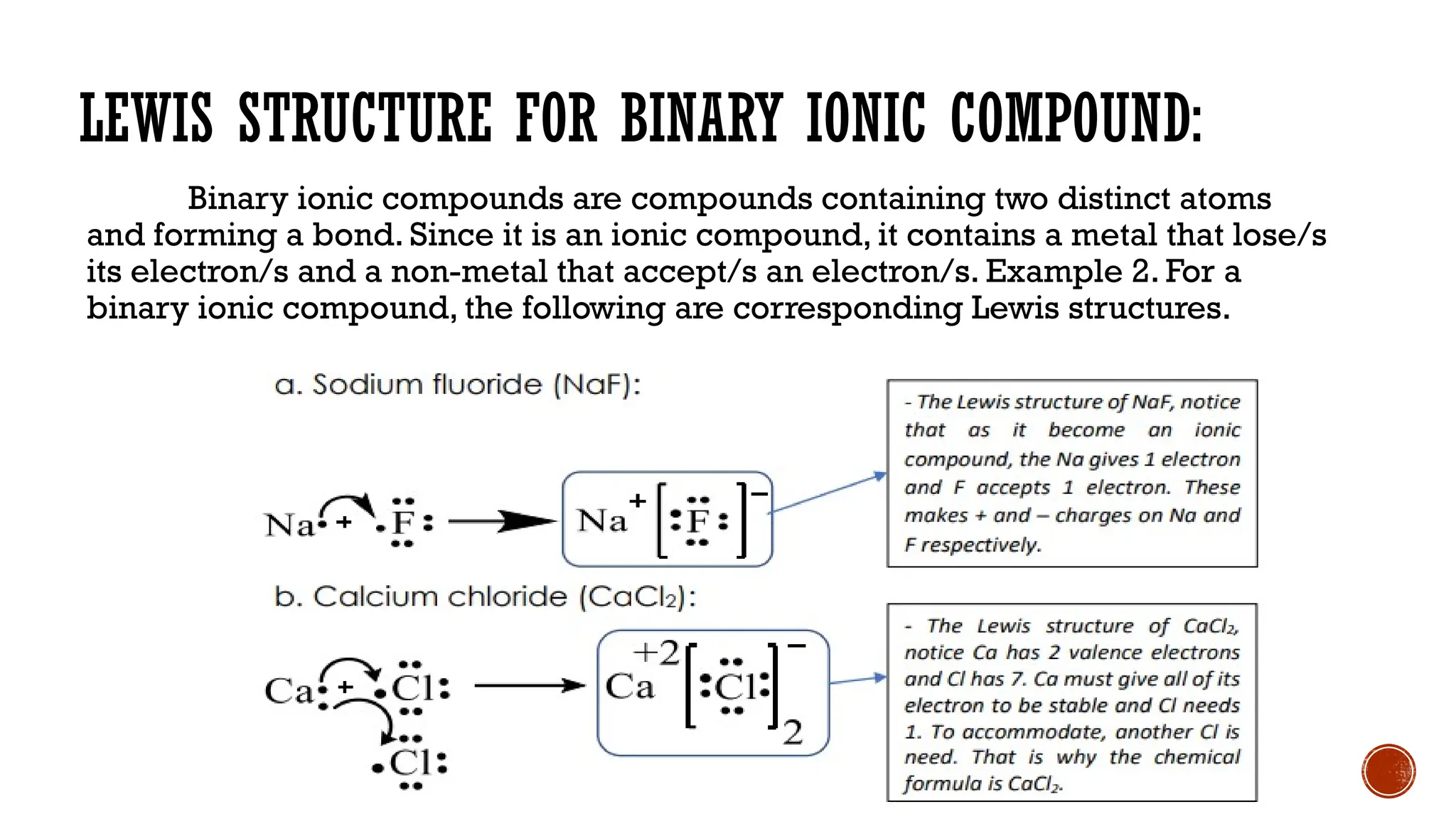
The document explains the Lewis structure of molecular compounds, detailing the role of valence electrons in forming ionic and covalent bonds. It outlines the concept of the octet rule, the stability of monoatomic elements, and provides examples of Lewis structures for monoatomic atoms, binary ionic compounds, and polyatomic ions. The discussion highlights the electron transfer and sharing mechanisms crucial for chemical bonding and stability.