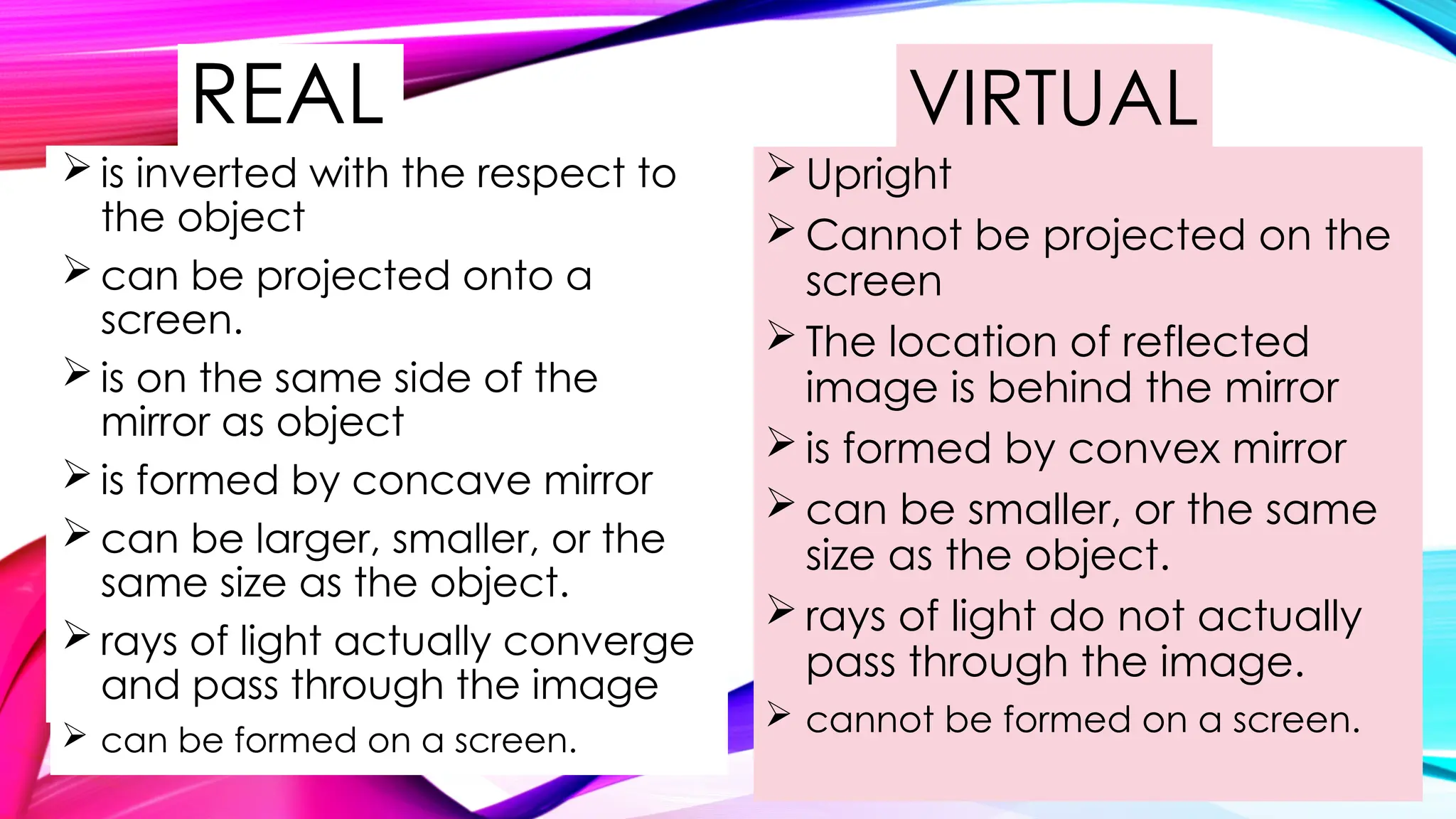
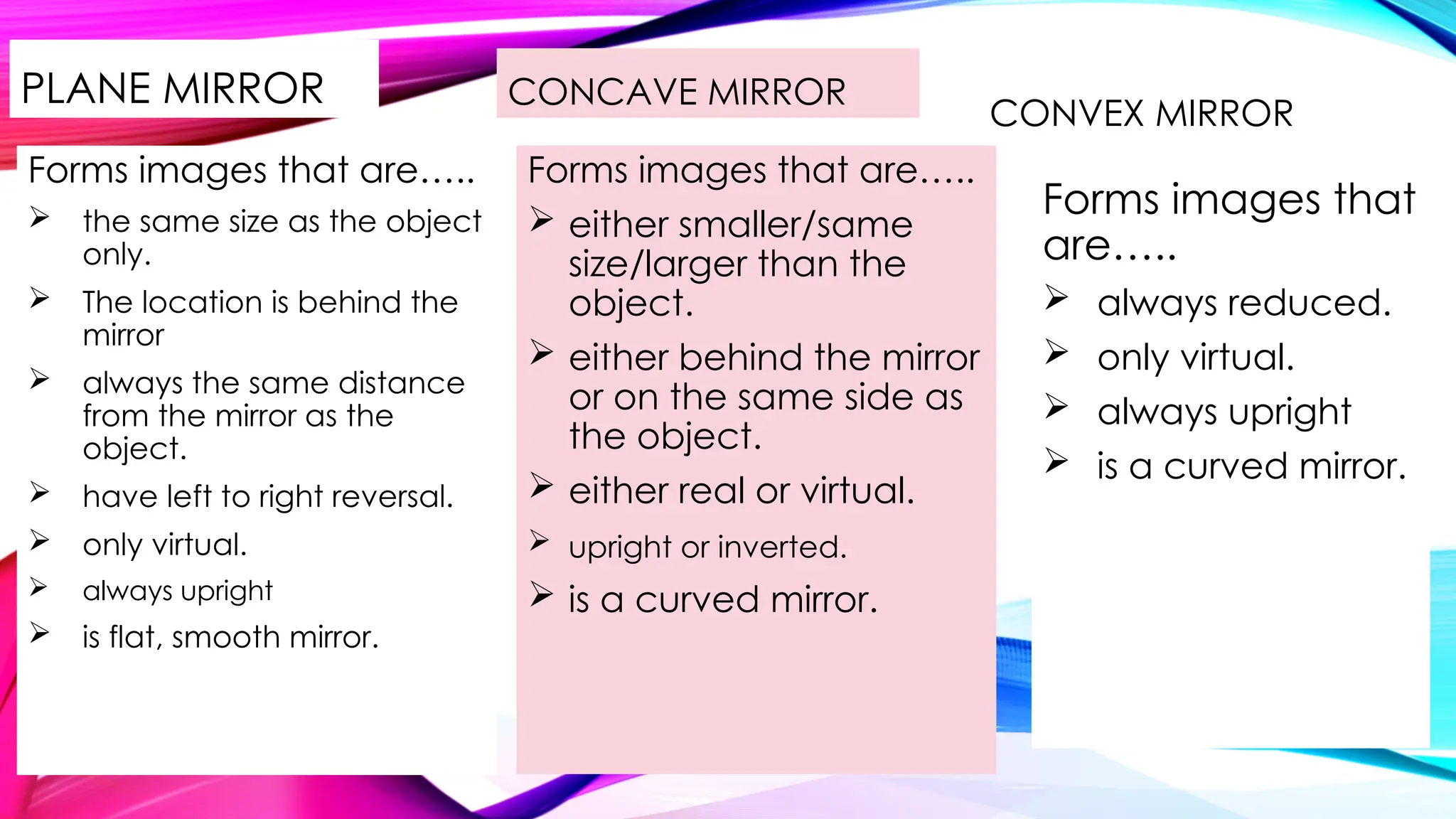
The document outlines the differences between real and virtual images, highlighting characteristics such as projection capability, orientation, and formation method. It explains that real images are inverted and can be projected onto a screen, while virtual images are upright and cannot be projected. Additionally, it describes the properties of plane, concave, and convex mirrors, as well as the characteristics of convex and concave lenses.