Embed presentation
Download to read offline


![Python Code
Calculating the Mean in Python:
sample = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
mean = sum(sample) / len(sample)
print(mean) # prints 3.0
Calculating the Weighted Mean in Python:
sample = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
weights = [0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2]
weighted_mean = sum(s * w for s, w in zip(sample ,
weights)) / sum(weights)
print(weighted_mean) # prints 3.0
Copyright © 2024. All rights Reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meanandweightedmean-241115135715-2c49d1f5/75/Difference-between-Mean-and-Weighted-Mean-5-2048.jpg)

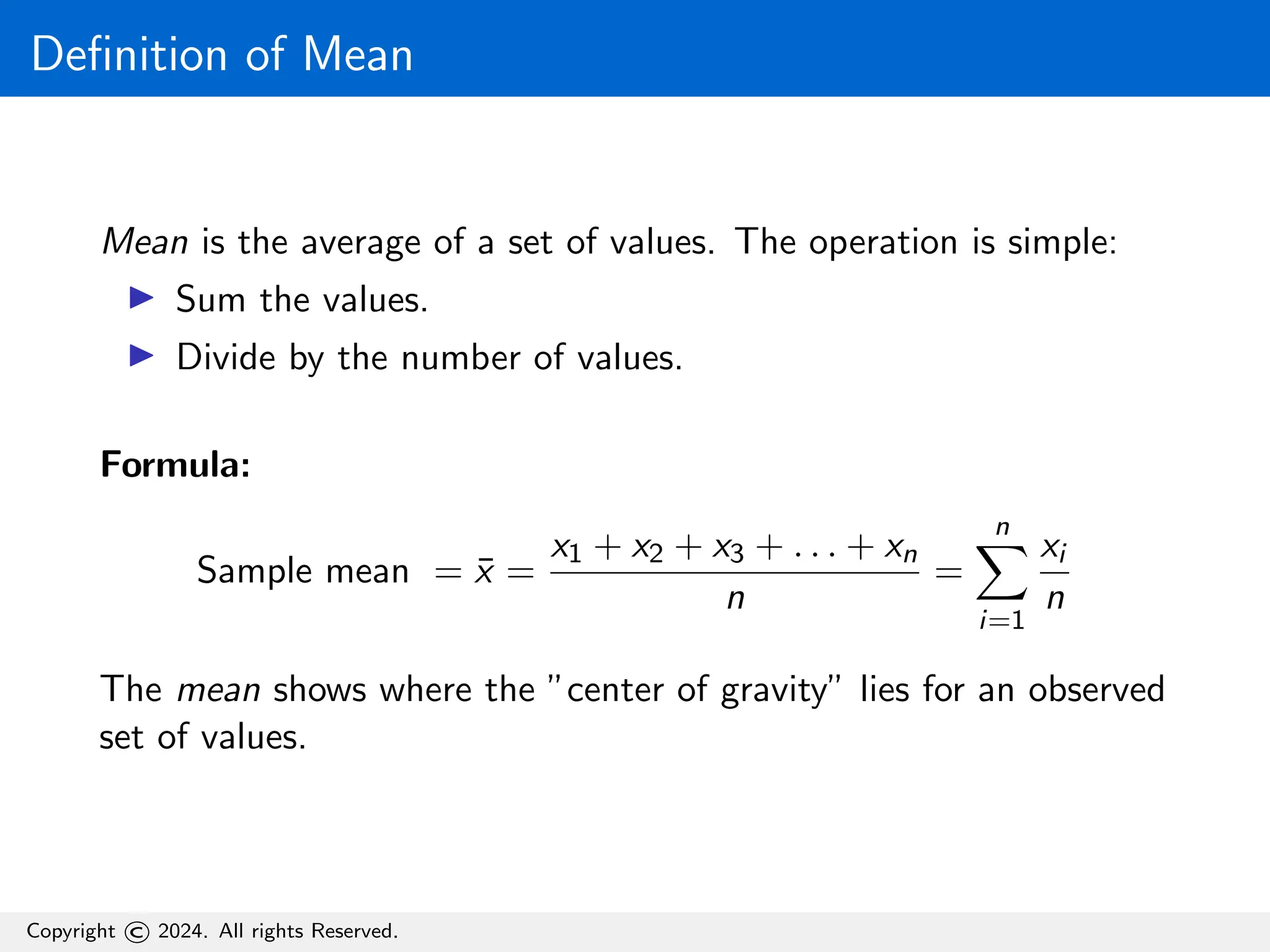
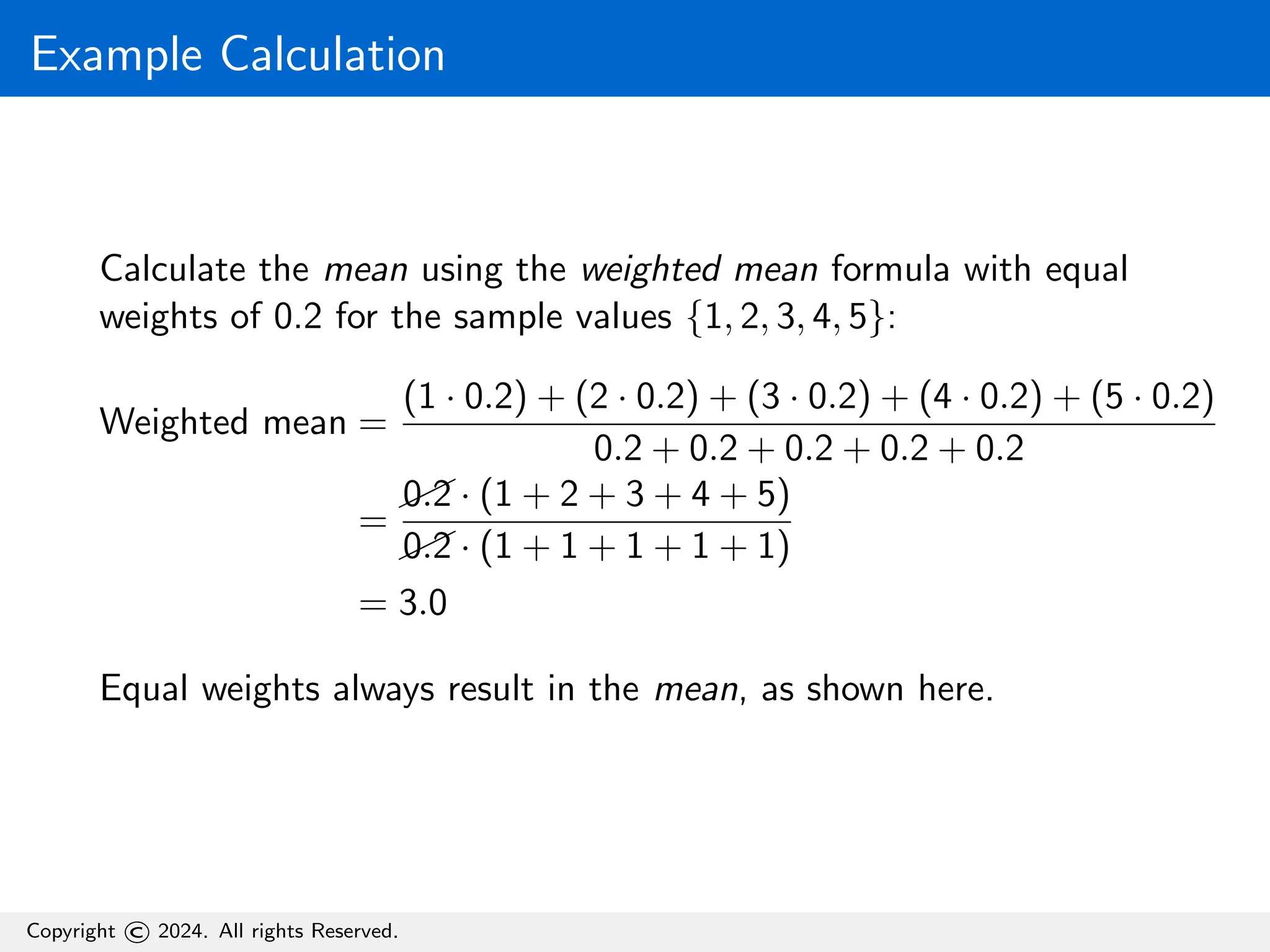
The document defines the mean as the average of a set of values, illustrating the calculation with a formula and a sample example. It further explains the weighted mean, which assigns weights to values, and emphasizes that when weights are equal, the weighted mean equals the mean. Additionally, the document provides Python code for calculating both the mean and weighted mean.




![Python Code
Calculating the Mean in Python:
sample = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
mean = sum(sample) / len(sample)
print(mean) # prints 3.0
Calculating the Weighted Mean in Python:
sample = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
weights = [0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.2]
weighted_mean = sum(s * w for s, w in zip(sample ,
weights)) / sum(weights)
print(weighted_mean) # prints 3.0
Copyright © 2024. All rights Reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meanandweightedmean-241115135715-2c49d1f5/75/Difference-between-Mean-and-Weighted-Mean-5-2048.jpg)
