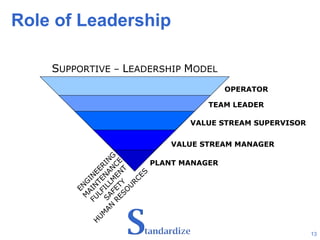
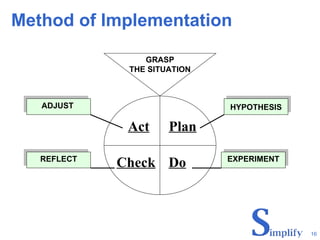
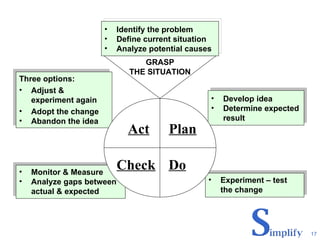
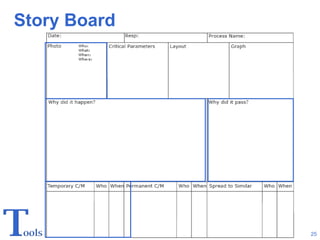
The document discusses Andersen Enterprise's continuous improvement methodology and tools. It describes Andersen's manufacturing philosophy of pursuing continuous improvement to stabilize, standardize, and simplify work processes. Three key tools are mentioned - the Continuous Improvement Board for quick employee ideas, the Focus Board for team problem solving of specific issues, and the Story Board for deeper root cause analysis involving engineers and leaders.