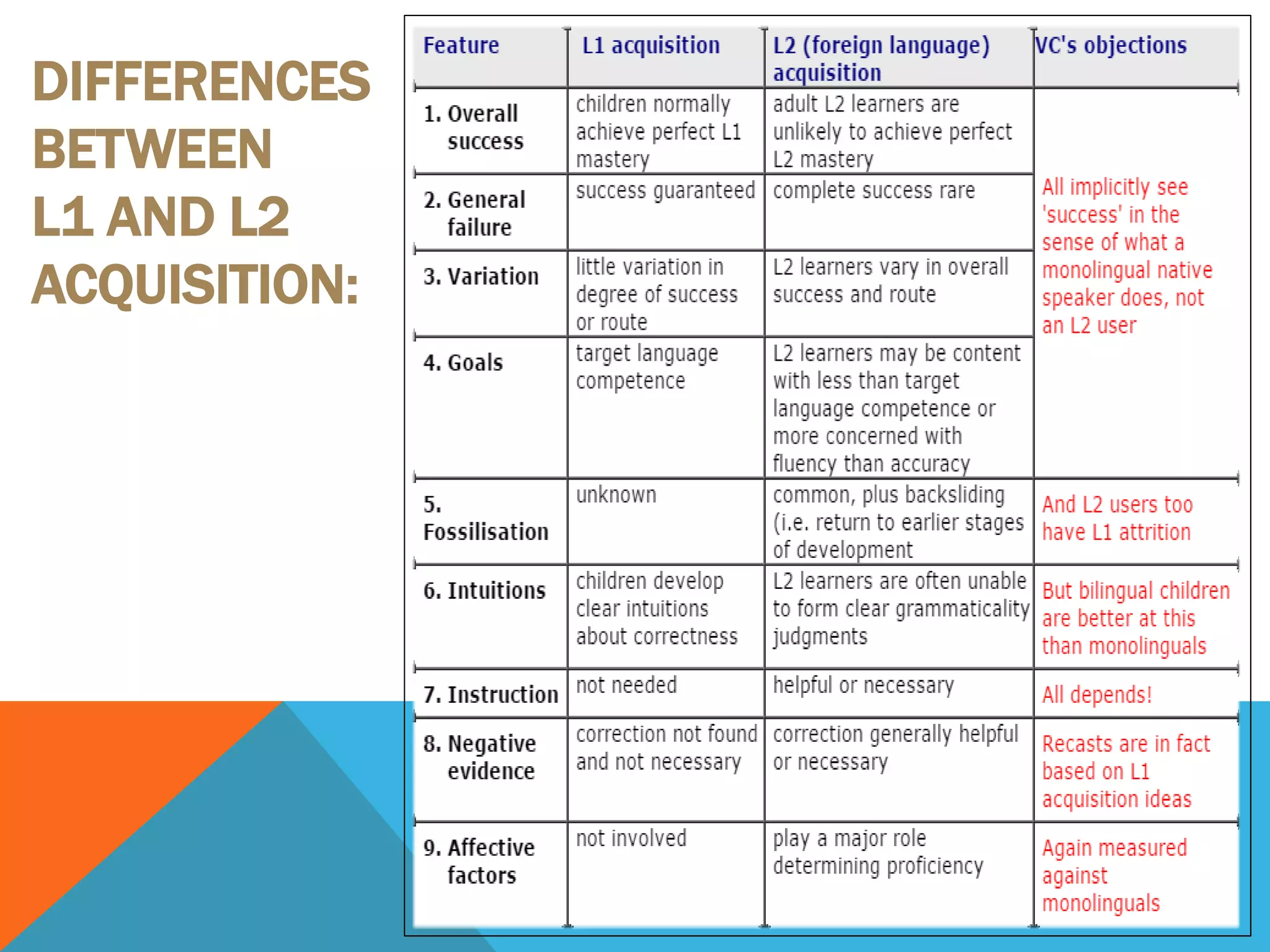
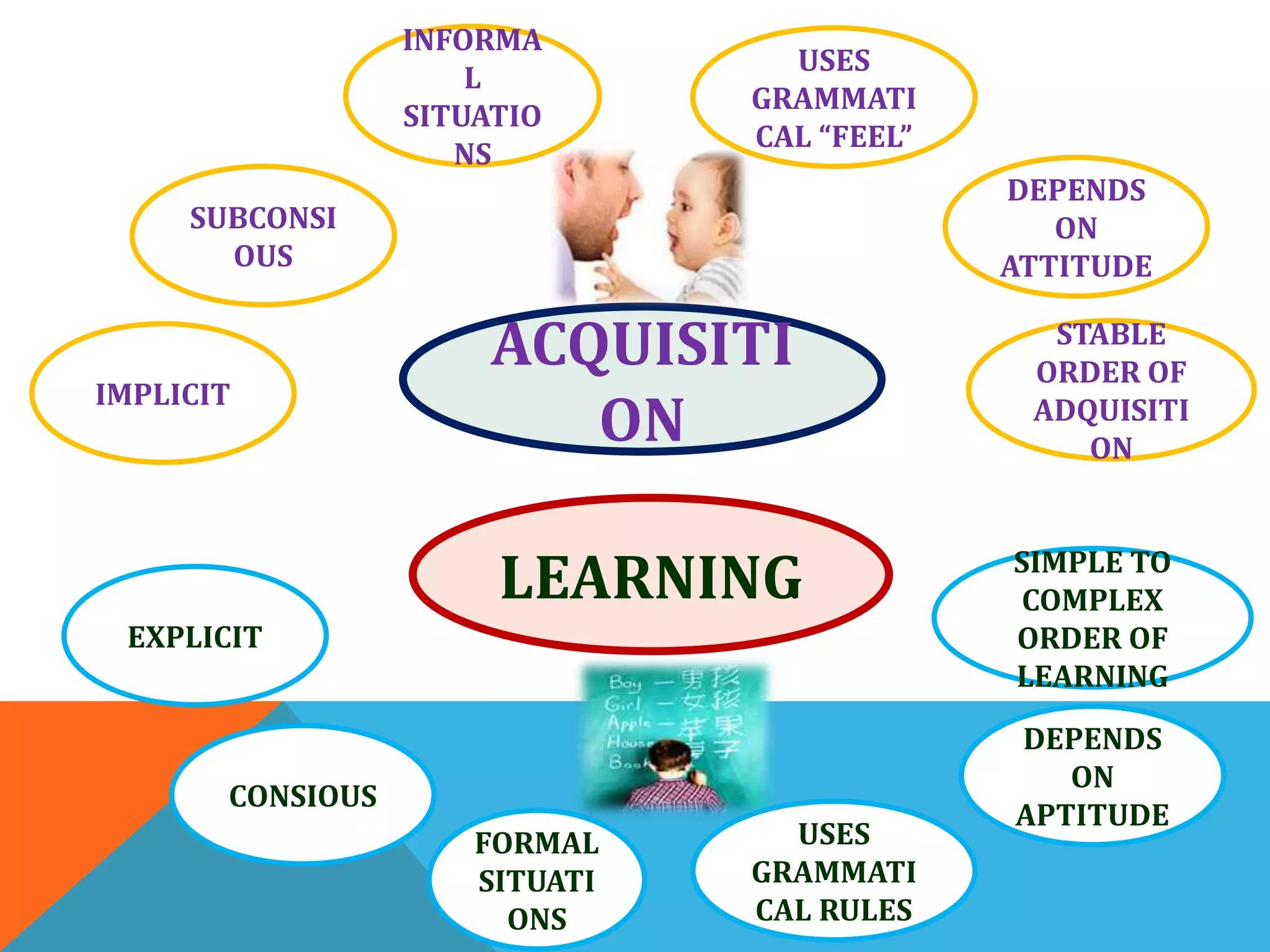
The document discusses various theories and perspectives on language acquisition. It begins by defining language and noting Noam Chomsky's theory of an innate Language Acquisition Device. It then contrasts Chomsky's view with behaviorist theories that language is acquired through conditioning. The document also addresses differences between first and second language acquisition, as well as biological and environmental influences on language learning. It notes that acquisition is generally implicit while learning is explicit, and that adults and children acquire language differently.